Ecuador: A Geographic and Geopolitical Crossroads in South America
Related Articles: Ecuador: A Geographic and Geopolitical Crossroads in South America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Ecuador: A Geographic and Geopolitical Crossroads in South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Ecuador: A Geographic and Geopolitical Crossroads in South America
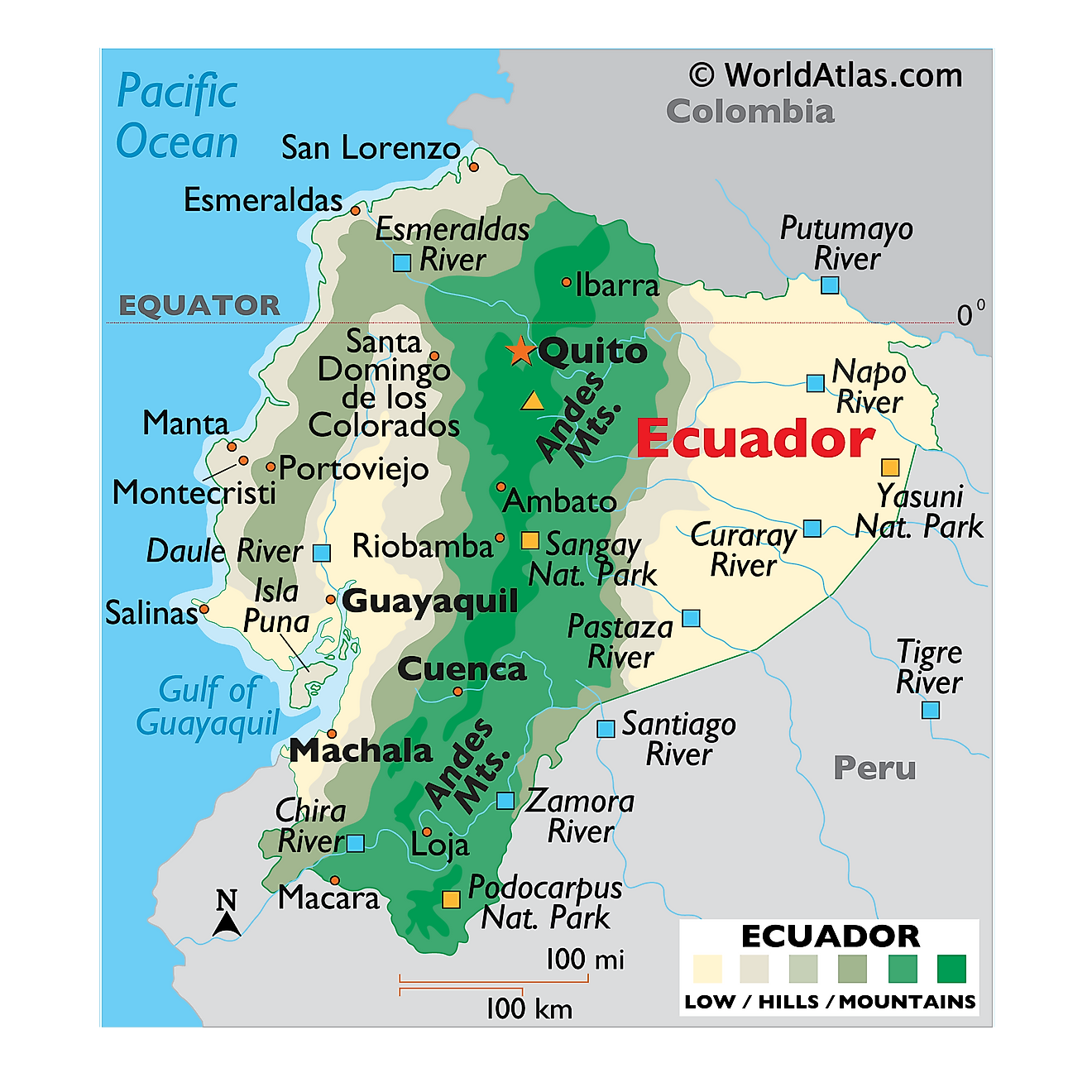
Ecuador occupies a unique position on the South American continent, a fact readily apparent when examining its cartographic representation. Its location straddles the equator, giving it its name, and encompasses a diverse range of geographical features, from the Andes Mountains to the Amazon rainforest and the Pacific coastline. This diversity is reflected in the country’s rich biodiversity and cultural tapestry, making it a compelling subject of geographical study and a significant player in regional affairs.
Geographical Features and Their Significance
A map of Ecuador immediately reveals its three distinct geographical regions: the Costa (coast), the Sierra (Andes), and the Oriente (Amazon rainforest). The coastal region, characterized by a relatively flat terrain, boasts fertile plains ideal for agriculture, particularly banana, cacao, and shrimp farming. Major port cities like Guayaquil are crucial for international trade, connecting Ecuador to global markets. The coastal climate is generally tropical, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
The Sierra region, dominated by the Andes Mountains, presents a dramatically different landscape. This area is characterized by high altitudes, volcanic peaks, and deep valleys. The Andes divide Ecuador into several distinct ecological zones, supporting diverse flora and fauna. The high altitude creates a cooler, temperate climate, suitable for growing potatoes, grains, and other Andean crops. Major cities like Quito, the capital, are situated within this region, offering spectacular views and access to significant cultural and historical sites. The volcanic activity has also contributed to the formation of fertile soils, supporting agriculture. However, the mountainous terrain presents challenges for transportation and infrastructure development.
The Oriente, or Amazonian region, covers a significant portion of eastern Ecuador. It is characterized by dense rainforest, a complex river system, and extraordinary biodiversity. This region is home to numerous indigenous communities and holds significant untapped natural resources. However, its remoteness and challenging terrain pose significant obstacles to development and sustainable resource management. The Amazon basin plays a critical role in global climate regulation, highlighting the importance of its conservation.
Political and Economic Implications of Ecuador’s Geography
Ecuador’s geography significantly influences its political and economic landscape. The diverse regions have led to distinct regional identities and sometimes competing interests. The coastal region, historically focused on export-oriented agriculture, often has different priorities than the Andean highlands, where agriculture is more subsistence-based. The Oriente, with its vast natural resources and indigenous populations, presents unique challenges in terms of development and resource management.
The country’s location on the equator and its access to both the Pacific Ocean and the Amazon basin have implications for its international trade and relations. Its proximity to major South American economies like Colombia and Peru influences its regional alliances and trade agreements. The Galapagos Islands, a unique archipelago located off the coast, contribute significantly to Ecuador’s tourism industry and are a testament to the country’s remarkable biodiversity. However, this biodiversity faces threats from climate change and unsustainable practices, requiring careful management and international cooperation.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the capital of Ecuador? Quito is the capital city of Ecuador.
-
What are the main geographical regions of Ecuador? The three main regions are the Costa (coast), the Sierra (Andes), and the Oriente (Amazon rainforest).
-
What is the climate like in Ecuador? Ecuador’s climate varies considerably depending on altitude and region. The coast is tropical, the Andes have a temperate climate, and the Amazon is hot and humid.
-
What are the major economic activities in Ecuador? Significant sectors include agriculture (bananas, cacao, flowers), oil extraction, and tourism.
-
What is the significance of the Galapagos Islands? They are a unique archipelago with exceptional biodiversity, attracting significant tourism and supporting crucial ecological research.
-
What are the main challenges facing Ecuador’s development? Challenges include poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and the need for sustainable resource management.
-
What are Ecuador’s main trading partners? Ecuador’s trading partners vary, but significant markets include the United States, China, and other countries in the region.
-
What is the political system of Ecuador? Ecuador is a republic with a president as head of state and government.
Tips for Understanding Ecuador’s Geography
To gain a deeper understanding of Ecuador’s geography, it is beneficial to utilize various resources:
-
Detailed maps: Examine high-resolution maps showcasing topographic features, elevation, and major cities. Online mapping tools offer interactive features that enhance understanding.
-
Satellite imagery: Satellite imagery provides a visual perspective on the country’s diverse landscapes and allows for the observation of land use changes.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) data: GIS data provides detailed information on various geographical aspects, enabling analysis of environmental factors, population distribution, and infrastructure development.
-
Academic resources: Consult academic journals and publications on Ecuadorian geography and environmental studies to gain in-depth knowledge.
-
Travel guides and documentaries: These resources offer visual representations and narrative accounts that enhance understanding of the country’s diverse geographical regions.
Conclusion
Ecuador’s geography is a defining characteristic, shaping its culture, economy, and politics. The interplay between the coastal plains, the Andean highlands, and the Amazon rainforest creates a complex and fascinating landscape. Understanding this geographical diversity is crucial for comprehending the challenges and opportunities facing the nation. Continued research and sustainable development practices are essential to preserving Ecuador’s unique natural heritage and fostering its economic and social progress. Further study of Ecuador’s geographical features and their impact on various aspects of national life is essential for informed policymaking and international collaboration.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Ecuador: A Geographic and Geopolitical Crossroads in South America. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!