Charting the World’s Grasslands: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Charting the World’s Grasslands: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the World’s Grasslands: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the World’s Grasslands: A Comprehensive Overview

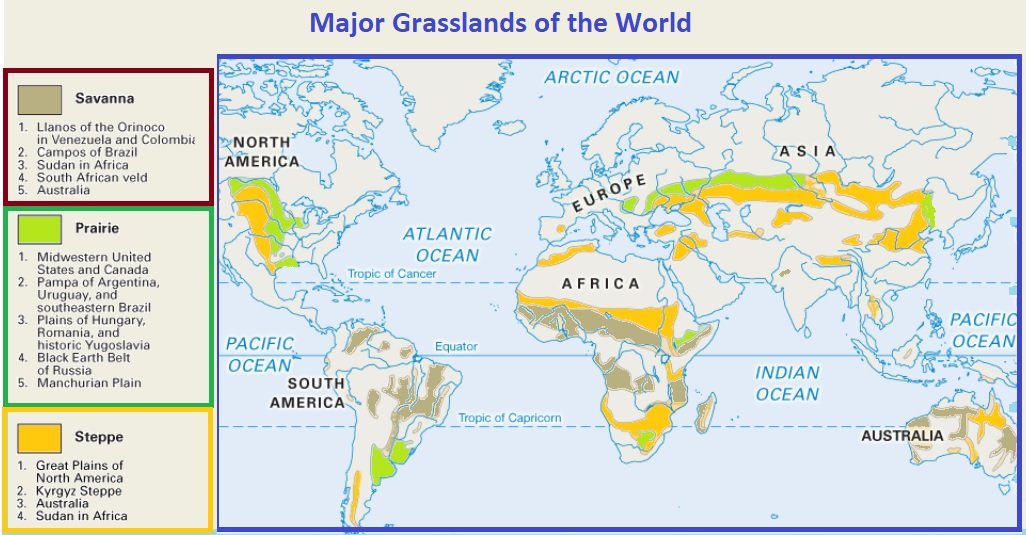
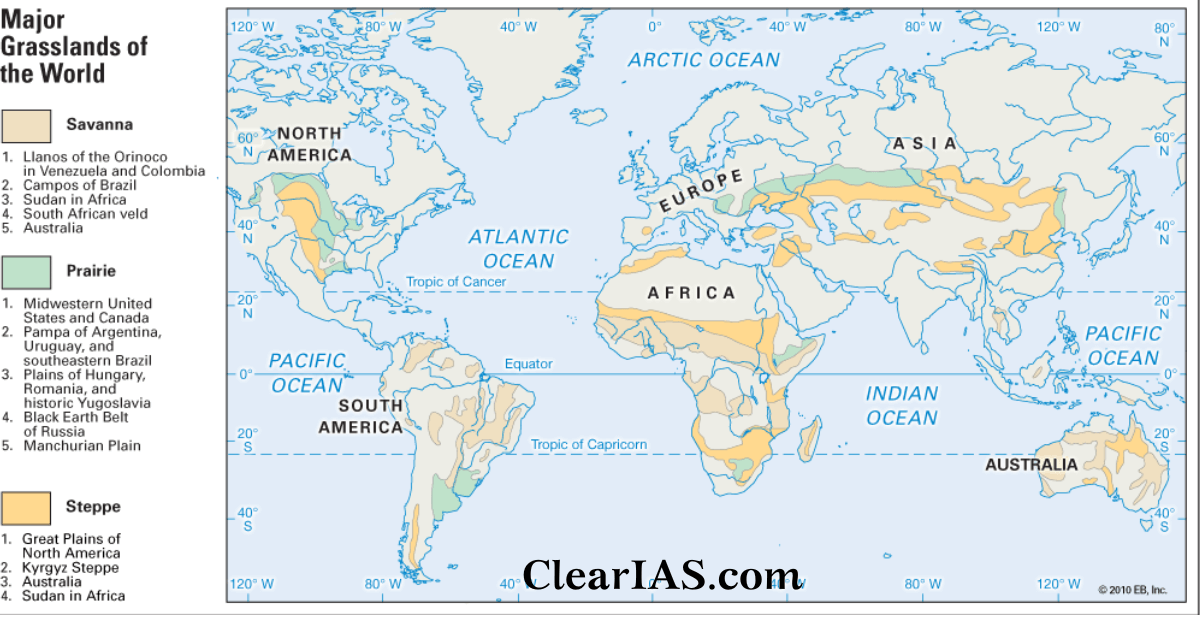
Grasslands, encompassing savannas, prairies, steppes, and pampas, constitute a significant portion of the Earth’s terrestrial ecosystems. Their vast expanse and ecological importance necessitate detailed and accurate representation, a task fulfilled by various types of grassland maps. These cartographic representations provide crucial information for researchers, policymakers, and land managers, facilitating effective conservation efforts and sustainable resource management. This article explores the different types of such maps, their creation methodologies, applications, and limitations.
Types of Grassland Maps and Their Data Sources
Several approaches exist for creating maps depicting grassland distribution and characteristics. The choice of method depends on the specific objectives and the available resources.
-
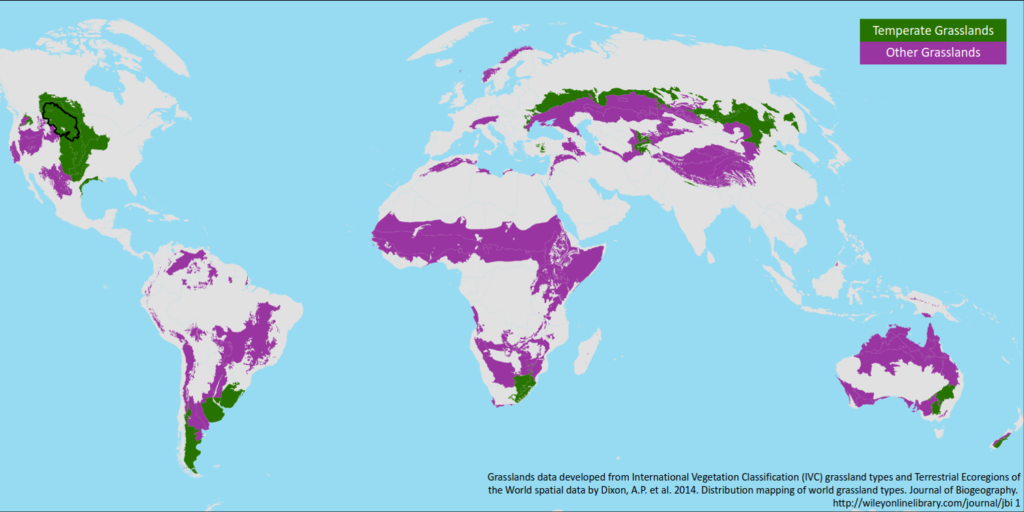
Vegetation Maps: These maps depict the dominant vegetation types across a given area, often using a classification system based on plant species composition and structure. Data sources for these maps include satellite imagery, aerial photography, field surveys, and existing vegetation databases. Resolution varies considerably, from coarse-scale global maps to highly detailed regional maps. Accuracy depends heavily on the data quality and the classification scheme used.
-
Bioclimatic Maps: These maps use climate data, such as temperature and precipitation, to predict the potential distribution of different grassland types. Climate data from weather stations and climate models are combined with ecological models to estimate suitable habitats for various grassland species. These maps provide a useful tool for understanding the environmental factors influencing grassland distribution but may not always accurately reflect the actual vegetation cover due to factors not incorporated in the models, such as soil type or fire regimes.
-
Soil Maps: Soil properties significantly influence grassland composition and productivity. Soil maps, showing the distribution of different soil types, are therefore valuable tools for understanding grassland ecosystems. These maps rely on soil surveys, laboratory analyses, and remote sensing techniques. Integration with vegetation maps allows for a more complete understanding of grassland characteristics.
-
Land Use/Land Cover Maps: These maps depict how land is utilized, including areas designated for grazing, agriculture, or conservation. Data for these maps come from satellite imagery, land records, and field observations. This type of map is particularly useful for assessing the impact of human activities on grasslands and for planning land management strategies.
-
Biodiversity Maps: These maps focus on the distribution of grassland biodiversity, including species richness and endemism. Data sources include species occurrence records, biodiversity surveys, and ecological modeling. These maps are crucial for identifying areas of high conservation value and for guiding biodiversity protection efforts.
Creation Methodologies and Technological Advancements
The creation of accurate and detailed grassland maps involves a multi-step process. Initially, data acquisition is crucial, involving field surveys, remote sensing (satellite and aerial imagery), and existing databases. This raw data is then processed and analyzed using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software. This involves georeferencing, image classification, data integration, and spatial analysis techniques. Advances in remote sensing technology, particularly the increased availability of high-resolution satellite imagery and the development of advanced image processing algorithms, have significantly improved the accuracy and detail of grassland maps. The use of machine learning techniques is also becoming increasingly prevalent, enabling automated classification of vegetation types and improved accuracy in predicting grassland distribution.
Applications and Benefits of Grassland Mapping
Grassland maps serve a multitude of purposes, providing critical information for:
-
Conservation Planning: Identifying areas of high biodiversity, endemism, or ecological significance for prioritization in conservation efforts.
-
Sustainable Land Management: Informing grazing management practices, promoting sustainable agriculture, and mitigating the impacts of land degradation.
-
Climate Change Research: Assessing the vulnerability of grasslands to climate change and predicting future changes in grassland distribution.
-
Ecosystem Services Assessment: Quantifying the provision of ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and pollination, provided by grasslands.
-
Biodiversity Monitoring: Tracking changes in grassland biodiversity over time to assess the effectiveness of conservation measures.
-
Policy Development: Informing the development of policies related to grassland conservation, sustainable land use, and biodiversity protection.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite significant advancements, limitations remain in the creation and application of grassland maps. These include:
-
Data Availability: In many regions, data on grassland vegetation, soil properties, and biodiversity is limited or incomplete, hindering the creation of comprehensive maps.
-
Map Accuracy: The accuracy of grassland maps depends heavily on the quality of the data used and the methods employed. Errors in data acquisition, processing, and analysis can lead to inaccuracies in the final map.
-
Scale and Resolution: The scale and resolution of grassland maps vary considerably, affecting their applicability for different purposes. High-resolution maps are often necessary for detailed assessments, but are costly and time-consuming to produce.
-
Dynamic Nature of Grasslands: Grasslands are dynamic ecosystems, subject to change due to climate variability, land use change, and other factors. Maintaining up-to-date maps requires continuous monitoring and updating.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is the difference between a grassland map and a vegetation map? A: A vegetation map is a broader category that includes grasslands as one type of vegetation. A grassland map focuses specifically on the distribution and characteristics of grasslands.
-
Q: How often are grassland maps updated? A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the map’s purpose and the rate of change in the grassland ecosystem. Some maps are static, while others are updated regularly using remote sensing data.
-
Q: What are the main limitations of using climate data to predict grassland distribution? A: Climate data alone does not fully capture the complexity of grassland ecosystems. Soil properties, fire regimes, and human activities also significantly influence grassland distribution.
-
Q: How can grassland maps contribute to climate change mitigation? A: Grassland maps can help identify areas suitable for carbon sequestration projects, enabling targeted efforts to mitigate climate change.
Tips for Using Grassland Maps Effectively
-
Consider the map’s purpose and scale: Select a map that is appropriate for the specific application and spatial extent of interest.
-
Assess data sources and methodology: Evaluate the quality of the data used and the methods employed in creating the map to assess its reliability.
-
Integrate multiple data sources: Combine information from different types of maps to obtain a more complete understanding of grassland ecosystems.
-
Account for uncertainty: Recognize that grassland maps are representations of reality and contain inherent uncertainties.
Conclusion
Grassland maps are invaluable tools for understanding, managing, and conserving these vital ecosystems. Advances in technology and data availability are continuously improving the accuracy and detail of these maps. However, challenges remain in data acquisition, map accuracy, and the dynamic nature of grasslands. By carefully considering the limitations and integrating diverse data sources, grassland maps can effectively support research, policy development, and conservation efforts, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of these globally important ecosystems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the World’s Grasslands: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!