Annotating Google Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Annotating Google Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Annotating Google Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Annotating Google Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
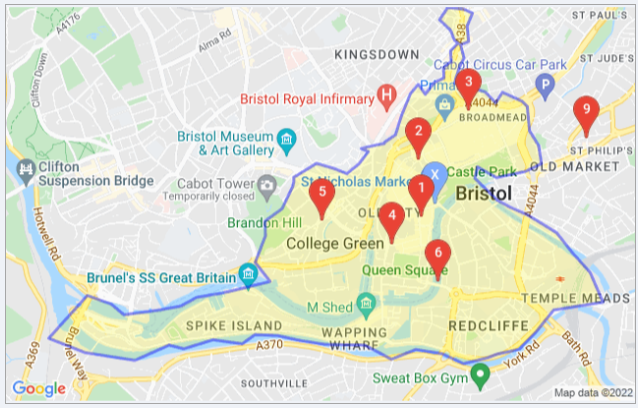
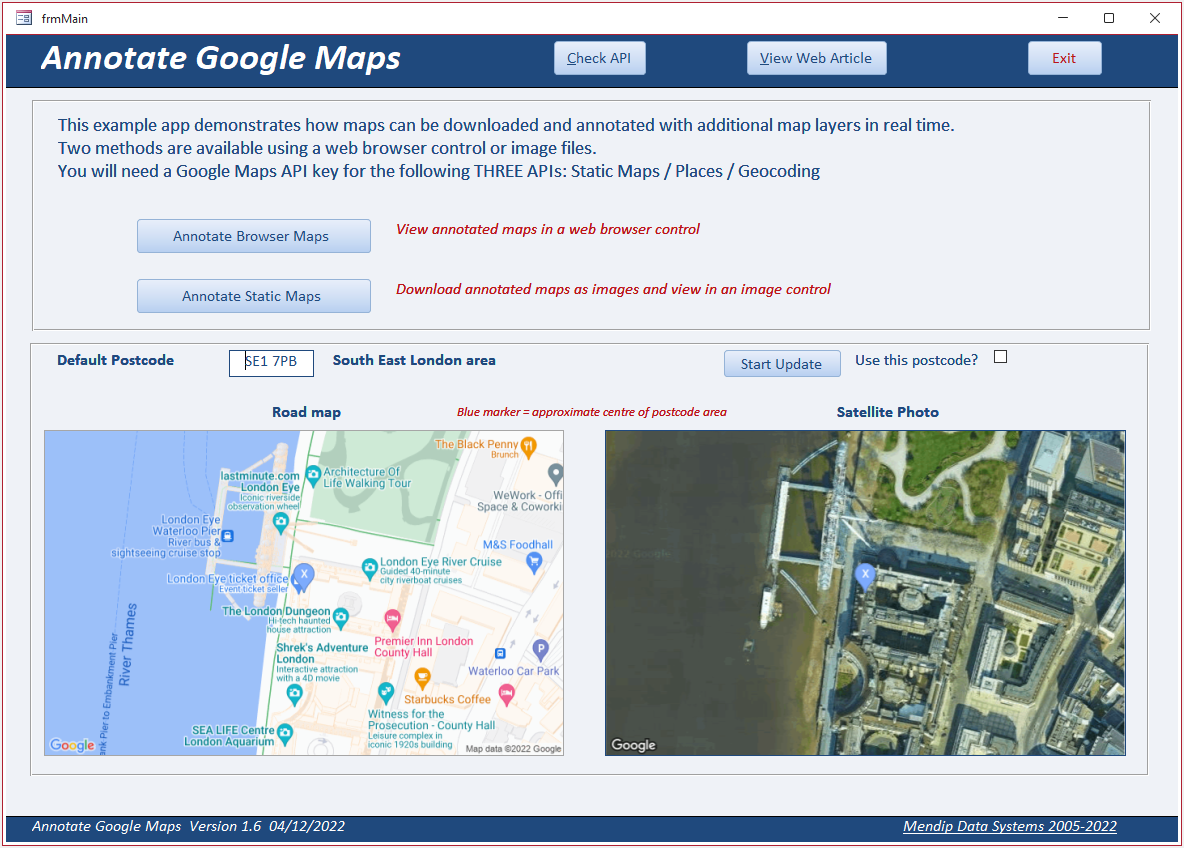
Google Maps’ functionality extends beyond simple navigation. The ability to add visual annotations significantly enhances its utility for various purposes, from planning routes and highlighting areas of interest to creating detailed visual representations for presentations and collaborative projects. This guide explores the diverse methods available for adding visual information directly onto a Google Map, detailing the process and highlighting the advantages of each approach.
Methods for Adding Visual Information to Google Maps
Several techniques allow for the addition of visual information to Google Maps, each with its strengths and limitations. These methods cater to different needs and technical proficiencies.
1. Using the Google Maps Drawing Tools (For Basic Annotations):
The simplest method involves utilizing the built-in drawing tools within Google Maps. This functionality allows for basic shapes – lines, polygons, and markers – to be added directly to the map interface. The process is intuitive:
-
Accessing the Drawing Tools: The availability of these tools may vary slightly depending on the device and Google Maps version. Generally, these tools are accessed through a dedicated "drawing" or "add a marker" option, often found within a more extensive menu accessible via the three vertical dots or a "+" icon.
-
Adding Shapes: Once the drawing tools are activated, the user can select the desired shape (line, polygon, or marker) and then click and drag on the map to create the shape. Markers represent specific points, lines connect two or more points, and polygons create closed shapes encompassing an area.
-
Customization: Basic customization options are usually available, such as color selection and line thickness. However, more advanced customization is limited.
-
Limitations: This method is suitable for simple annotations. Complex shapes or detailed illustrations are not easily achievable. Furthermore, saved annotations are typically only visible to the user who created them, unless shared explicitly via a link.
2. Employing Third-Party Applications (For Advanced Annotations):
Numerous third-party applications offer advanced capabilities for annotating Google Maps. These applications often provide more sophisticated drawing tools, allowing for greater precision and customization. They frequently enable the creation of more complex shapes, the addition of images and text, and the sharing of annotated maps with collaborators.
-
Application Selection: The selection of a suitable application depends on the specific requirements. Some applications specialize in route planning and annotation, while others focus on creating interactive maps for presentations or collaborative projects.
-
Import/Export Functionality: Many applications support the import and export of various file formats, including KML and GeoJSON, allowing for seamless integration with other Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software.
-
Collaboration Features: Several applications offer collaborative features, allowing multiple users to simultaneously work on the same map.
-
Advanced Features: Advanced features may include measurement tools, area calculation capabilities, and the ability to add multiple layers of information to a single map.
3. Utilizing Screen Capture and Image Editing Software (For Static Annotations):
This method involves taking a screenshot of the desired Google Map area and then using image editing software to add annotations. This approach provides maximum flexibility and control over the visual elements.
-
Screenshot Capture: The process begins by capturing a screenshot of the relevant Google Map section using the operating system’s built-in screenshot functionality or a dedicated screen capture application.
-
Image Editing: The captured image is then opened in an image editing program (such as Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or even simpler applications like Microsoft Paint). The annotation is added using the software’s drawing tools. This allows for precise control over the visual elements, including the use of text, images, and various shapes.
-
File Format Selection: The final annotated image can be saved in a suitable format (e.g., JPEG, PNG) for sharing or archiving.
-
Limitations: This method results in a static image; it does not maintain the interactive functionality of the original Google Map. Updates to the underlying map will not be reflected in the annotated image.
Benefits of Annotating Google Maps
The ability to visually enrich Google Maps offers several significant benefits across various domains:
-
Enhanced Communication: Annotations improve communication by providing clear visual representations of information, making complex data easier to understand. This is particularly useful for presentations, reports, and collaborative projects.
-
Improved Planning: For projects involving site surveys, route planning, or resource allocation, annotations allow for the precise identification and marking of key locations and areas.
-
Data Visualization: Visual representations of data on a map provide a powerful means of understanding spatial patterns and relationships.
-
Increased Efficiency: Annotating maps can streamline workflows by providing a central repository for information relevant to a specific project or task.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can annotations be saved and accessed later? A: The ability to save annotations depends on the method used. The built-in Google Maps tools offer limited saving options, while third-party applications often provide robust saving and retrieval mechanisms. Screen captures are saved as static images.
Q: Can annotations be shared with others? A: Sharing capabilities vary. Built-in tools offer limited sharing options. Third-party applications often provide more sophisticated sharing features, allowing collaboration and the distribution of annotated maps. Screen captures can be easily shared via email or other file-sharing services.
Q: Are there limitations on the types of annotations that can be added? A: The types of annotations are limited by the chosen method. The built-in Google Maps tools are restricted to basic shapes. Third-party applications and image editing software offer much greater flexibility.
Tips for Effective Annotation
-
Clarity and Simplicity: Prioritize clarity and simplicity in annotations. Avoid overly complex designs that might obscure the intended information.
-
Consistent Style: Maintain a consistent style throughout the annotation process to ensure visual coherence.
-
Legend/Key: If multiple annotations are used, include a legend or key to explain the meaning of different symbols or colors.
-
Appropriate Scale: Ensure the annotation scale is appropriate for the map’s scale to avoid misinterpretations.
-
File Management: Maintain organized file management for annotated maps, especially when working with multiple files or collaborators.
Conclusion
Annotating Google Maps offers a powerful way to enhance the platform’s functionality and unlock its potential for various applications. The choice of method depends heavily on the complexity of the annotation requirements and the level of technical expertise available. By understanding the different approaches and following best practices, users can leverage the power of visual annotation to create informative, engaging, and effective representations of spatial information.
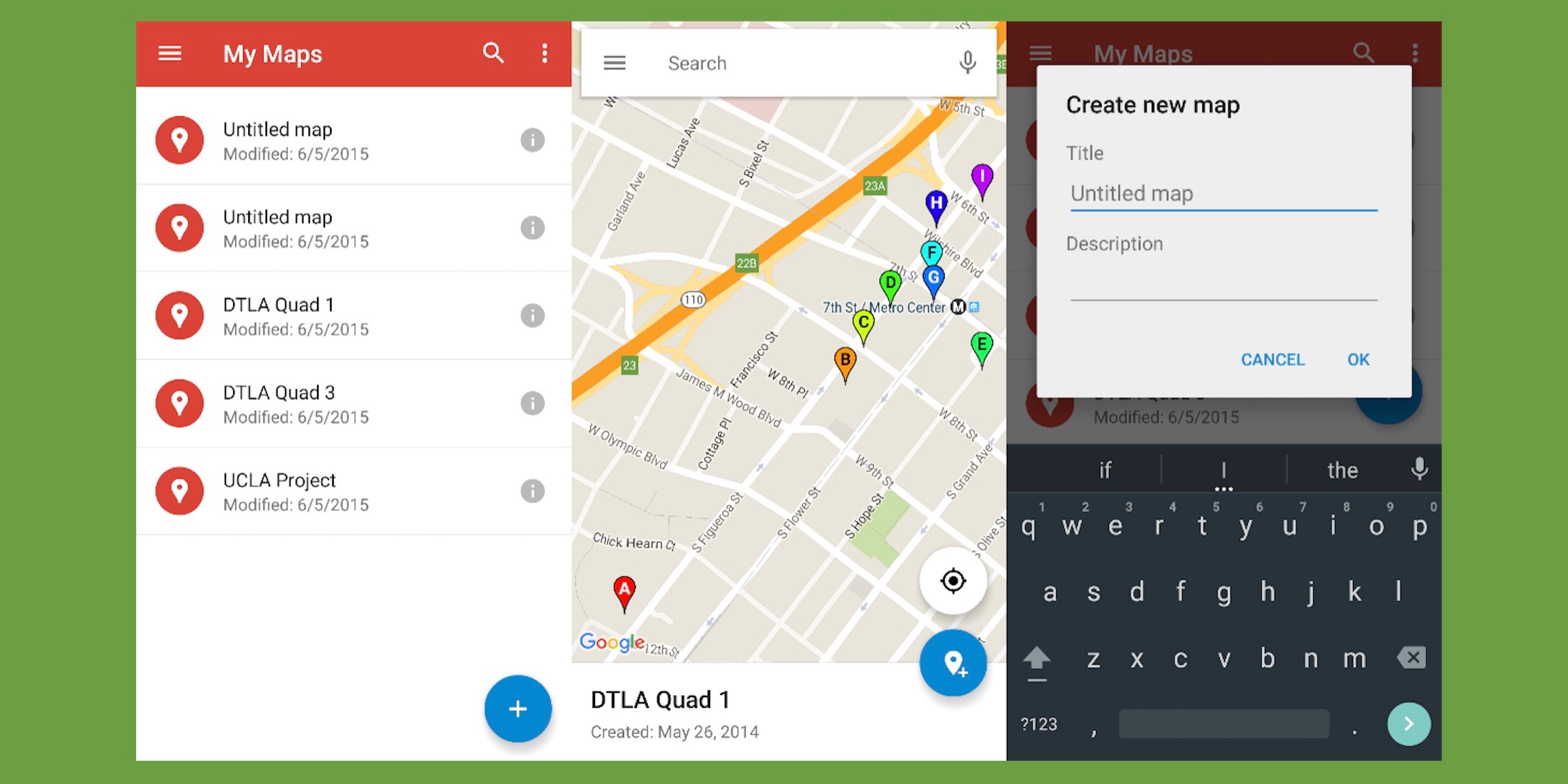


![A Step-by-Step Guide to Text Annotation [+Free OCR Tool]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5d7b77b063a9066d83e1209c/627d1251e047d52e001159a5_6270a027e69528cb016a9bcf_Screenshot%25202022-05-02%2520at%252021.21.51-min.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Annotating Google Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!