Belize’s Geographical Position: A Central American Jewel
Related Articles: Belize’s Geographical Position: A Central American Jewel
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Belize’s Geographical Position: A Central American Jewel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Belize’s Geographical Position: A Central American Jewel

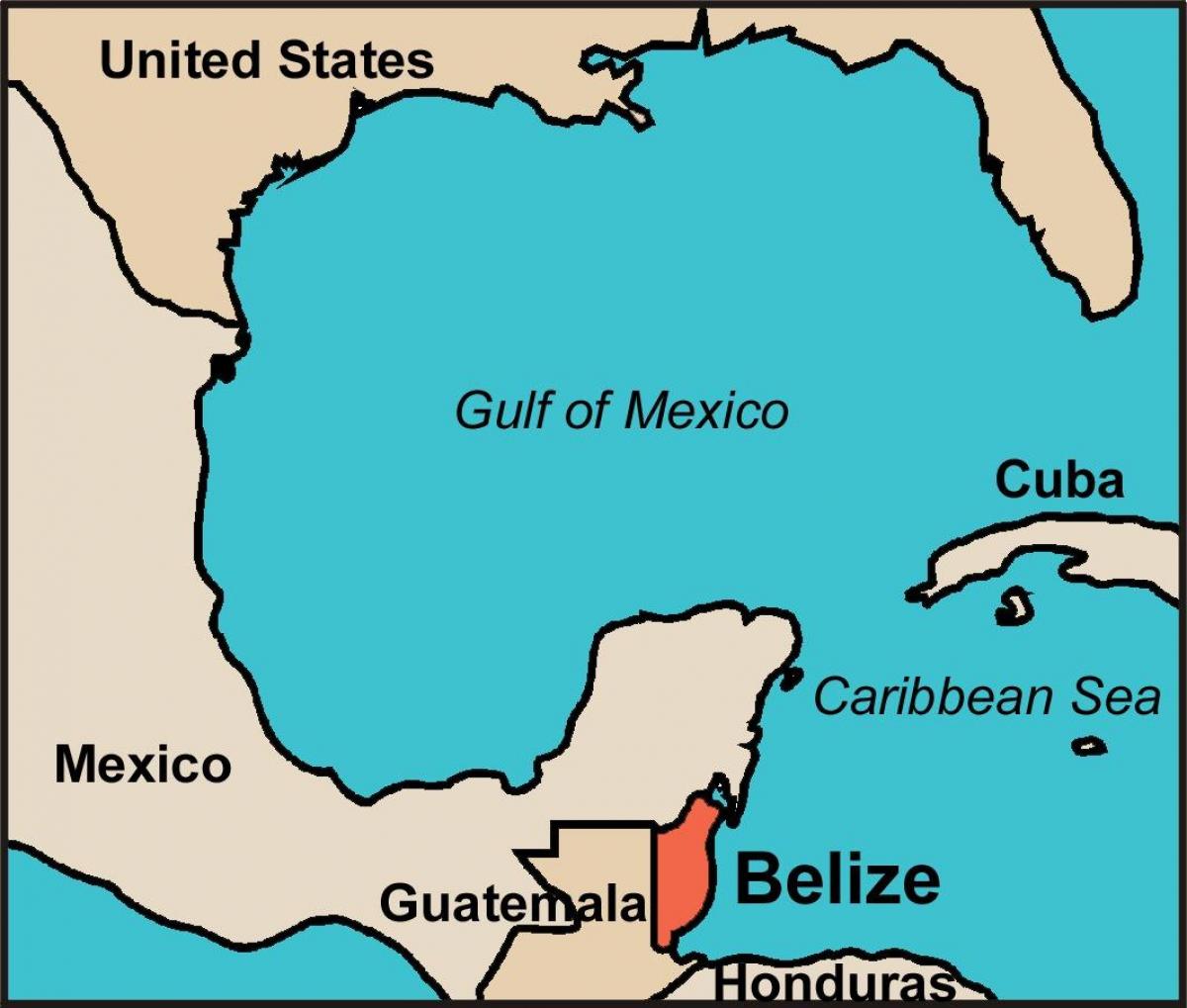
Belize occupies a unique geographical position in Central America, situated on the northeastern coast of the Yucatán Peninsula. Its precise coordinates are roughly between 15°53’N latitude and 88°47’W longitude. This location provides a compelling blend of diverse ecosystems, rich biodiversity, and strategic geopolitical importance.
Regional Context: The country’s position on the Caribbean Sea, bordering Mexico to the north and Guatemala to the west and south, significantly influences its climate, culture, and economy. Its proximity to Mexico facilitates trade and tourism, while its southern border with Guatemala shapes its socio-political landscape and presents both opportunities and challenges. The Caribbean Sea provides access to vital maritime trade routes and supports a thriving tourism industry based on its stunning coral reefs and idyllic beaches.
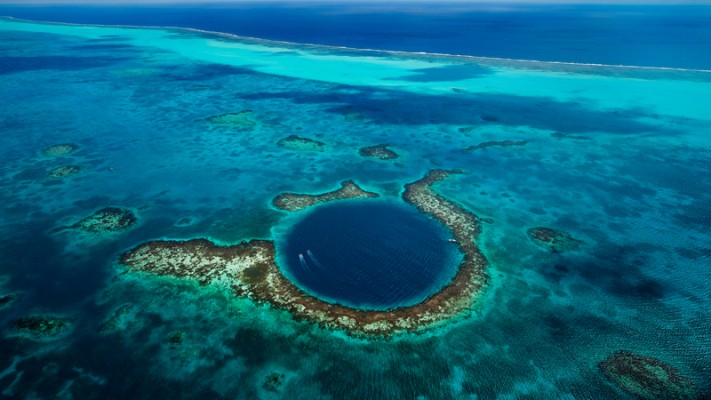
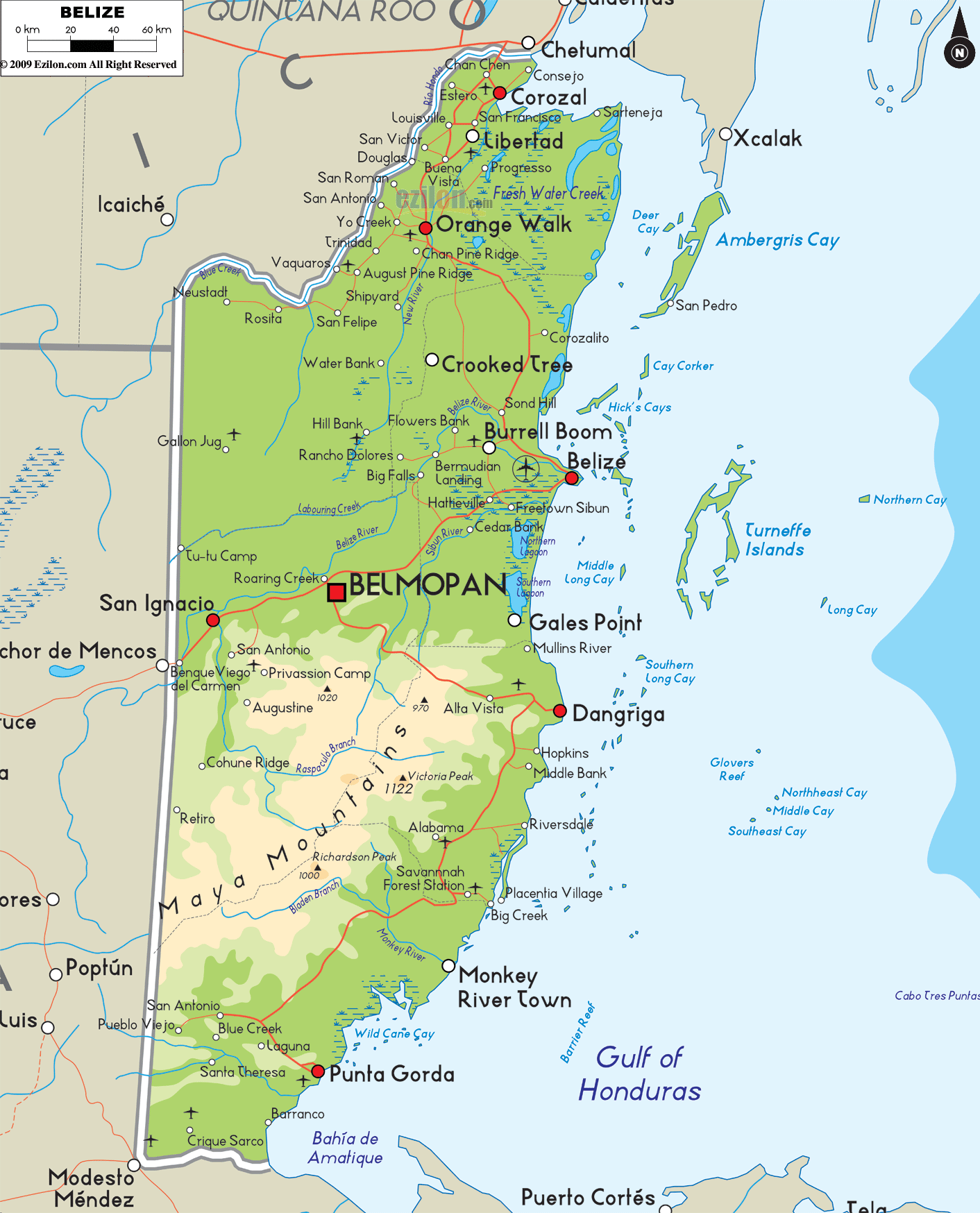
Cartographic Representation: Maps depicting Belize consistently show its relatively small size compared to its neighbours. Its elongated shape, extending roughly 290 kilometers from north to south and averaging about 110 kilometers in width, is clearly visible. The country’s coastline, featuring the Belize Barrier Reef, the second-largest coral reef system globally, is a prominent feature in any detailed map. Numerous cayes (small islands) dot the coastal waters, further enhancing the visual appeal and ecological significance reflected in cartographic representations.
Ecological Significance: Belize’s location contributes significantly to its extraordinary biodiversity. The country is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, mangroves, savannas, and the aforementioned Belize Barrier Reef. This geographical position at the confluence of North and South American biomes results in a unique blend of flora and fauna, supporting a rich ecosystem that attracts researchers, conservationists, and ecotourists alike. The country’s position within the Caribbean hurricane belt necessitates careful environmental management and disaster preparedness.
Economic Implications: The strategic location facilitates trade with both North and Central America. Its access to the Caribbean Sea and the proximity to major shipping lanes supports its export-oriented economy, primarily focused on agricultural products, seafood, and tourism. The growing tourism sector, fueled by the country’s natural beauty and diverse ecosystems, contributes significantly to the national economy. However, dependence on tourism also exposes the country to external economic shocks and environmental vulnerabilities.
Geopolitical Considerations: Belize’s location presents both opportunities and challenges in the geopolitical arena. Its proximity to Mexico and Guatemala requires careful diplomatic navigation. The country’s history and ongoing territorial disputes with Guatemala underscore the complexities of its geopolitical positioning. Furthermore, its strategic location within the Caribbean makes it a region of interest for various international actors, requiring a careful balancing act in foreign policy.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What is Belize’s relationship with its neighboring countries? A: Belize shares borders with Mexico to the north and Guatemala to the west and south. These relationships are complex, shaped by historical events, economic interactions, and ongoing territorial disputes, particularly with Guatemala.
-
Q: What is the significance of the Belize Barrier Reef? A: The Belize Barrier Reef is the second-largest coral reef system in the world and a significant contributor to the country’s biodiversity and tourism industry. Its location along the coast is crucial for its protective function and ecological value.
-
Q: How does Belize’s location affect its climate? A: Belize’s location within the Caribbean region results in a tropical climate, characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The country is also situated within the hurricane belt, making it vulnerable to severe weather events.
Tips for Understanding Belize’s Geographical Context:
- Utilize detailed physical maps to understand the country’s topography, including its coastal features and inland mountainous regions.
- Consult climate maps to appreciate the influence of its geographical location on temperature, rainfall, and hurricane risk.
- Explore satellite imagery to visualize the extent of the Belize Barrier Reef and other significant ecosystems.
- Analyze political maps to understand the country’s borders and its relationships with neighboring states.
Conclusion:
Belize’s geographical position plays a defining role in shaping its unique character. The country’s location on the northeastern coast of the Yucatán Peninsula, bordering Mexico and Guatemala, and its access to the Caribbean Sea, are crucial determinants of its biodiversity, economy, and geopolitical dynamics. Understanding this location is essential for comprehending the country’s strengths, challenges, and future prospects. The interplay of its physical geography, ecological richness, and regional context continues to shape its development and international relations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Belize’s Geographical Position: A Central American Jewel. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!