A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Tropical Rainforests
Related Articles: A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Tropical Rainforests
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Tropical Rainforests. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Tropical Rainforests

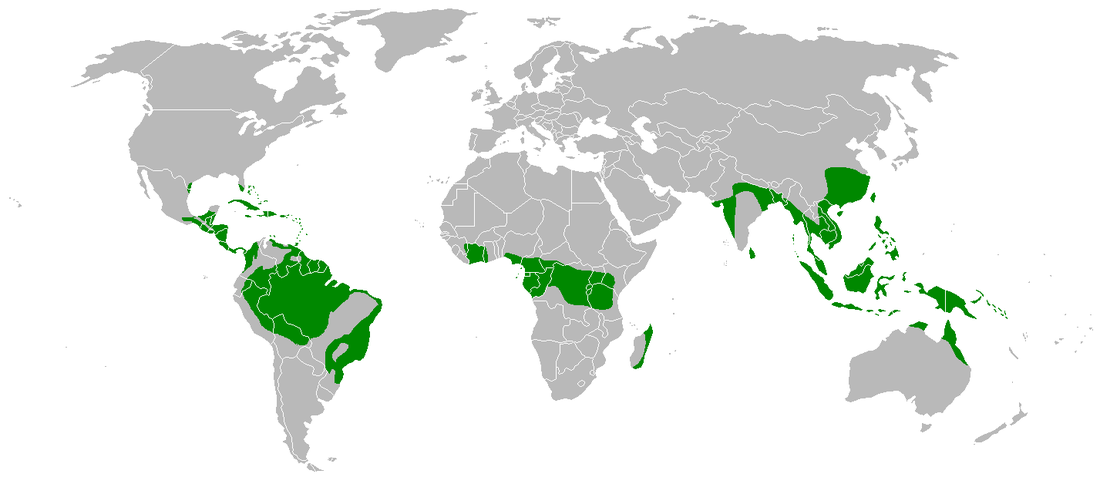
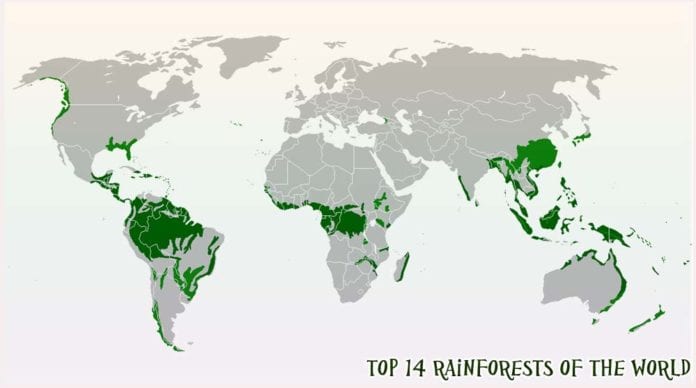
Tropical rainforests, characterized by high rainfall, dense vegetation, and exceptional biodiversity, are vital ecosystems distributed across the globe. Their location is not uniform; instead, they are concentrated in specific latitudinal bands and influenced by complex geographical and climatic factors. A map depicting their distribution reveals crucial insights into their ecological importance and global significance.
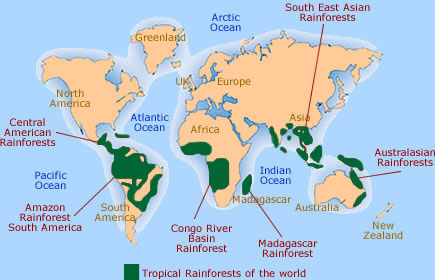
The primary regions supporting these crucial ecosystems are located within the tropics, generally between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. However, the precise boundaries are not fixed, influenced by altitude, proximity to oceans, and prevailing wind patterns. South America boasts the largest contiguous area of rainforest, primarily within the Amazon Basin, extending across Brazil, Colombia, Peru, and several other nations. The Congo Basin in Central Africa represents another significant concentration, covering parts of the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon, and neighboring countries. Southeast Asia, particularly Indonesia, Malaysia, and Papua New Guinea, contains another major belt, characterized by a high level of endemism (species found nowhere else). Smaller, yet equally important, pockets exist in other tropical regions, including Madagascar, Australia, and Central America.
Examination of a global map illustrating these areas highlights the uneven distribution of these ecosystems. This unevenness is a direct consequence of the intricate interplay of climate, geography, and soil conditions. High rainfall, typically exceeding 2000 mm annually, is a prerequisite, coupled with consistently high temperatures. The availability of sunlight and fertile soil further contribute to the lush vegetation and exceptional biodiversity. Variations in these factors explain why rainforest regions are not continuous but rather fragmented, exhibiting differences in species composition and ecosystem structure.
The importance of these ecosystems extends far beyond their geographical boundaries. They are often referred to as the "lungs of the planet," due to their significant role in global carbon sequestration. The dense vegetation absorbs substantial amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide, thereby mitigating climate change. Furthermore, these forests regulate local and regional climates, influencing rainfall patterns and temperature fluctuations. Their vast root systems prevent soil erosion and maintain water cycles, contributing to water security in surrounding areas.
Beyond climate regulation, these forests are unparalleled repositories of biodiversity. They harbor an estimated 50% of the world’s plant and animal species, many of which are still undiscovered. This biodiversity underpins numerous ecosystem services, including pollination, seed dispersal, nutrient cycling, and pest control. Many of these species hold potential for medicinal and other applications, highlighting their economic value. Indigenous communities have for millennia relied on these ecosystems for their livelihoods, drawing sustenance, medicine, and building materials from the forest. The loss of these forests not only threatens biodiversity but also jeopardizes the cultural heritage and well-being of these communities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What are the primary threats to tropical rainforests?
-
A: Deforestation driven by agriculture, logging, mining, and infrastructure development poses the greatest threat. Climate change, including altered rainfall patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events, further exacerbates these pressures.
-
Q: How are rainforests mapped?
-
A: Mapping relies on a combination of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground-based surveys. Remote sensing techniques are crucial for monitoring deforestation and assessing changes in forest cover over time.
-
Q: What is the significance of biodiversity hotspots within rainforests?
-
A: Biodiversity hotspots are areas with exceptionally high levels of endemic species facing significant threats. Their identification is crucial for prioritizing conservation efforts and protecting irreplaceable biodiversity.
Tips for Understanding Rainforest Maps:
-
Focus on scale: Different maps employ varying scales, affecting the level of detail shown. Larger-scale maps provide greater precision, while smaller-scale maps offer a broader overview.
-
Consider data sources: The accuracy and reliability of a map depend on the data sources used. Maps based on recent, high-resolution data are generally more accurate than those based on older or lower-resolution data.
-
Analyze patterns: Examine the distribution of rainforest regions in relation to climatic and geographical factors. This helps to understand the environmental controls shaping their distribution.
-
Compare maps over time: Analyzing changes in rainforest cover over time reveals the impact of deforestation and other pressures. This temporal analysis is vital for monitoring trends and informing conservation strategies.
Conclusion:
A global map of these crucial ecosystems reveals a complex and dynamic picture of their distribution and the factors influencing their survival. Their immense biodiversity, role in climate regulation, and contribution to human well-being necessitate their protection. Understanding their geographical distribution, the threats they face, and the ongoing efforts to conserve them is paramount for securing a sustainable future for both the planet and its inhabitants. Continued research, monitoring, and effective conservation strategies are crucial to mitigating the ongoing loss and ensuring the long-term preservation of these vital ecosystems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Tropical Rainforests. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!