Djibouti: A Strategic Crossroads in the Horn of Africa
Related Articles: Djibouti: A Strategic Crossroads in the Horn of Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Djibouti: A Strategic Crossroads in the Horn of Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Djibouti: A Strategic Crossroads in the Horn of Africa
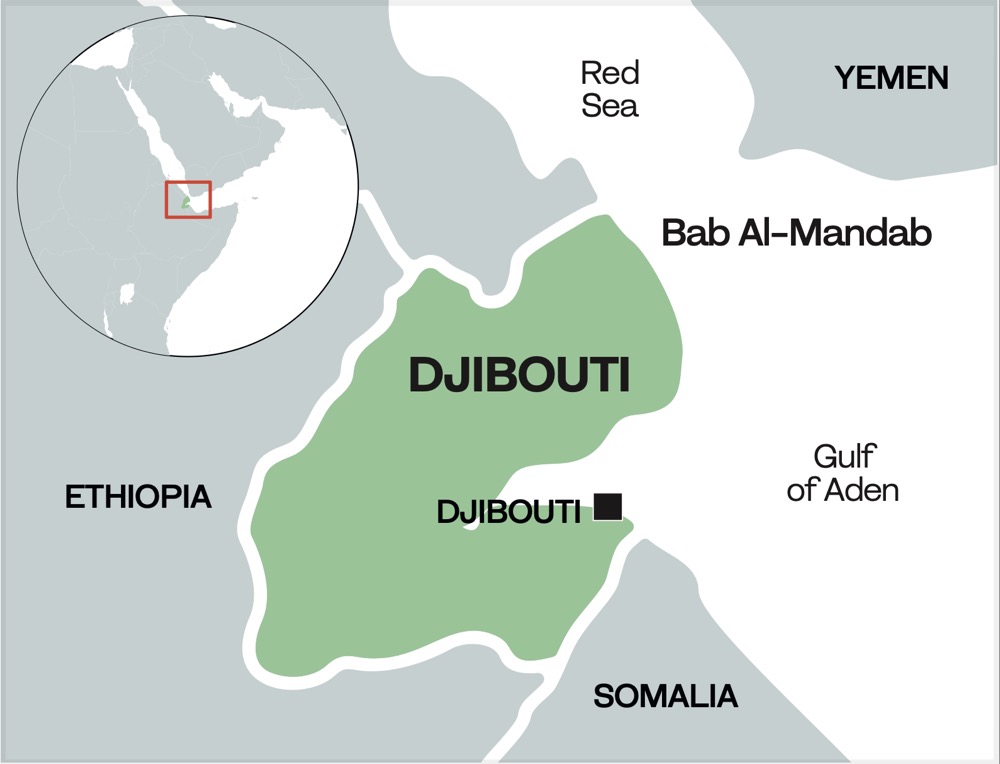
Djibouti, a small nation situated at the Horn of Africa, holds a geopolitical significance far exceeding its size. Its strategic location, bordering Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia, and commanding access to the Red Sea and the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, makes it a crucial node in global trade and a focal point for regional power dynamics. Understanding its geographical context within the larger African landscape is crucial to appreciating its importance.
The country’s geography is defined by its arid to semi-arid climate and diverse topography. Much of the land is characterized by volcanic plateaus and plains, interspersed with low mountains and coastal lowlands. Lake Assal, one of the lowest points on Earth, lies in the Danakil Depression, a region of intense geological activity. This dramatic landscape presents both challenges and opportunities. The lack of significant freshwater resources necessitates careful water management, while the geothermal potential offers avenues for renewable energy development.
Djibouti’s coastline, stretching approximately 350 kilometers, is a major asset. The port of Djibouti City, the nation’s capital, serves as a vital gateway for landlocked Ethiopia, handling a significant portion of its imports and exports. This role underscores the country’s importance in regional trade and underscores its economic interconnectedness with its neighbors. The Bab-el-Mandeb strait, a narrow passage connecting the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, is a critical chokepoint for global shipping, making Djibouti’s coastal position strategically invaluable. The high volume of maritime traffic contributes significantly to the nation’s economy, through port fees and related services.
The strategic importance of Djibouti extends beyond its economic role. The country hosts numerous military bases, reflecting its geopolitical significance. The presence of foreign military forces, including the United States, France, and China, highlights the global interest in securing access to this strategically important region. These bases contribute to regional security operations and counter-terrorism efforts, but also raise questions about sovereignty and potential geopolitical tensions.
The nation’s demographics are equally significant. Djibouti is a relatively small country with a population predominantly composed of Afro-Arabs and Somali ethnic groups, alongside smaller communities representing other regional backgrounds. This diversity contributes to a rich cultural tapestry but also presents challenges related to social cohesion and national identity. The country’s relatively young population presents opportunities for economic growth through workforce expansion, but necessitates investment in education and job creation to manage potential unemployment.
Understanding Djibouti’s Economic Landscape
Djibouti’s economy is heavily reliant on service industries, particularly port services, which account for a substantial portion of its GDP. The country is actively seeking to diversify its economy, investing in sectors like tourism, energy (including geothermal and solar power), and telecommunications. Efforts to improve infrastructure and attract foreign investment are crucial to realizing this diversification. Challenges remain, however, including the country’s dependence on external aid and vulnerability to climate change, which exacerbates water scarcity and threatens agricultural productivity.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its strategic advantages, Djibouti faces several challenges. Water scarcity is a major constraint on development, requiring careful water resource management and investment in water infrastructure. The country’s vulnerability to climate change impacts, including droughts and rising sea levels, poses significant threats to its economy and environment. Furthermore, maintaining political stability and addressing issues of social equity are crucial for sustainable development.
Despite these challenges, Djibouti possesses considerable opportunities. Its strategic location offers the potential for further development of its port facilities and related services, expanding its role as a regional trade hub. The development of renewable energy resources could enhance energy security and reduce reliance on imported fuels. Investment in education and skills development can empower its young population and contribute to economic diversification.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Djibouti’s primary source of income? Djibouti’s economy is largely driven by its port services, which are crucial for regional trade.
-
What are the major environmental challenges facing Djibouti? Water scarcity and vulnerability to climate change, including droughts and rising sea levels, are major environmental concerns.
-
What is the role of foreign military bases in Djibouti? Foreign military bases contribute to regional security operations and counter-terrorism efforts, but also raise questions about national sovereignty.
-
What are Djibouti’s efforts to diversify its economy? The country is investing in sectors such as tourism, energy (renewable energy sources), and telecommunications.
-
What are the main ethnic groups in Djibouti? The population is primarily composed of Afro-Arabs and Somali ethnic groups.
Tips for Understanding Djibouti
-
Consider the geopolitical context: Djibouti’s location at the crossroads of major shipping lanes and its proximity to several nations significantly influences its role in regional and global affairs.
-
Analyze the economic drivers: Focus on the importance of port services and the ongoing efforts to diversify the economy.
-
Evaluate the environmental vulnerabilities: Understand the challenges posed by water scarcity and climate change.
-
Examine the social dynamics: Consider the interplay of various ethnic groups and the importance of social cohesion.
-
Assess the strategic alliances: Analyze the impact of foreign military presence and its implications for national sovereignty and regional stability.
Conclusion
Djibouti’s small landmass belies its immense geopolitical and economic importance. Its strategic location, coupled with its port facilities, makes it a crucial player in regional and global trade. However, the country faces significant challenges related to water scarcity, climate change, and economic diversification. Addressing these challenges effectively, while leveraging its strategic advantages, is crucial for Djibouti’s sustainable development and its continued role as a vital link in the Horn of Africa. Further research and analysis are needed to fully understand the complex interplay of factors shaping this dynamic nation.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Djibouti: A Strategic Crossroads in the Horn of Africa. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!