Gabon: A Geographic Overview and Strategic Importance
Related Articles: Gabon: A Geographic Overview and Strategic Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Gabon: A Geographic Overview and Strategic Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Gabon: A Geographic Overview and Strategic Importance
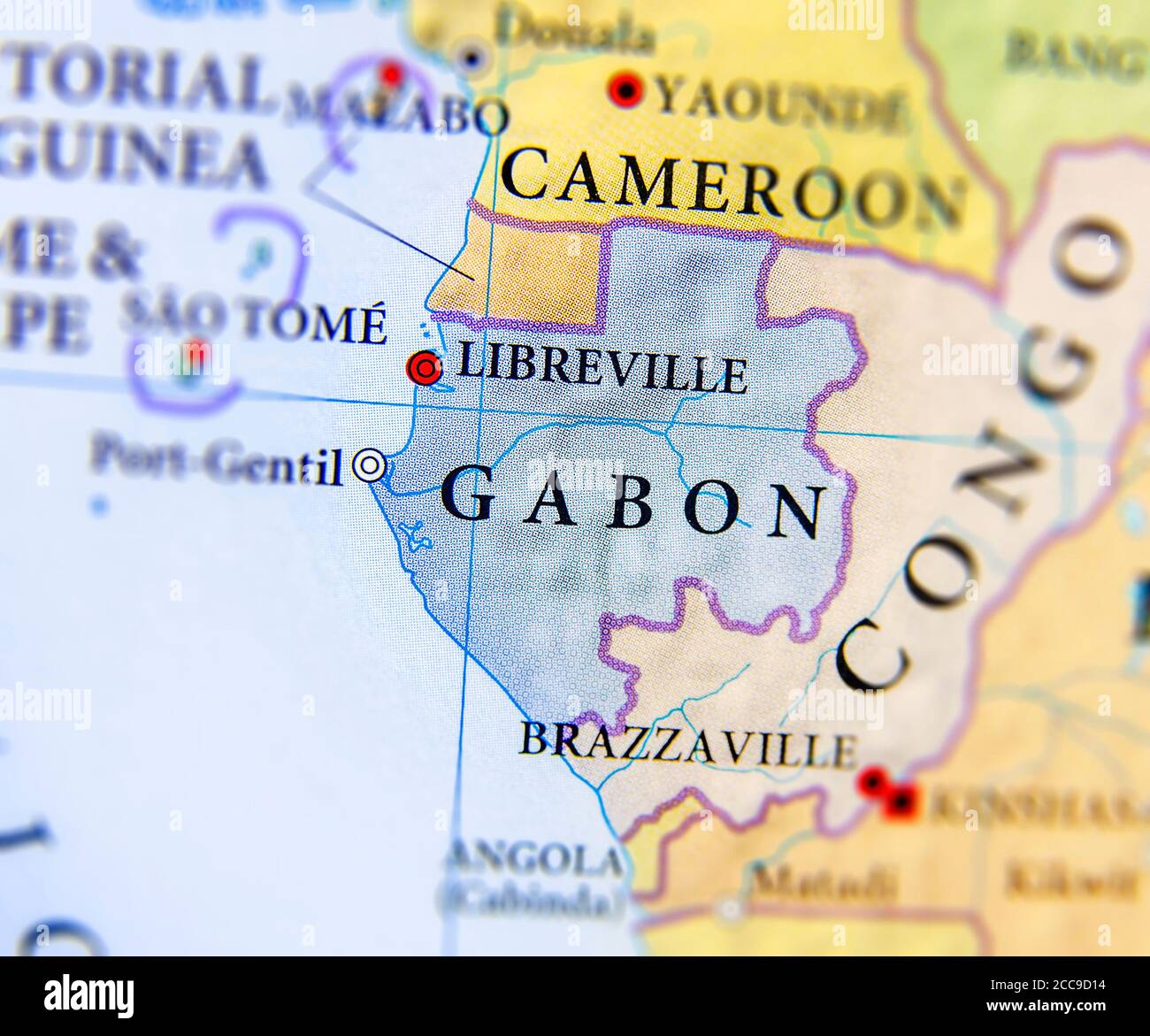
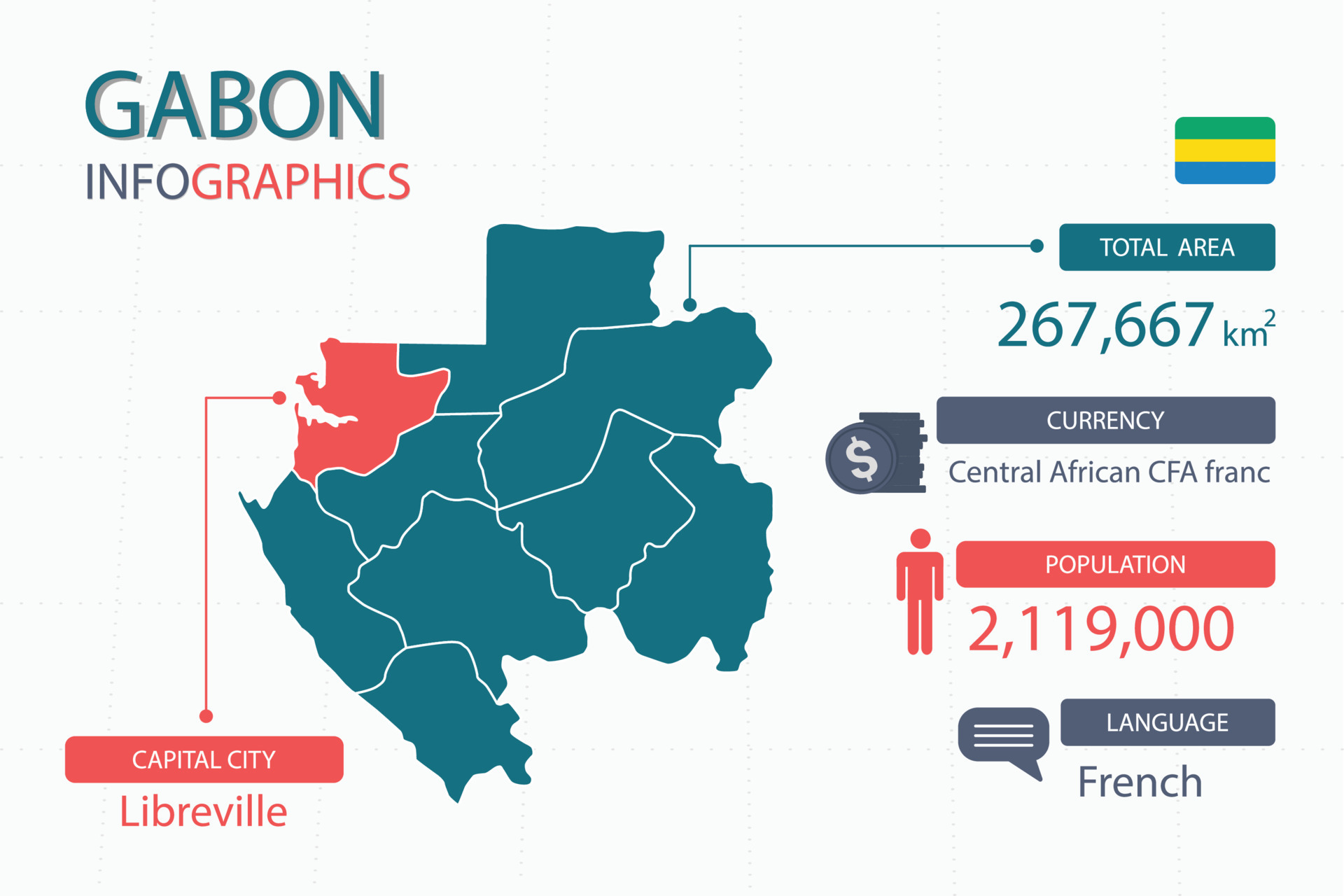
Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, occupies a unique position on the western coast of central Africa. Its geographic features, encompassing diverse ecosystems and abundant natural resources, contribute significantly to its regional and global importance. Understanding its cartographic representation is crucial to grasping its geopolitical significance and the challenges it faces.
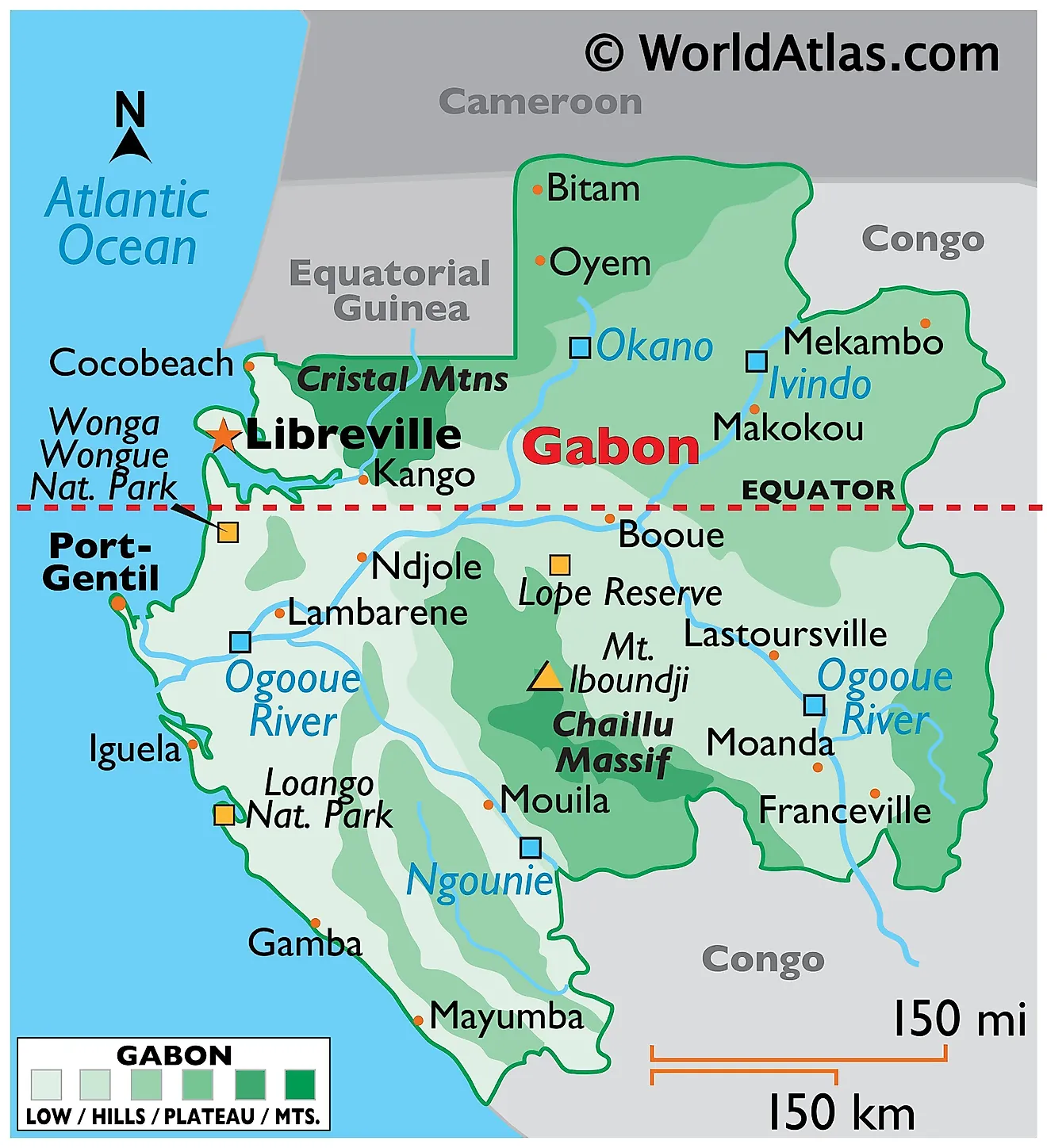
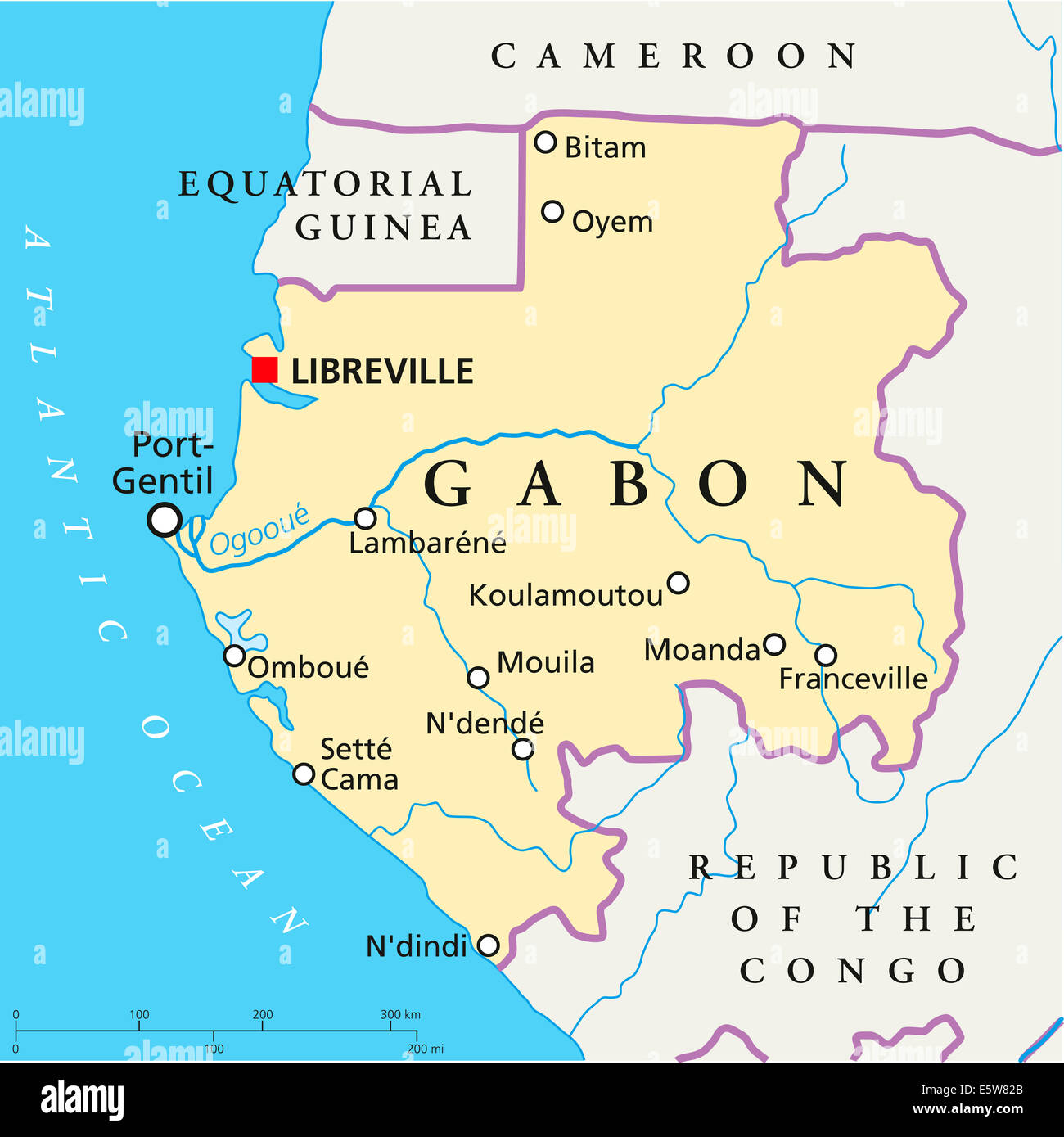
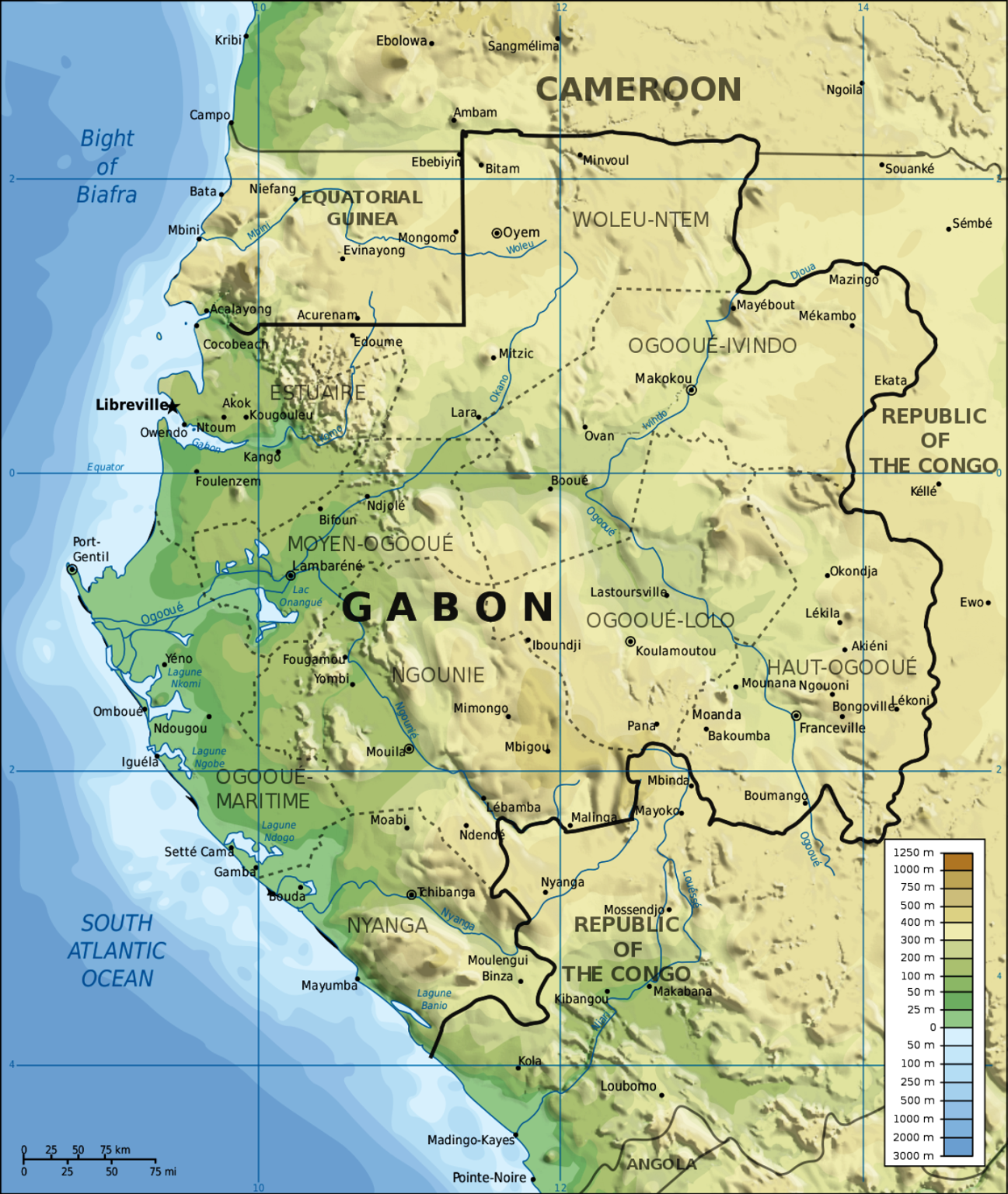
The country’s shape, as depicted on a map, reveals a slender coastal strip that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, gradually widening inland towards the east. This relatively narrow coastal area gives way to extensive rainforests, which constitute a substantial portion of the nation’s territory. These forests, part of the Congo Basin, are among the largest and most biodiverse in the world. The northern and eastern borders are defined by neighboring countries: Equatorial Guinea to the north, Cameroon to the northeast, and the Republic of the Congo to the east and south. The southern boundary is largely defined by the Ogooué River and the Atlantic Ocean.
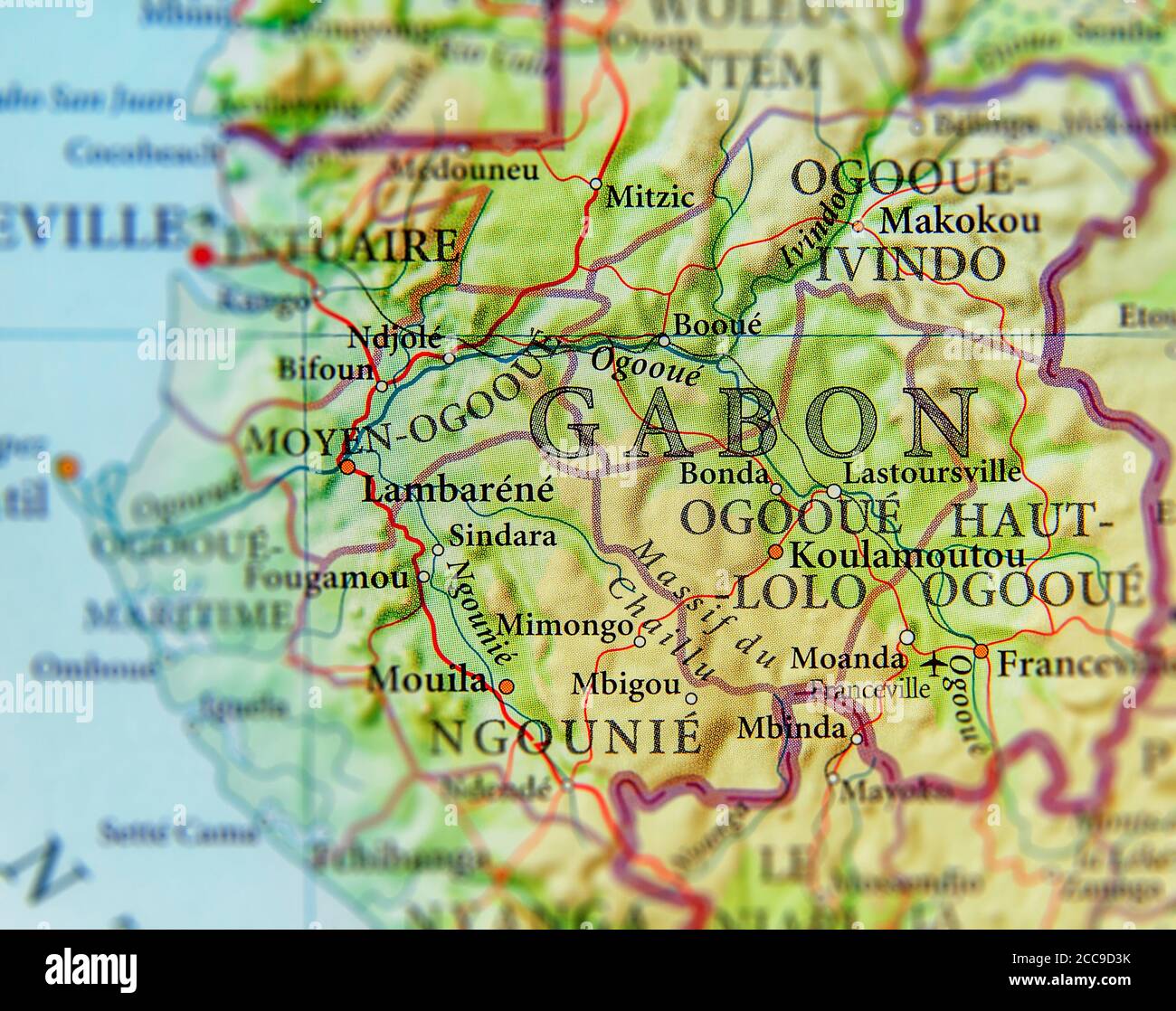
Several significant geographical features are readily apparent on any detailed map. The Ogooué River, Gabon’s most important river system, flows from the east towards the west, creating a vast delta before emptying into the Atlantic. This river system plays a vital role in the country’s transportation infrastructure and the ecology of the region. Numerous smaller rivers and tributaries intersect the landscape, contributing to the complex hydrological network. The coastline, characterized by estuaries, lagoons, and mangrove forests, offers various ecological niches and strategic port locations. The interior is predominantly composed of rolling hills and plateaus, rising gradually towards the eastern border. Mount Iboundji, the highest point in the country, stands as a notable geographical feature in the southeast.
The map also highlights the country’s relatively low population density, considering its size. This sparseness of population is largely due to the challenging terrain in the interior and the concentration of human settlements along the coastal areas and river systems. This distribution pattern influences the development of infrastructure and resource management strategies.
Gabon’s strategic importance stems from several factors evident in its geographical context. Firstly, its location along the Atlantic coast provides access to vital shipping lanes and global markets. Its ports serve as crucial gateways for the export of natural resources and the import of essential goods. Secondly, the abundance of natural resources, including oil, manganese, uranium, and timber, significantly contributes to its economic influence in the region and globally. These resources are unevenly distributed across the country, as shown on resource maps overlaid on the general geographic map. This uneven distribution presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of development and resource management.
Thirdly, Gabon’s vast rainforest plays a crucial role in global carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation. The preservation of this ecosystem is of paramount importance not only for Gabon but also for the global environment. The integrity of this rainforest, clearly visible on satellite imagery and detailed maps, is directly linked to global climate change mitigation efforts. The map also shows the extensive protected areas and national parks established to safeguard this biodiversity.
Finally, Gabon’s geopolitical position places it at the crossroads of several regional dynamics. Its relationships with neighboring countries are influenced by shared resources, border security concerns, and economic cooperation. Understanding its regional context, as depicted on maps showing neighboring countries and their respective resources, is crucial to analyzing its political and economic stability.
FAQs regarding Gabon’s Geography:
-
What is the primary geographical feature of Gabon? The Ogooué River system is the most significant geographical feature, shaping the country’s transportation, ecology, and settlement patterns.
-
What is the predominant type of terrain in Gabon? While the coastal region is relatively flat, the interior is characterized by rolling hills and plateaus, culminating in Mount Iboundji, the highest point.
-
How does Gabon’s coastline contribute to its importance? The coastline provides access to the Atlantic Ocean, facilitating trade and the export of natural resources. Its estuaries, lagoons, and mangroves support diverse ecosystems.
-
What is the significance of Gabon’s rainforest? Its vast rainforest plays a crucial role in global carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation, impacting global climate change mitigation efforts.
-
What are the major natural resources found in Gabon? Gabon is rich in oil, manganese, uranium, and timber, significantly contributing to its economy.
Tips for understanding Gabon’s map:
-
Analyze the scale of the map to understand the relative distances and sizes of different geographical features.
-
Pay attention to the key, or legend, to understand the different symbols and colors used to represent various geographical features and resources.
-
Compare Gabon’s map to maps of neighboring countries to understand its regional context and geopolitical significance.
-
Utilize online resources, such as satellite imagery and interactive maps, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the terrain and resource distribution.
-
Consider the implications of Gabon’s geography for its economic development, environmental sustainability, and political stability.
Conclusion:
Gabon’s geographic features significantly shape its national identity, economic opportunities, and regional influence. Its location, resources, and ecosystems present both advantages and challenges. A thorough understanding of its cartographic representation, including its topography, hydrology, and resource distribution, is essential for informed decision-making regarding sustainable development, resource management, and regional cooperation. Further research into the specific details of its geographic features, coupled with an awareness of its geopolitical context, provides a comprehensive understanding of this crucial central African nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Gabon: A Geographic Overview and Strategic Importance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!