A Cartographic Examination of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region
Related Articles: A Cartographic Examination of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Cartographic Examination of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Cartographic Examination of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region
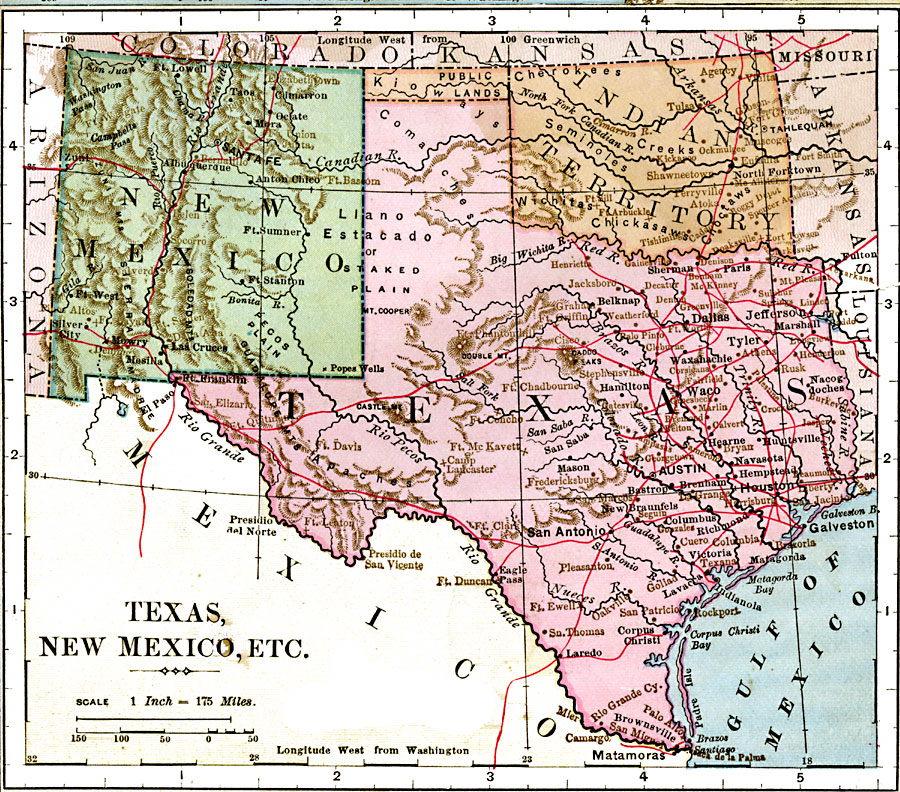
The boundary between New Mexico and Texas, as depicted on a map, represents a complex interplay of historical events, geographical features, and contemporary political realities. Understanding this boundary requires an examination of its formation, the physical landscape it traverses, and the implications of its location for both states. This analysis will explore these aspects, providing a comprehensive overview of this significant cartographic delineation.
Historical Context: The current border’s configuration is a product of centuries of territorial disputes and negotiations. Spanish colonial claims, Mexican independence, and subsequent annexation by the United States all contributed to the evolution of the boundary. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which concluded the Mexican-American War, formally established much of the current demarcation. However, even this treaty left ambiguities requiring further surveying and legal interpretation to resolve conflicting claims. The resulting boundary lines, often following natural features like rivers and mountain ranges where feasible, also incorporate survey markers and legal descriptions that define its precise location in areas where natural boundaries are less distinct. This historical context is crucial to interpreting the map’s representation of the border, as it reveals the often-contested nature of territorial claims and the compromises involved in establishing a stable boundary.
Geographical Features: The New Mexico-Texas border is not a straight line; it follows a varied and often irregular path. Significant portions follow the course of the Rio Grande River, a powerful and historically important waterway. However, the river’s meandering course and occasional shifts have necessitated adjustments to the border’s official location to account for avulsion (sudden changes in river course). Other sections of the boundary traverse less defined terrain, requiring precise surveying and marker placement to define the state line. Mountain ranges, plains, and deserts all contribute to the diversity of the landscape along this boundary, impacting transportation, resource management, and population distribution. The geographical features depicted on a map provide crucial context for understanding the challenges of administering and managing this border region.
Political and Administrative Implications: The cartographic representation of the state line has significant implications for governance and administration. Issues of jurisdiction, resource allocation, and law enforcement are all directly impacted by the border’s location. For instance, disputes over water rights in the Rio Grande basin require careful consideration of the boundary’s definition. Similarly, the allocation of federal and state funds for infrastructure projects, environmental protection, and social services necessitates a precise understanding of jurisdictional boundaries. The map, therefore, serves as a fundamental tool for resolving disputes and facilitating efficient governance within this shared border region.
Economic and Social Impacts: The border’s location significantly influences economic activity and social interactions between the two states. Cross-border trade, transportation networks, and cultural exchange are all shaped by the geographical proximity and the political relationship between New Mexico and Texas. The map provides a framework for understanding the flow of goods, services, and people across the boundary, highlighting areas of high economic interdependence and areas where transportation infrastructure may be lacking. Additionally, the map aids in analyzing the social and cultural dynamics of communities situated along the border, which often experience a blending of Texan and New Mexican traditions and identities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What is the total length of the New Mexico-Texas border? A: The exact length varies slightly depending on the method of measurement, but it is approximately 800 miles.
-
Q: Does the Rio Grande River form the entire border? A: No, while a significant portion of the border follows the Rio Grande, other sections traverse different terrains.
-
Q: What historical events shaped the current border? A: The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) played a crucial role, but the border’s definition has also been influenced by earlier Spanish and Mexican claims and subsequent surveys and legal interpretations.
-
Q: Are there any ongoing disputes regarding the border’s location? A: While major disputes are rare, minor adjustments and clarifications may occur due to natural processes such as river avulsion.
-
Q: How does the border impact resource management? A: The border’s location is critical for shared resource management, particularly concerning water rights in the Rio Grande basin.
Tips for Interpreting Maps of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region:
-
Pay close attention to the scale of the map to understand the distances involved.
-
Identify key geographical features, such as rivers, mountains, and plains, to grasp the terrain’s complexity.
-
Examine the border’s precise location relative to towns, cities, and infrastructure.
-
Consult multiple maps and sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
-
Consider the historical context when analyzing the border’s current configuration.
Conclusion:
The cartographic representation of the New Mexico-Texas border is far more than a simple line on a map. It reflects a complex history, a diverse geography, and significant political and socio-economic implications. Understanding this boundary requires a multi-faceted approach, integrating historical research, geographical analysis, and consideration of the contemporary challenges and opportunities presented by this shared border region. A detailed analysis, informed by appropriate mapping and supporting documentation, provides crucial insights for effective governance, resource management, and cross-border cooperation between the two states. The map, therefore, remains an essential tool for understanding the past, present, and future of this significant territorial boundary.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Cartographic Examination of the New Mexico-Texas Border Region. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!