Amsterdam as a Microcosm: Exploring Global Connections Through Urban Cartography
Related Articles: Amsterdam as a Microcosm: Exploring Global Connections Through Urban Cartography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Amsterdam as a Microcosm: Exploring Global Connections Through Urban Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Amsterdam as a Microcosm: Exploring Global Connections Through Urban Cartography

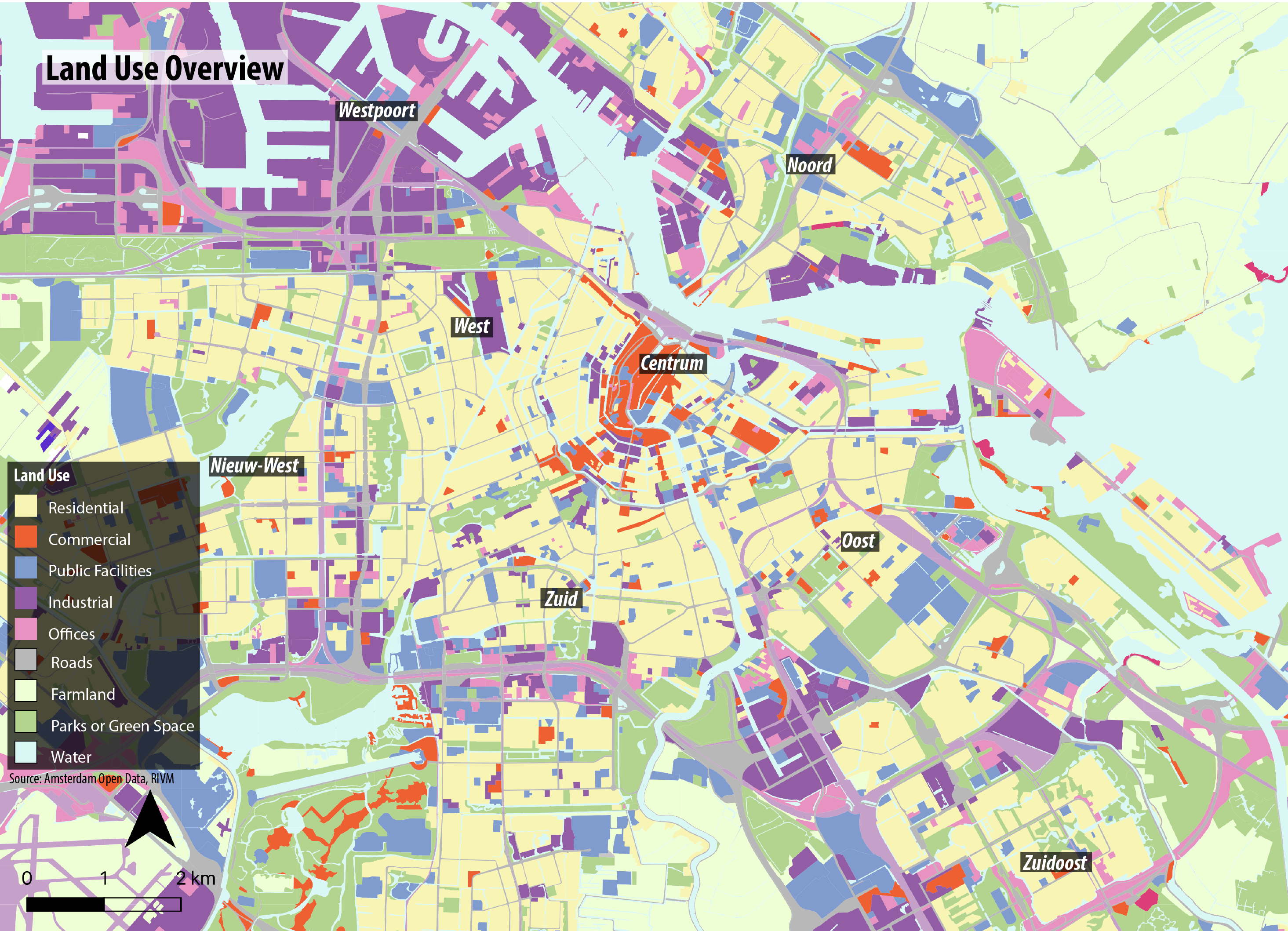
Amsterdam’s unique position as a global hub is often reflected in its urban landscape. The city’s intricate canal system, its diverse population, and its role in international trade and culture all contribute to a rich tapestry of global interconnectedness. Analyzing Amsterdam through a cartographic lens reveals a complex interplay of historical, economic, and social forces that shaped not only the city itself but also its influence on the wider world. This analysis explores the ways in which Amsterdam’s geographical location, historical development, and contemporary activities contribute to its global significance, highlighting its role as a nexus of international exchange.
Historical Context: From Trading Post to Cosmopolitan Center
Amsterdam’s rise to prominence is intrinsically linked to its strategic location. Situated at the mouth of the Amstel River, with access to the Zuiderzee (now IJsselmeer) and the North Sea, the city enjoyed a naturally advantageous position for trade. Early maps depict a small settlement gradually expanding its influence, reflecting the growth of its maritime activities. The Dutch Golden Age, beginning in the 17th century, saw Amsterdam become a leading commercial power. This period witnessed an influx of goods and people from across the globe, solidifying the city’s position as a major international trading center. Maps from this era illustrate the vast network of trade routes connecting Amsterdam to the East Indies, the Americas, and various European ports. This global reach is further evidenced by the architectural styles, cultural influences, and religious diversity that characterized the city’s development.
The city’s expansion during this era is clearly depicted in historical maps. These maps not only show the physical growth of the city’s boundaries but also provide insights into the development of its infrastructure, such as canals, warehouses, and fortifications. This infrastructure was crucial in facilitating trade and supporting the city’s burgeoning population. The detailed depiction of harbors, wharves, and shipbuilding yards further emphasizes the importance of maritime commerce to Amsterdam’s prosperity.
Contemporary Amsterdam: A Global Node
Amsterdam’s significance extends beyond its historical legacy. Contemporary maps reveal a city that remains a crucial node in global networks. Its position as a major European transportation hub, with its Schiphol Airport and extensive rail connections, underscores its continued importance in facilitating international movement of people and goods. Furthermore, the city’s robust financial sector, its thriving creative industries, and its prominent role in international organizations all contribute to its global influence.
Modern cartographic representations of Amsterdam often highlight the city’s diverse population, reflecting its status as a multicultural metropolis. These maps might illustrate the distribution of different ethnic groups or highlight the locations of various cultural institutions and places of worship. This representation underscores the city’s open and inclusive nature, attracting individuals from around the world and fostering a rich tapestry of cultural exchange.
Analyzing Spatial Patterns: Infrastructure and Global Interconnectivity
The spatial organization of Amsterdam’s infrastructure further demonstrates its global connections. The concentric canal rings, a defining feature of the city, reflect a historical pattern of expansion and development. However, these canals also serve as arteries for the flow of goods and people, facilitating efficient transport within the city and connecting it to the wider world. Modern transportation networks, including highways, trams, and bicycle paths, overlay this historical infrastructure, creating a complex and efficient system that supports the city’s global functions.
Analyzing the distribution of businesses, particularly those with international operations, reveals further insights into Amsterdam’s global role. Clusters of multinational corporations, international organizations, and financial institutions highlight the concentration of global economic activity within the city. These spatial patterns are clearly visible on contemporary maps, showcasing the city’s strategic importance in the global economy.
Amsterdam’s Influence: Beyond Geographic Boundaries
Amsterdam’s global influence extends beyond its physical boundaries. The city’s role as a center for innovation, particularly in areas such as technology and sustainable development, has a global impact. Its contributions to international discussions on climate change, social justice, and human rights demonstrate its commitment to addressing global challenges. Furthermore, the city’s cultural institutions, museums, and artistic communities contribute to the global dissemination of knowledge and artistic expression. These contributions are often documented and analyzed through various forms of cartography, including thematic maps focusing on specific aspects of the city’s global influence.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How does Amsterdam’s geography contribute to its global significance? A: Amsterdam’s location at the mouth of the Amstel River, providing access to the sea and major trade routes, was historically crucial for its development as a major trading center. This strategic position continues to support its role as a significant transportation hub.
-
Q: What role did the Dutch Golden Age play in shaping Amsterdam’s global connections? A: The Dutch Golden Age saw Amsterdam become a leading global trading power, establishing extensive trade networks across the globe and attracting a diverse population, significantly shaping its current global interconnectedness.
-
Q: How does Amsterdam’s contemporary infrastructure support its global role? A: Amsterdam’s modern infrastructure, including its airport, rail network, and efficient internal transportation systems, supports the city’s role as a major transportation and economic hub.
-
Q: How does Amsterdam contribute to global discussions on important issues? A: Amsterdam actively participates in and hosts international discussions on climate change, social justice, and human rights, contributing its expertise and influencing global policy.
Tips for Understanding Amsterdam’s Global Significance
- Examine historical maps to trace the city’s growth and the development of its infrastructure.
- Analyze contemporary maps to understand the distribution of global businesses and institutions within the city.
- Research the city’s history and its role in major historical events to grasp its global impact.
- Explore the diversity of Amsterdam’s population and its cultural institutions to understand its multicultural character.
Conclusion
Amsterdam’s position as a global city is not merely a matter of geographical location; it is the product of centuries of historical development, strategic planning, and a commitment to international cooperation. By examining its urban landscape through a cartographic lens, a comprehensive understanding of its global connections emerges. The city’s historical legacy, its contemporary infrastructure, and its active participation in global affairs all contribute to its significant role on the world stage. Further research into Amsterdam’s spatial organization and its global networks will continue to reveal the depth and complexity of this fascinating urban landscape and its enduring influence.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Amsterdam as a Microcosm: Exploring Global Connections Through Urban Cartography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!