Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in North Carolina: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in North Carolina: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in North Carolina: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in North Carolina: A Comprehensive Overview
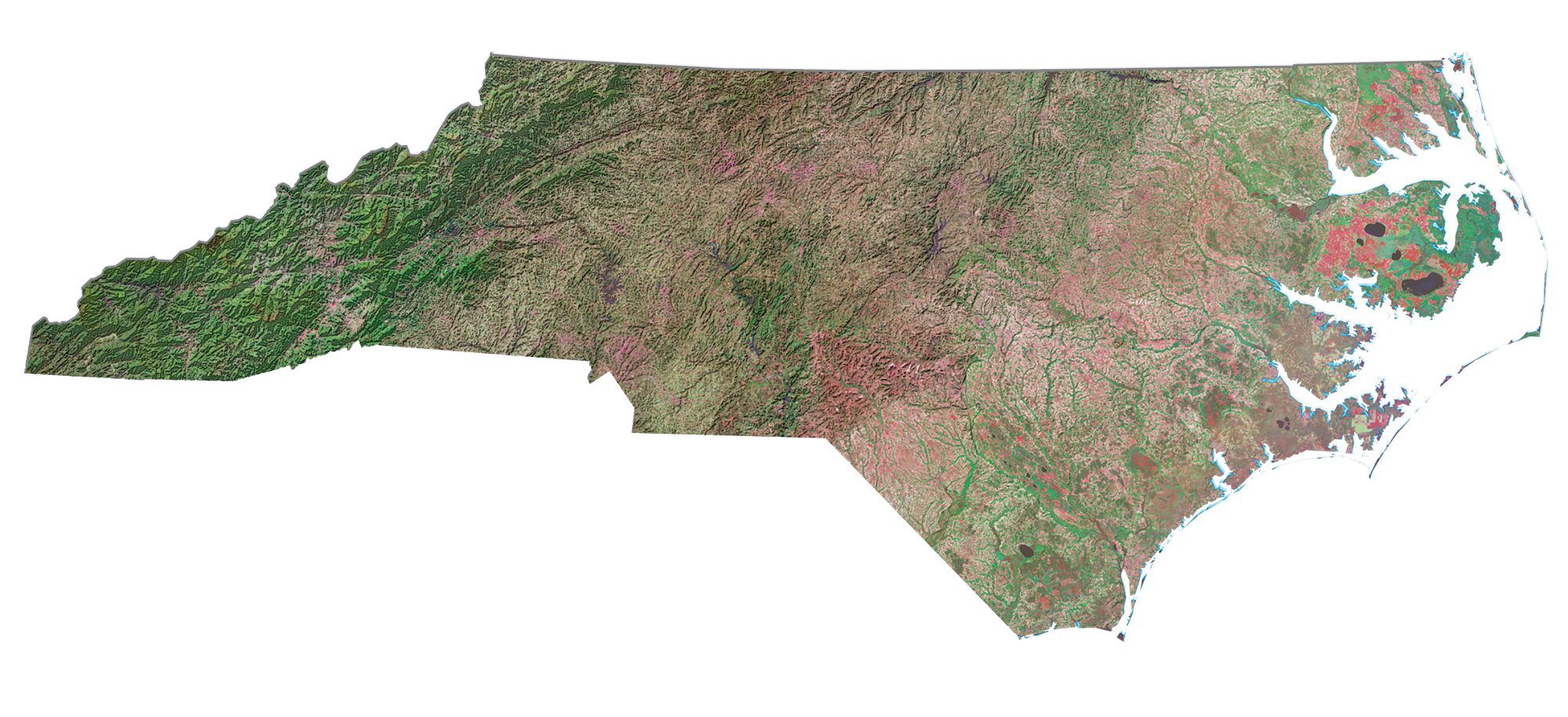
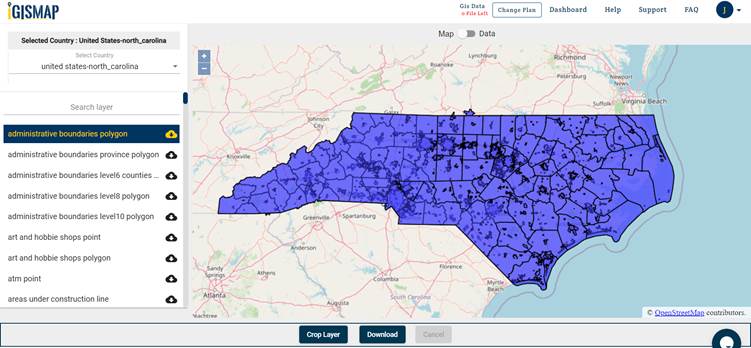
North Carolina leverages Geographic Information Systems (GIS) extensively across various sectors, contributing significantly to efficient governance, informed decision-making, and improved public services. This technology allows for the spatial analysis and visualization of vast datasets, offering unprecedented insights into the state’s complex geography and diverse population. The application of GIS spans environmental management, infrastructure planning, public health initiatives, emergency response, and economic development, demonstrating its versatility and transformative potential.
Applications Across Sectors:
The state’s use of GIS is multifaceted. In environmental management, the technology facilitates the monitoring of forest health, the assessment of water quality, the identification of areas vulnerable to flooding, and the planning of conservation efforts. Detailed maps illustrate habitat distribution, allowing for effective wildlife management and the preservation of biodiversity. Predictive modeling, powered by GIS, aids in anticipating environmental changes and mitigating their potential impact.
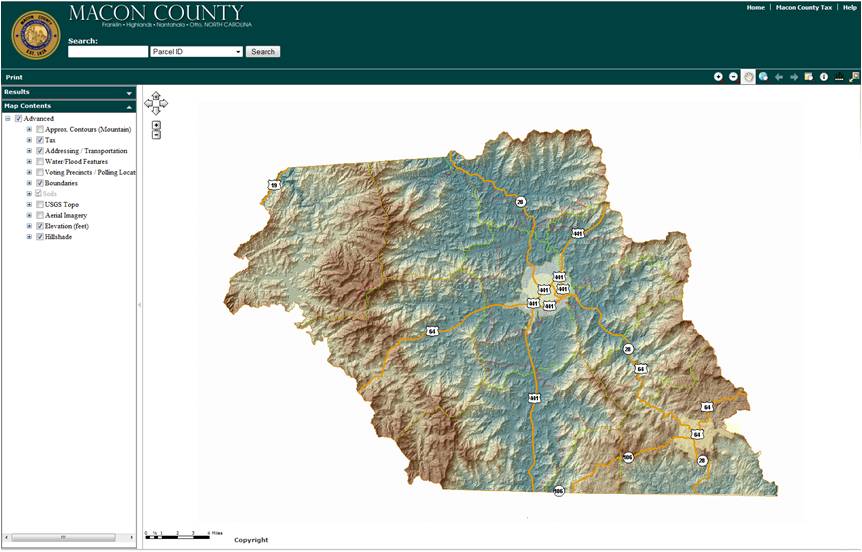
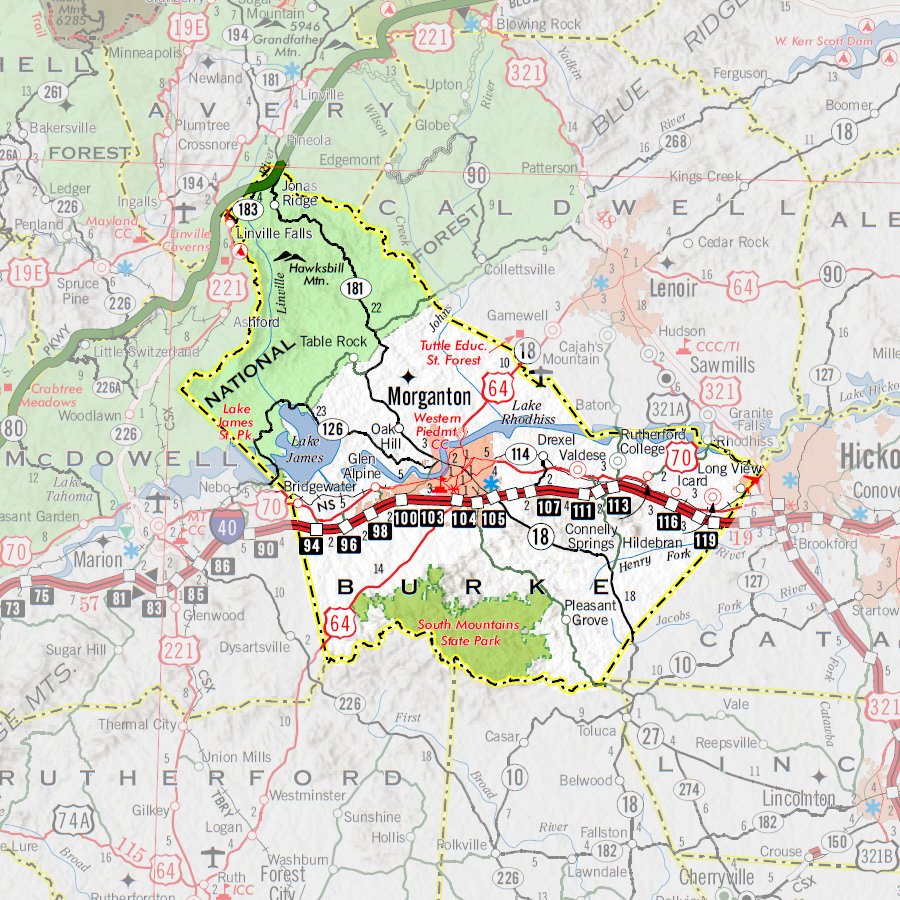
Infrastructure planning benefits significantly from GIS capabilities. The accurate representation of road networks, utility lines, and other infrastructure elements allows for efficient planning of new developments and the maintenance of existing systems. This includes optimizing transportation routes, identifying areas requiring infrastructure upgrades, and streamlining utility service delivery. GIS enables cost-effective and strategically sound infrastructure investments.
Public health initiatives are enhanced through the spatial analysis of disease outbreaks, demographic data, and healthcare facility locations. Identifying high-risk areas allows for targeted interventions and resource allocation, improving public health outcomes. The technology also supports the development of effective emergency response plans, enabling rapid deployment of resources during crises.
Economic development strategies rely heavily on GIS data. Analyzing factors such as population density, proximity to transportation networks, and available resources assists in identifying optimal locations for businesses and attracting investment. This detailed spatial understanding fosters economic growth and enhances regional competitiveness. Similarly, GIS supports workforce development initiatives by mapping skills gaps and matching individuals with employment opportunities.
Data Integration and Analysis:
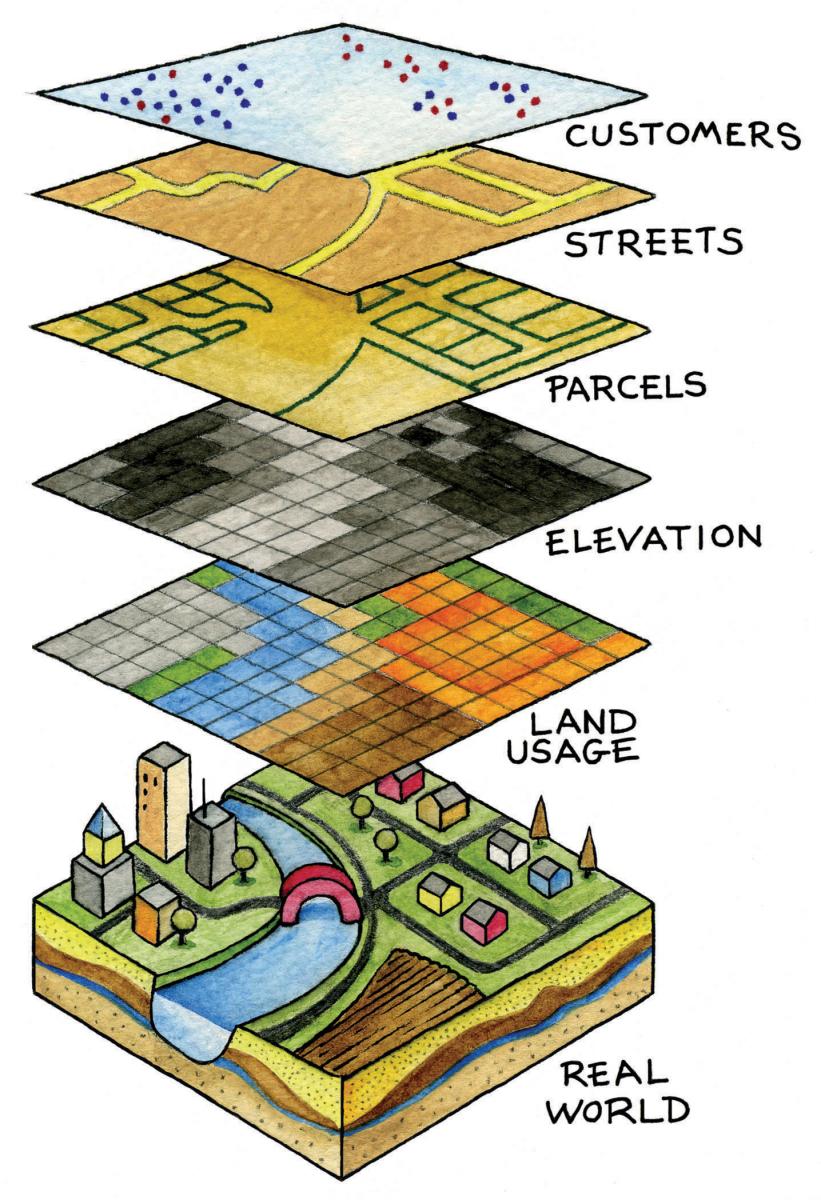
The effectiveness of GIS in North Carolina hinges on the integration of diverse datasets. These datasets include demographic information, environmental data, infrastructure inventories, and socioeconomic indicators. The ability to combine and analyze these datasets provides a holistic understanding of the state’s complexities, enabling more informed and comprehensive decision-making. Advanced spatial analysis techniques, such as overlay analysis and geostatistics, uncover previously hidden patterns and relationships within the data.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends:
The field of GIS is constantly evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging regularly. The integration of remote sensing data from satellites and drones provides high-resolution imagery, enhancing the accuracy and detail of spatial analyses. Cloud-based GIS platforms offer enhanced accessibility and collaboration capabilities, allowing multiple users to work on projects simultaneously. The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) promises to further automate processes and improve the accuracy of predictions and analyses. These advancements will continue to expand the capabilities and applications of GIS in North Carolina.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What types of data are commonly used in North Carolina’s GIS systems? North Carolina’s GIS systems utilize a wide range of data, including but not limited to: demographic data (population, age, income), environmental data (soil type, land cover, water quality), infrastructure data (roads, utilities, buildings), and socioeconomic data (poverty rates, unemployment).
-
How is GIS used in emergency management? GIS plays a crucial role in emergency response by providing real-time situational awareness. It aids in mapping affected areas, identifying evacuation routes, and coordinating the deployment of emergency personnel and resources.
-
What are the benefits of using GIS for infrastructure planning? GIS enables efficient infrastructure planning by optimizing resource allocation, minimizing costs, and improving the overall effectiveness of infrastructure projects. It allows for the identification of potential conflicts and the assessment of environmental impacts.
-
How accessible is GIS data in North Carolina? Many GIS datasets are publicly accessible through the state’s official GIS portals, promoting transparency and facilitating public participation in decision-making processes.
Tips for Effective GIS Implementation:
-
Data quality assurance: Maintaining high data quality is crucial for reliable analyses and informed decision-making. Regular data validation and updating are essential.
-
Collaboration and communication: Successful GIS implementation requires effective collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, private organizations, and the public. Clear communication is vital.
-
Training and capacity building: Investing in training and development programs ensures that personnel have the necessary skills to effectively utilize GIS technologies and interpret spatial data.
-
Integration with other systems: Integrating GIS with other information systems, such as databases and modeling tools, enhances its functionality and analytical capabilities.
Conclusion:
The utilization of GIS in North Carolina represents a significant investment in efficient governance and informed decision-making. Its application across diverse sectors demonstrates its transformative potential in improving public services, managing resources effectively, and fostering economic growth. Continued investment in GIS technology, data infrastructure, and workforce development will further enhance its contribution to the state’s progress and prosperity. The ongoing advancements in GIS technology, coupled with the commitment to data integration and accessibility, promise to further solidify its role as a critical tool for shaping the future of North Carolina.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in North Carolina: A Comprehensive Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!