Deconstructing China’s Ethnic Distribution: A Geographic and Sociopolitical Analysis
Related Articles: Deconstructing China’s Ethnic Distribution: A Geographic and Sociopolitical Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deconstructing China’s Ethnic Distribution: A Geographic and Sociopolitical Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deconstructing China’s Ethnic Distribution: A Geographic and Sociopolitical Analysis

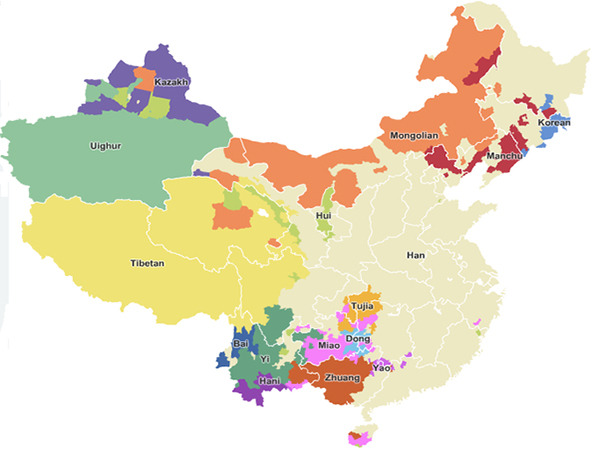
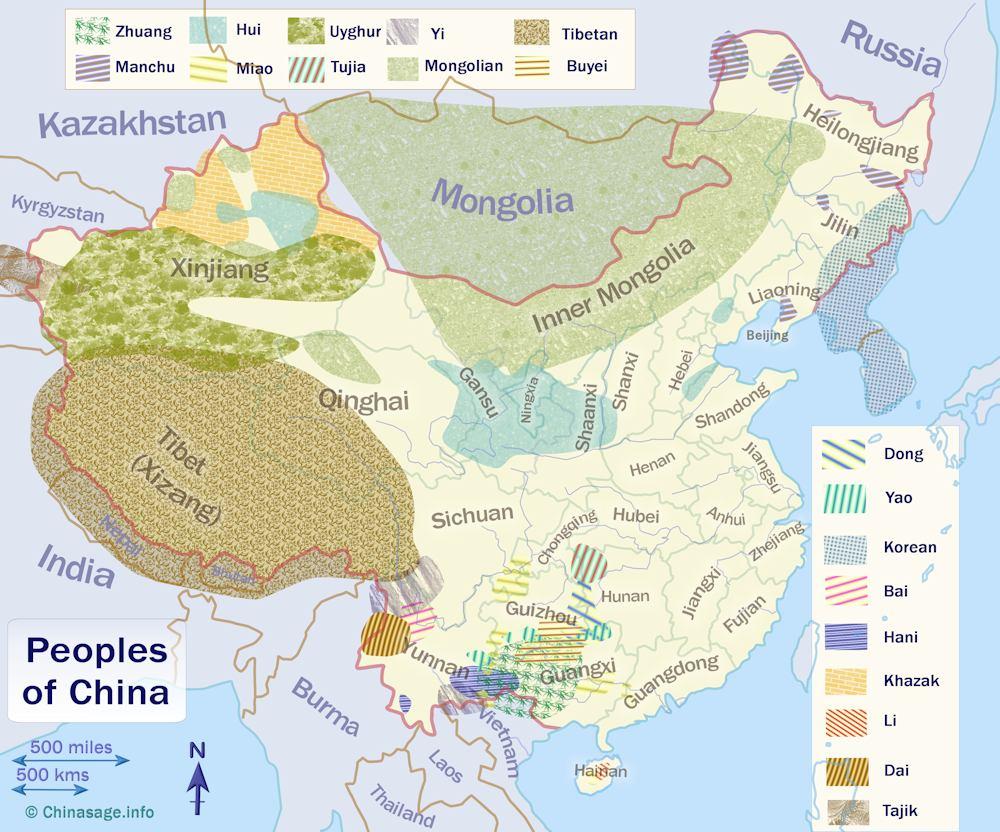
China’s population is remarkably diverse, encompassing a multitude of ethnic groups, each with its unique cultural heritage, linguistic traditions, and historical experiences. Understanding the spatial distribution of these groups is crucial for comprehending the nation’s complex social fabric, political landscape, and economic development. Analysis of this distribution reveals intricate patterns of concentration and dispersal, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of national unity and regional disparity.
The Han Chinese, constituting the overwhelming majority of the population, exhibit a widespread distribution across the country. However, their density varies significantly, with higher concentrations observed in the eastern plains and coastal regions, historically centers of agricultural production and economic activity. Conversely, the density declines considerably in the less accessible western regions, characterized by mountainous terrain and arid landscapes.
In contrast to the widespread distribution of the Han Chinese, many of the minority ethnic groups exhibit more localized concentrations. These groups often occupy specific geographic areas, reflecting historical migration patterns, adaptation to unique environmental conditions, and the persistence of traditional livelihoods. For example, the Tibetan population is predominantly concentrated in the Tibetan Autonomous Region and adjacent areas of Sichuan, Yunnan, and Qinghai provinces, mirroring the region’s high-altitude environment and pastoralist traditions. Similarly, the Uyghur population is largely found in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, a vast territory characterized by its desert and oasis ecosystems. The Zhuang people, the largest minority group, are predominantly located in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, a region known for its karst topography and subtropical climate.
This uneven distribution has significant socio-political implications. The establishment of autonomous regions and prefectures, designed to provide greater self-governance to minority groups, is a direct reflection of this geographical concentration. These administrative divisions aim to protect minority cultures and languages, while simultaneously fostering economic development and integration within the broader national framework. However, the effectiveness of these policies remains a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny, particularly concerning issues of cultural preservation, economic disparities, and the balance between regional autonomy and national unity.
Mapping the ethnic distribution also highlights the challenges of infrastructure development and service provision in remote and sparsely populated areas. Reaching minority communities often necessitates significant investment in transportation, communication, and healthcare infrastructure, presenting both logistical and financial hurdles. Furthermore, the cultural sensitivity required in delivering services to diverse populations demands careful consideration of local customs, beliefs, and linguistic needs.
The interplay between ethnicity and economic development is another crucial aspect requiring examination. While some minority areas have witnessed significant economic growth, often fueled by natural resource exploitation or strategic government investment, others continue to lag behind national averages. This disparity can exacerbate existing social tensions and contribute to feelings of marginalization, underscoring the need for equitable development policies that address the specific needs and capabilities of each ethnic group.
The historical context is essential for a complete understanding of the current ethnic distribution. Centuries of migration, conquest, and resettlement have shaped the current demographic landscape. The impact of historical policies, including those promoting internal migration and the resettlement of specific ethnic groups, is also a significant factor in shaping the patterns observed today. Analyzing these historical processes is crucial for interpreting the contemporary distribution and understanding the underlying dynamics of ethnic relations.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding China’s Ethnic Distribution:
-
What is the basis for defining ethnic groups in China? The classification of ethnic groups in China is a complex process, incorporating factors such as language, culture, history, and self-identification. However, the official categorization remains subject to ongoing debate and refinement.
-
How accurate are the official statistics on ethnic populations? The accuracy of official population statistics is a subject of ongoing discussion. Challenges include the complexities of self-identification, the fluidity of ethnic boundaries, and potential variations in data collection methodologies across different regions.
-
What role does ethnicity play in Chinese politics? Ethnicity plays a significant, albeit complex, role in Chinese politics. The government acknowledges the existence of ethnic minorities and has implemented policies aimed at promoting their cultural preservation and economic development. However, tensions and challenges persist regarding the balance between national unity and regional autonomy.
-
How does the ethnic distribution affect economic development in China? The uneven distribution of ethnic groups significantly influences economic development patterns. While some minority regions have experienced rapid economic growth, others continue to lag behind, creating regional disparities and social challenges.
-
What are the challenges in promoting equality among different ethnic groups? Promoting equality among China’s diverse ethnic groups presents significant challenges, including addressing economic disparities, protecting cultural heritage, promoting linguistic diversity, and fostering mutual understanding and respect.
Tips for Understanding China’s Ethnic Map:
-
Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical migration patterns and policies affecting ethnic groups is crucial for interpreting the current distribution.
-
Analyze regional variations: The density and distribution of ethnic groups vary significantly across different regions, reflecting historical, geographical, and socio-economic factors.
-
Examine the role of autonomous regions: The establishment of autonomous regions is a significant aspect of China’s approach to managing ethnic diversity, but its effectiveness requires ongoing evaluation.
-
Focus on socio-economic indicators: Analyzing economic indicators and access to services in different ethnic communities provides insights into the challenges of equitable development.
-
Consult diverse sources: Utilize a range of sources, including academic research, government publications, and media reports, to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion:
The ethnic map of China is not merely a static representation of population distribution; it is a dynamic reflection of the nation’s complex history, social structure, and political landscape. Understanding the spatial distribution of ethnic groups is essential for informed policy-making, fostering social cohesion, and promoting equitable development. Ongoing research and critical analysis are necessary to refine understanding of the intricate interplay between geography, ethnicity, and socio-political dynamics in China. The challenges associated with managing ethnic diversity require ongoing attention and innovative solutions to ensure a harmonious and prosperous future for all citizens.


![Map of Ethnic Composition of China [2320 × 1868] : r/MapPorn](https://preview.redd.it/k7pxco8z4tuz.png?auto=webpu0026s=1e5400d89e616346df0e614a65fc3993fda45d68)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deconstructing China’s Ethnic Distribution: A Geographic and Sociopolitical Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!