Decoding Southern California’s Meteorological Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: Decoding Southern California’s Meteorological Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Decoding Southern California’s Meteorological Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding Southern California’s Meteorological Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis

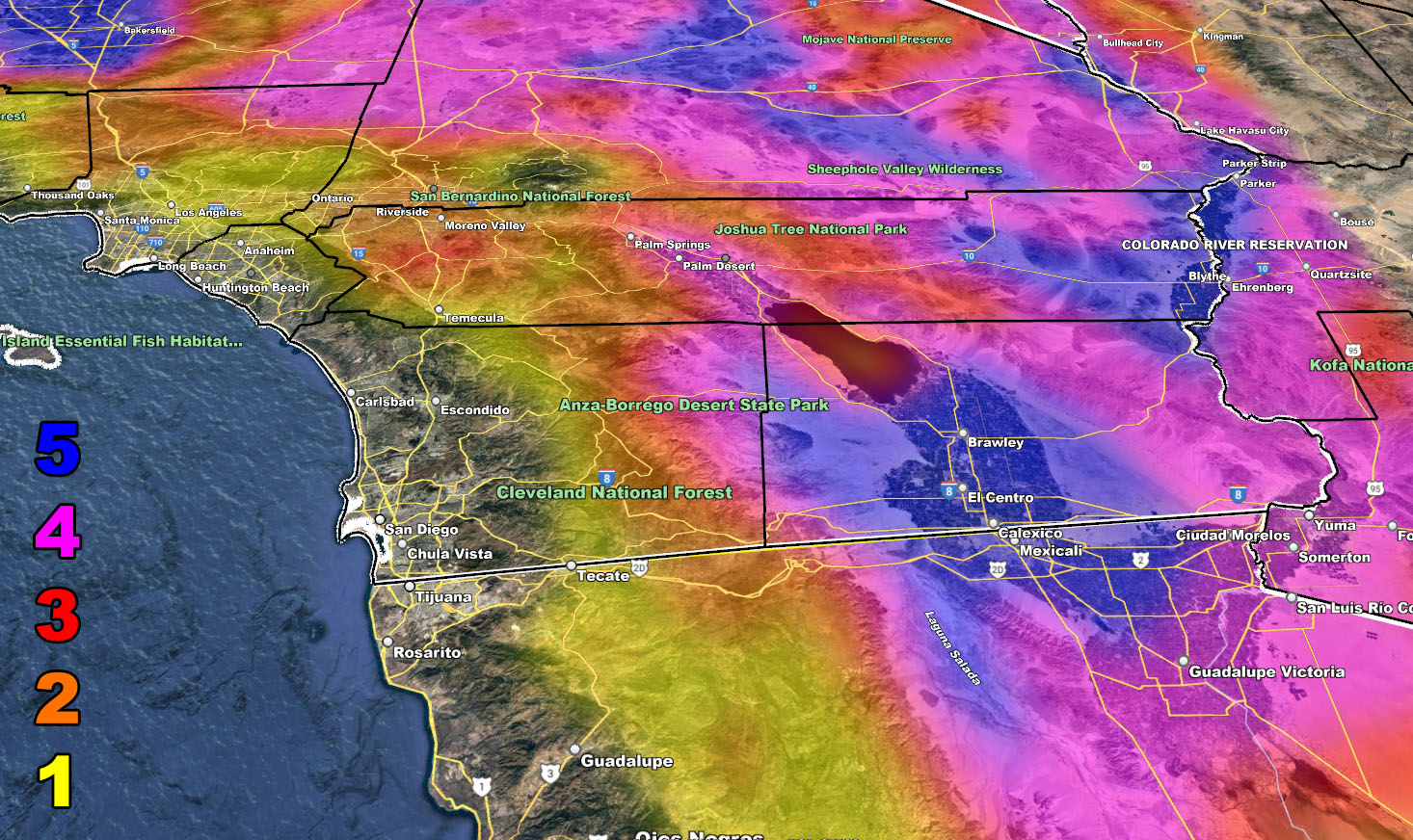
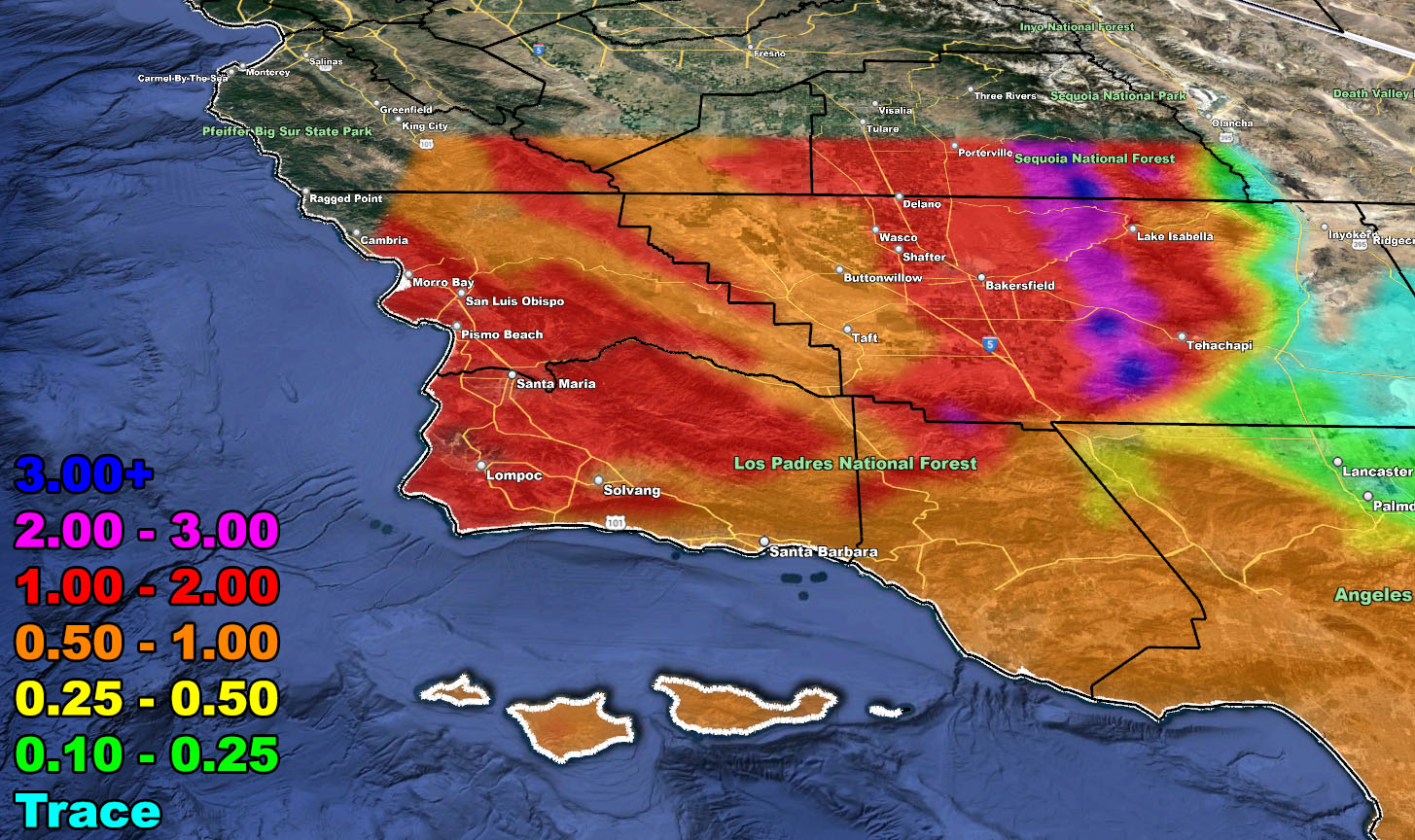
Southern California’s diverse geography significantly influences its weather patterns, creating a complex meteorological picture. Understanding this complexity is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and tourism to emergency management and public health. Analyzing weather data presented on a map of the region reveals distinct microclimates and predictable weather phenomena. The information conveyed provides critical insights for informed decision-making across numerous applications.
Geographical Influences on Weather Patterns
The region’s topography plays a dominant role in shaping its weather. The Pacific Ocean moderates temperatures, leading to a generally mild climate, particularly along the coast. However, the presence of mountain ranges, notably the Transverse Ranges and the Peninsular Ranges, significantly alters this coastal influence. These ranges create a rain shadow effect, resulting in significantly less precipitation in inland areas compared to coastal regions. The mountains also channel airflows, creating localized variations in temperature, wind speed, and humidity. The Santa Ana winds, for example, are strong, dry, and often warm winds that originate in the deserts and descend through mountain passes, leading to increased fire risk and dramatically altering coastal temperatures.
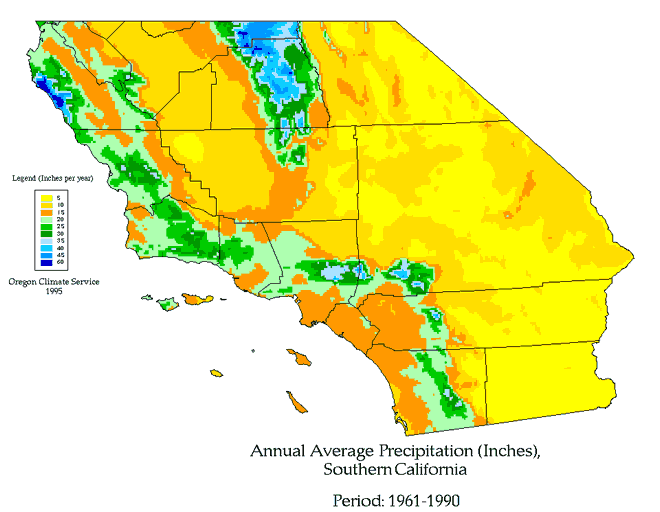
Coastal areas typically experience a Mediterranean climate characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Inland valleys, on the other hand, experience hotter summers and cooler winters with less rainfall. Desert regions, such as the Mojave and Colorado deserts, are characterized by extreme temperature variations between day and night and very low precipitation. Elevation significantly impacts temperature, with higher altitudes experiencing cooler temperatures than lower altitudes. This variation creates a mosaic of microclimates across the region, making accurate, localized weather forecasting a challenge.
Interpreting the Visual Representation of Weather Data
A weather map of Southern California typically displays a variety of data points to represent the current atmospheric conditions. Isotherms, lines connecting points of equal temperature, illustrate the spatial distribution of temperature across the region. Isobars, lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, indicate areas of high and low pressure, which are crucial for understanding wind patterns and potential precipitation. Symbols representing various weather phenomena, such as rain, snow, fog, and thunderstorms, are strategically placed to indicate their location and intensity. Color-coded regions may depict temperature ranges, precipitation amounts, or wind speeds, providing a visual representation of the weather’s spatial variability. The inclusion of topographical features on the map further enhances understanding by showing how mountains and valleys influence weather patterns.
Data Sources and Technological Advancements
The information displayed on a Southern California weather map is derived from numerous sources. Ground-based weather stations collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation. Weather balloons, launched regularly, provide upper-atmosphere data, crucial for predicting weather systems’ movement and evolution. Satellite imagery provides a comprehensive overview of cloud cover, temperature, and precipitation across the entire region. Radar systems track precipitation and provide crucial information during storms. The integration of these diverse data sources through sophisticated computer models produces highly accurate and detailed weather forecasts. Technological advancements in data acquisition, processing, and visualization continually improve the accuracy and detail of weather maps.
The Importance of Accurate Weather Information
Precise and timely weather information is vital for numerous sectors in Southern California. Agriculture relies heavily on accurate forecasts to optimize irrigation, planting, and harvesting schedules. The tourism industry uses weather predictions to inform visitor planning and outdoor activity scheduling. Emergency management agencies utilize weather maps to anticipate and respond to extreme weather events, such as wildfires, floods, and heatwaves. Public health officials use weather data to anticipate and mitigate health risks associated with extreme temperatures and air quality. The construction industry also benefits from weather predictions to plan work schedules and ensure worker safety. Transportation systems rely on accurate weather information for efficient operations and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How accurate are Southern California weather forecasts?
- A: Accuracy varies depending on the forecast’s timeframe and location. Short-term forecasts (1-3 days) are generally more accurate than long-term forecasts (7-10 days). Mountainous areas and desert regions often present greater forecasting challenges due to their complex topography.
-
Q: What are the key factors influencing Southern California’s weather?
- A: The Pacific Ocean, mountain ranges, and desert regions are the primary influences, creating distinct microclimates and varying weather patterns across the region.
-
Q: Where can reliable weather information for Southern California be found?
- A: Reputable sources include the National Weather Service (NWS), local news media, and established meteorological websites.
-
Q: How does elevation impact weather in Southern California?
- A: Higher elevations generally experience cooler temperatures and increased precipitation compared to lower elevations.
Tips for Utilizing Weather Information Effectively
- Pay close attention to weather advisories and warnings issued by official sources.
- Consult multiple weather sources for a comprehensive understanding of the forecast.
- Consider the specific microclimate of your location when interpreting weather forecasts.
- Plan activities accordingly, considering potential weather impacts.
- Be prepared for sudden weather changes, especially in mountainous and desert regions.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of Southern California’s weather requires analyzing the interplay of geographical features and atmospheric conditions. The visual representation of this complex interplay, as depicted on a weather map, provides invaluable information for various sectors. Accurate and timely weather data is crucial for informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and effective resource management across the region. The continued advancements in meteorological technology and data analysis promise even more precise and detailed weather forecasting capabilities in the future, further enhancing preparedness and resilience in the face of diverse weather phenomena.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding Southern California’s Meteorological Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!