A Comparative Analysis of European and United States Cartography
Related Articles: A Comparative Analysis of European and United States Cartography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Analysis of European and United States Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Analysis of European and United States Cartography

Geographical representation, through maps, provides crucial insights into the spatial distribution of various features and facilitates understanding of global relationships. A comparison of European and United States cartography reveals distinct characteristics shaped by historical development, political structures, and cultural perspectives. This analysis explores these differences and highlights the importance of understanding these variations for effective navigation, spatial analysis, and international collaboration.
Geographical Scope and Scale: The United States, geographically larger than Western Europe, presents challenges different from those faced in mapping the smaller, more densely populated European continent. US maps often prioritize showcasing vast distances and diverse landscapes, incorporating extensive road networks, national parks, and state boundaries. In contrast, European maps frequently utilize larger scales, focusing on finer details within individual countries or regions. This difference reflects the need to depict intricate urban areas, national borders, and diverse topographical features within a relatively smaller area. The level of detail varies considerably depending on the map’s purpose, from broad overviews to highly detailed urban atlases.
Cartographic Conventions and Projections: Differences in cartographic conventions reflect the historical evolution of mapping practices in each region. While both regions utilize various map projections (Mercator, Lambert Conformal Conic, etc.), choices often reflect specific needs. The Mercator projection, for example, though distorting areas at higher latitudes, remains prevalent in many world maps due to its preservation of direction, a feature beneficial for navigation. However, its area distortion has led to the increased use of projections minimizing this effect, particularly in maps focused on spatial analysis or resource distribution. European maps might emphasize administrative boundaries and historical regions, while US maps may highlight states, counties, and major transportation corridors.
Data Representation and Themes: Thematic maps in both regions showcase diverse data sets, reflecting societal priorities and research interests. US maps often emphasize economic data, population distribution, and infrastructure development, reflecting the country’s large landmass and diverse economy. European maps, influenced by a history of denser populations and smaller national territories, may focus more on demographic density, environmental issues, and historical patterns of settlement. This difference in thematic focus reflects the unique challenges and opportunities presented by each region’s geography and socio-economic structures.
Technological Advancements and Digital Mapping: The digital revolution has profoundly impacted cartography in both the US and Europe. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies provide unprecedented opportunities for data collection, analysis, and visualization. Both regions utilize advanced GIS software and satellite imagery to create highly detailed and dynamic maps. However, access to these technologies and the level of their implementation may vary depending on funding, technical expertise, and institutional priorities. Open-source mapping initiatives have further democratized access to geographical data, fostering collaboration and innovation across geographical boundaries.
Historical Influences and Cultural Perspectives: The historical development of cartography in each region has shaped contemporary mapping practices. The long history of nation-state formation in Europe has influenced the emphasis on precise boundary delineation and the representation of historical regions. The expansionist history of the United States, with its emphasis on westward expansion and territorial acquisition, is reflected in maps that often showcase vast distances and the interconnectedness of transportation networks. Cultural perspectives also influence the selection of map features and the overall aesthetic presentation.
FAQs:
-
Q: What are the key differences between European and US topographic maps? A: European topographic maps often feature higher resolution and greater detail, reflecting denser populations and smaller national territories. US topographic maps often cover larger areas, showcasing vast landscapes and extensive road networks.
-
Q: How do political boundaries influence map design? A: Political boundaries are fundamental to map design in both regions. However, the emphasis on specific boundaries (national, state, county) varies depending on the map’s purpose and scale. Historical boundaries may also be included, especially in European maps.
-
Q: What role does technology play in modern cartography? A: Technology, including GIS and remote sensing, has revolutionized cartography, enabling the creation of highly detailed and dynamic maps incorporating diverse data sources.
-
Q: How do cultural perspectives affect map creation? A: Cultural perspectives influence the selection of map features, the level of detail, and the overall aesthetic presentation.
Tips:
- When comparing maps from different regions, consider the map’s purpose, scale, and projection.
- Analyze the data represented on the map to understand the underlying themes and priorities.
- Pay attention to the cartographic conventions used, such as symbols, colors, and labels.
- Consult multiple maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area.
Conclusion:
The comparative analysis of European and United States cartography reveals a complex interplay of geographical factors, technological advancements, and cultural perspectives. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective spatial analysis, informed decision-making, and international collaboration. The continued evolution of mapping technologies and the increasing availability of geographical data promise further advancements in our ability to represent and understand the world’s diverse landscapes and societies. Further research into the specific historical and cultural influences on cartographic practices in both regions would provide a richer understanding of the multifaceted nature of geographical representation.
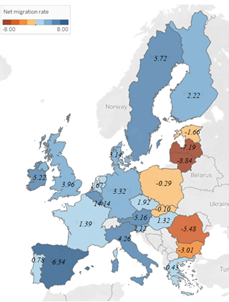



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Analysis of European and United States Cartography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!