Brazil’s Geographic Position and Influence in South America
Related Articles: Brazil’s Geographic Position and Influence in South America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Brazil’s Geographic Position and Influence in South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Brazil’s Geographic Position and Influence in South America
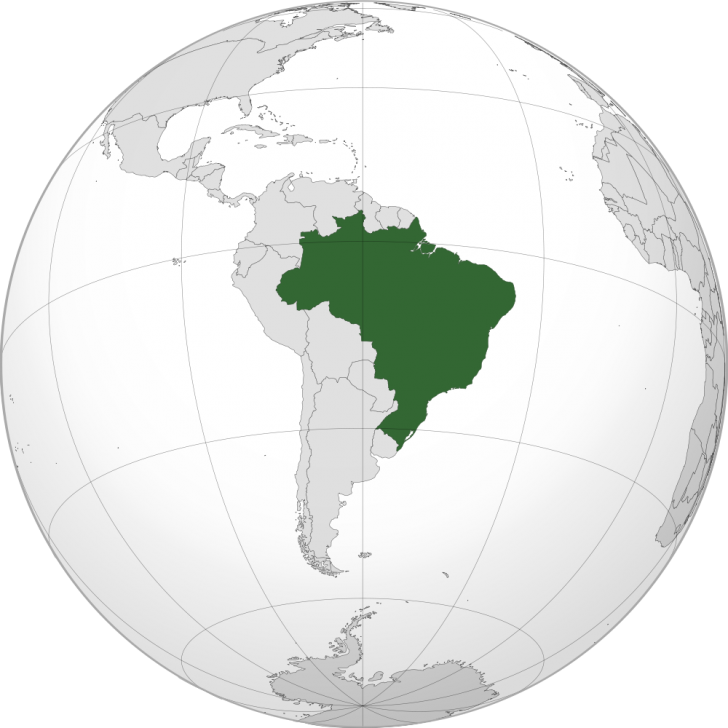
Brazil’s expansive territory dominates the eastern portion of South America, a geographical feature with significant implications for its economy, environment, and geopolitical standing. Its unique shape and location contribute to a diverse range of climates, ecosystems, and natural resources, influencing the nation’s development trajectory and global interactions. Understanding the country’s cartographic representation within the South American context reveals crucial insights into its multifaceted character.
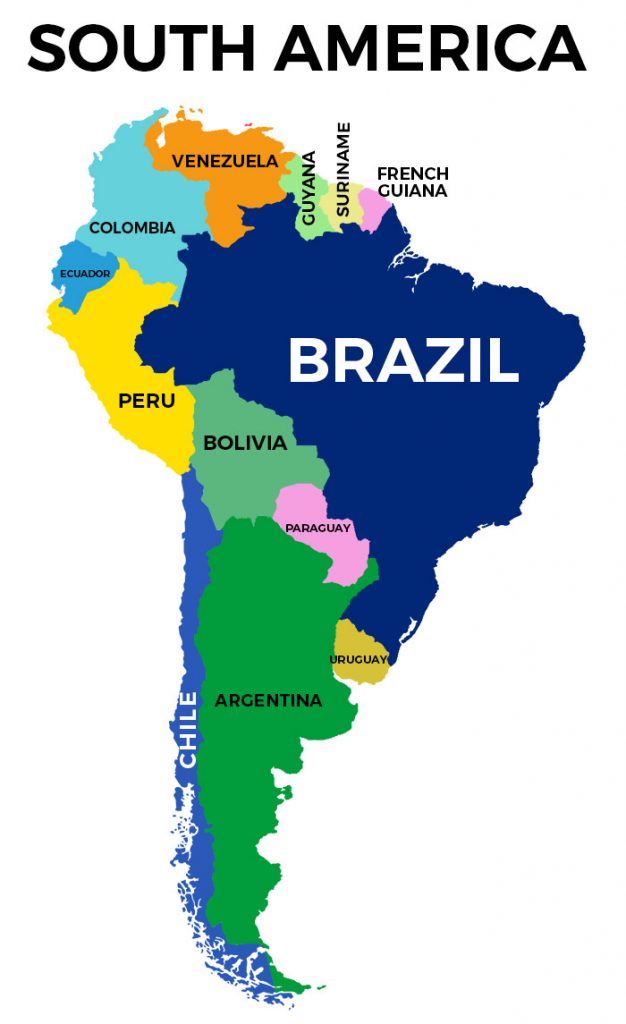
The country’s sheer size is immediately apparent on any map. Occupying nearly half of the continent’s landmass, Brazil stretches over 8.5 million square kilometers, bordering almost every other South American nation except Chile and Ecuador. This extensive land border network necessitates complex diplomatic relationships and fosters considerable regional interaction. The Amazon rainforest, a globally significant ecosystem, covers a substantial portion of the northern region, highlighting the country’s role as a crucial player in international environmental discussions and conservation efforts.
Brazil’s eastern coastline, extending thousands of kilometers along the Atlantic Ocean, offers access to vital shipping lanes and abundant marine resources. This coastal geography has historically shaped the country’s economic activities, driving the development of major port cities and influencing trade patterns. In contrast, the vast interior, characterized by the Amazon basin and the Cerrado savanna, presents both opportunities and challenges, impacting infrastructure development and resource management.
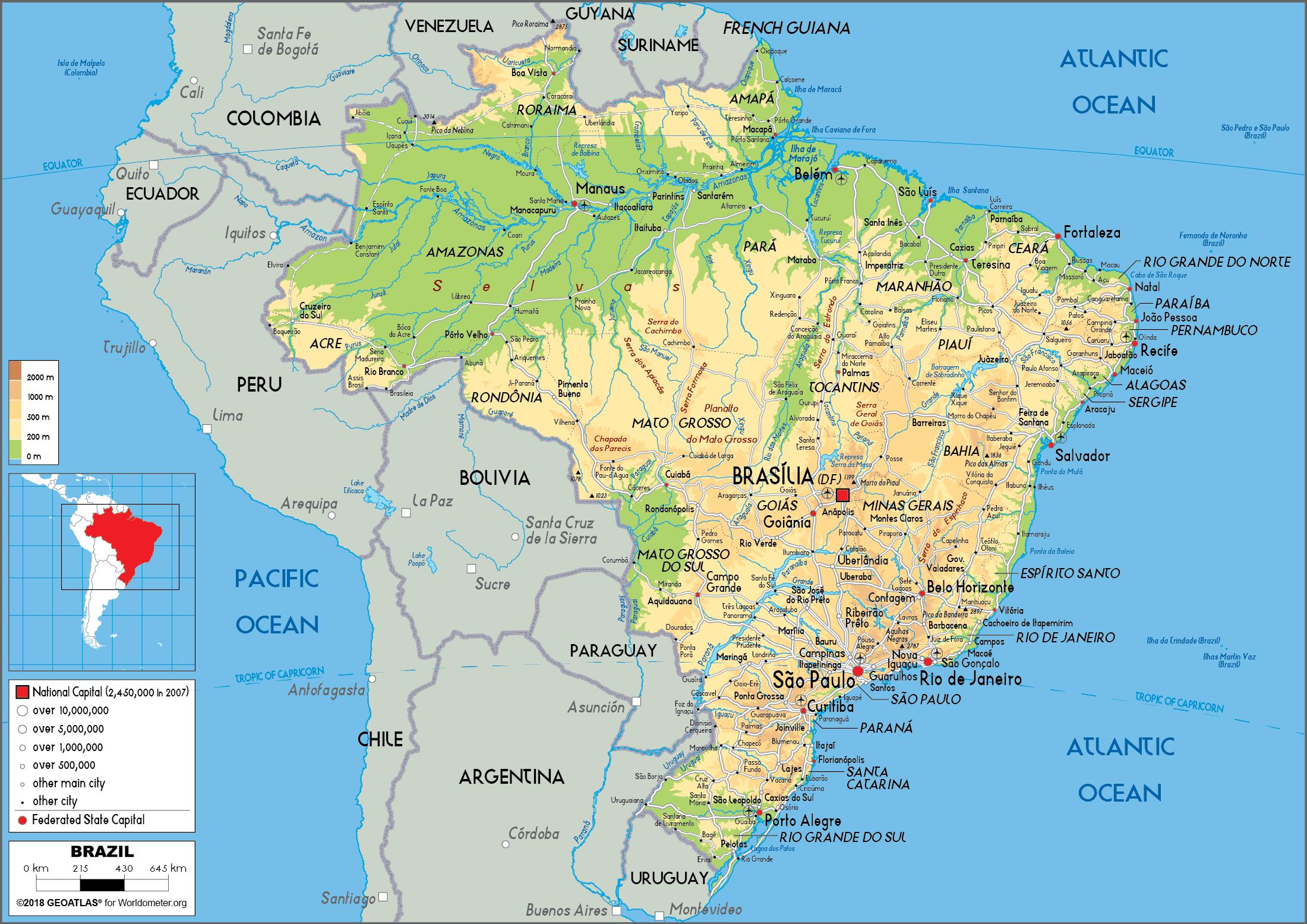
The map reveals a diverse topography. The Amazon basin, with its vast lowlands and extensive river systems, contrasts sharply with the highlands of the Brazilian Plateau in the southeast, a region characterized by significant elevation changes and diverse landscapes. This topographical variation contributes to the country’s rich biodiversity and creates distinct agricultural zones, impacting the production of various commodities. The Pantanal wetlands, located in the central-western region, represent another important ecological zone, highlighting the country’s remarkable biodiversity and the need for sustainable resource management.
The country’s location within the tropics influences its climate. While the Amazon region experiences a hot and humid tropical climate, other regions exhibit variations ranging from subtropical to temperate conditions. This climatic diversity supports a wide range of agricultural products, from coffee and soybeans to sugarcane and fruits, contributing significantly to the country’s agricultural exports. However, this climatic variability also presents challenges, such as susceptibility to droughts and floods, requiring effective disaster management strategies.
Brazil’s geographic position has profound geopolitical implications. Its size and strategic location make it a key player in regional and international affairs. The country’s influence extends beyond its borders, impacting regional organizations such as Mercosur and fostering bilateral relationships with numerous nations worldwide. Its vast natural resources and its growing economy further solidify its global prominence.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the major geographical regions of Brazil? Brazil comprises diverse regions, including the Amazon rainforest, the Cerrado savanna, the Pantanal wetlands, the Brazilian Highlands, and the coastal plains. Each region boasts unique characteristics impacting its economic activities and ecological importance.
-
What is the significance of the Amazon rainforest for Brazil? The Amazon rainforest is of immense ecological significance, playing a crucial role in global climate regulation and housing unparalleled biodiversity. Its conservation is vital not only for Brazil but for the entire planet. Its economic impact is also considerable, though sustainable management is crucial to prevent environmental degradation.
-
How does Brazil’s geography affect its economy? Brazil’s geography significantly shapes its economy. The extensive coastline facilitates trade, while the diverse climates and terrains support a wide range of agricultural and extractive industries. However, geographical challenges, such as the vast distances within the country, require significant investment in infrastructure.
-
What are the major rivers of Brazil? Brazil’s river systems are extensive, with the Amazon River being the most prominent, one of the world’s largest and most biodiverse river basins. Other significant rivers include the Paraná, São Francisco, and Tocantins, playing crucial roles in transportation, hydropower generation, and the country’s overall economy.
-
What are the major mountain ranges in Brazil? While not characterized by extensive mountain ranges like some other South American nations, Brazil possesses significant highland regions, notably the Brazilian Highlands, which significantly influence the country’s drainage patterns and regional climates.
Tips for Understanding Brazil’s Geography
- Utilize detailed maps showing elevation, climate zones, and vegetation types to gain a comprehensive understanding of the country’s geographical diversity.
- Analyze the distribution of major cities and economic activities in relation to the country’s geographical features to understand the spatial organization of economic processes.
- Investigate the interplay between Brazil’s geography and its environmental challenges, such as deforestation and water resource management.
- Examine the historical impact of geographical factors on the development of different regions within the country.
- Explore the role of Brazil’s geography in shaping its international relations and regional influence within South America.
Conclusion
Brazil’s geographical position within South America is a defining characteristic, shaping its economic activities, environmental conditions, and geopolitical influence. The country’s vast size, diverse ecosystems, and extensive coastline contribute to its global importance. Understanding its cartographic representation is essential for comprehending its complex internal dynamics and its significant role within the South American and global contexts. Further research into specific regions and their interactions will illuminate the multifaceted nature of this geographically significant nation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Brazil’s Geographic Position and Influence in South America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!