Charting Germania: A Cartographic Exploration of Roman Perceptions of Northern Europe
Related Articles: Charting Germania: A Cartographic Exploration of Roman Perceptions of Northern Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting Germania: A Cartographic Exploration of Roman Perceptions of Northern Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting Germania: A Cartographic Exploration of Roman Perceptions of Northern Europe

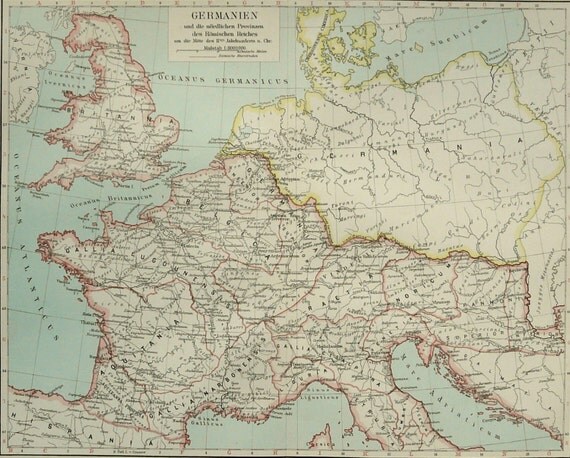
The depiction of Germania on Roman maps offers a crucial window into the Roman Empire’s understanding and interaction with the vast, largely unknown territories beyond its northern frontiers. These cartographic representations, far from being mere geographical records, reflect the anxieties, ambitions, and evolving knowledge of a powerful empire grappling with its barbarian neighbours. Analysis of these maps reveals a complex interplay of factual observation, speculation, and political agenda, highlighting the limitations and biases inherent in ancient cartography while providing valuable insights into the socio-political dynamics of the period.
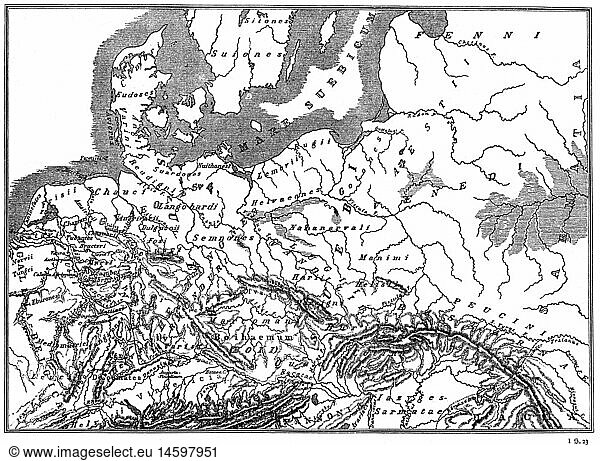
Early representations of Germania, dating back to the late Republic and early Empire, are often rudimentary and generalized. The limitations of exploration and the reliance on hearsay and limited eyewitness accounts resulted in maps featuring broad strokes rather than detailed topography. Coastal regions, more accessible to Roman traders and military expeditions, were typically depicted with greater accuracy than the inland areas, which remained largely shrouded in mystery. Rivers, notably the Rhine and Danube, served as important geographical markers, defining the boundaries of the known world and shaping the perceived limits of Germania. These rivers were not simply lines on a map; they represented formidable natural barriers and strategic frontiers, influencing Roman military strategy and administrative organization.
As Roman contact with Germania increased, particularly during the reign of Augustus and subsequent emperors, the cartographic representations evolved. While the level of detail remained uneven, the maps began to incorporate more specific geographical features. Forests, mountains, and tribal territories started to appear, albeit often with a degree of artistic license. The placement of specific tribes and settlements often reflected Roman political narratives, emphasizing the power of Rome and portraying barbarian societies as fragmented and less organized. This strategic cartography served to bolster Roman authority and justify military campaigns, presenting a picture of Germania that reinforced Roman dominance and control.
The Ptolemy’s Geographia, a monumental work of second-century CE, represents a significant advancement in the cartographic representation of Germania. Ptolemy’s map, based on a synthesis of existing geographical data and astronomical observations, offered a more detailed and structured representation of the region. It included a greater number of named places, rivers, and mountains, and attempted to present a more systematic organization of the tribal territories. However, even Ptolemy’s map is not without its inaccuracies and biases. The limitations of available information and the reliance on often unreliable sources resulted in distortions and inconsistencies. The depiction of tribal territories, for instance, often reflects Roman political perceptions rather than a precise reflection of ethnic boundaries.
The evolution of Roman maps of Germania reflects a continuous process of learning and adaptation. As Roman military campaigns and trade expanded, new geographical information became available, leading to revisions and refinements in the cartographic representations. This iterative process underscores the dynamic nature of ancient cartography, highlighting its close relationship with the political and military realities of the time. The maps were not static documents; they were constantly being updated and revised to reflect the changing understanding of the region.
Beyond the geographical information, the maps of Germania offer invaluable insights into Roman perceptions of the "other." The descriptions accompanying the maps often reveal Roman attitudes towards the Germanic tribes, characterizing them as either fierce warriors or primitive barbarians. These descriptions, often imbued with stereotypes and prejudices, reveal the complexities of Roman-Germanic relations and the challenges of intercultural understanding. The maps, therefore, become important sources for understanding the cultural and ideological contexts in which the Roman Empire interacted with its northern neighbours.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What were the primary sources of information for Roman maps of Germania? The primary sources included reports from military expeditions, accounts from traders and travelers, and possibly some limited indigenous information, although the latter is difficult to verify. The reliability of these sources varied considerably.
-
How accurate were the Roman maps of Germania? The accuracy varied significantly depending on the region and the period. Coastal areas were generally more accurately mapped than the interior. The maps often reflected Roman political agendas rather than precise geographical realities.
-
What role did these maps play in Roman administration and military strategy? These maps were essential tools for Roman administration and military planning. They facilitated the organization of military campaigns, the establishment of supply lines, and the management of frontier regions.
-
How did the depiction of Germania change over time? Initial depictions were rudimentary and generalized. Over time, with increased Roman contact, maps became more detailed, though inaccuracies and biases persisted.
-
What can these maps tell us about Roman-Germanic relations? The maps and their accompanying descriptions reveal Roman perceptions of the Germanic tribes, often reflecting stereotypes and prejudices. They offer valuable insights into the complexities of intercultural interactions and the challenges of cross-cultural understanding.
Tips for Analyzing Roman Maps of Germania
-
Consider the context: Analyze the map within the historical and political context of its creation. Understanding the motivations and biases of the mapmakers is crucial.
-
Compare different maps: Comparing maps from different periods and sources can reveal the evolution of Roman understanding of Germania.
-
Look beyond the geographical details: Pay attention to the accompanying text and descriptions, as these often reveal valuable insights into Roman perceptions of the Germanic people and their culture.
-
Identify potential biases: Be aware of the inherent limitations and biases of ancient cartography. Roman maps were not objective representations of reality.
-
Integrate with other sources: Combine map analysis with other historical sources, such as literary texts and archaeological evidence, for a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
The cartographic representations of Germania produced by the Roman Empire offer a multifaceted lens through which to examine the complex relationship between Rome and its northern neighbours. These maps, far from being simple geographical records, serve as valuable historical documents, reflecting the evolving knowledge, political agendas, and cultural perceptions of a powerful empire grappling with the challenges of its northern frontier. Careful analysis of these maps, considering their inherent limitations and biases, provides crucial insights into the geographical understanding, political strategies, and intercultural interactions that shaped the Roman world and its engagement with the peoples of Germania. Further research and comparative analysis of these maps, in conjunction with other historical sources, will continue to enrich our understanding of this pivotal period in European history.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting Germania: A Cartographic Exploration of Roman Perceptions of Northern Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!