Geolocating IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Geolocating IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Geolocating IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Geolocating IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview

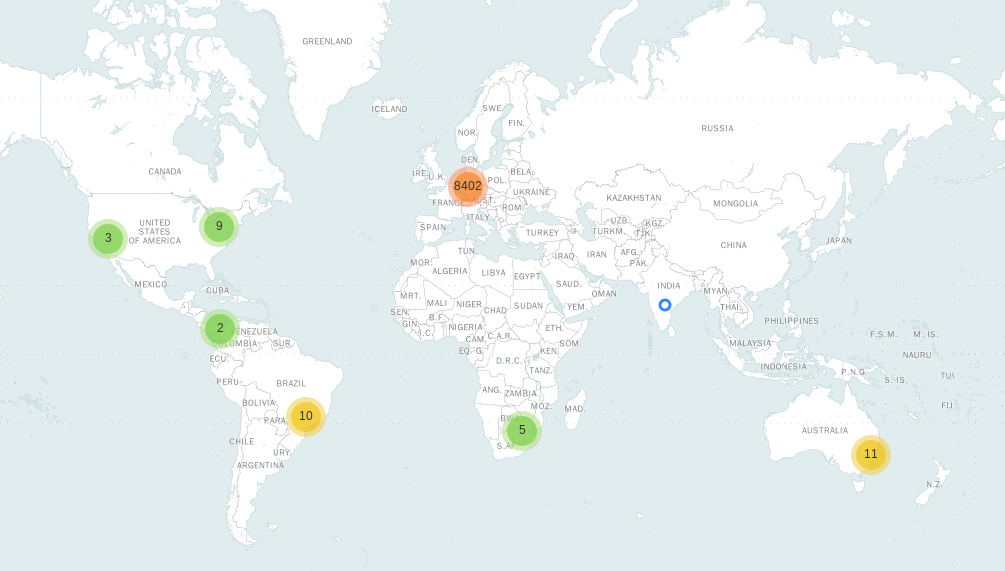
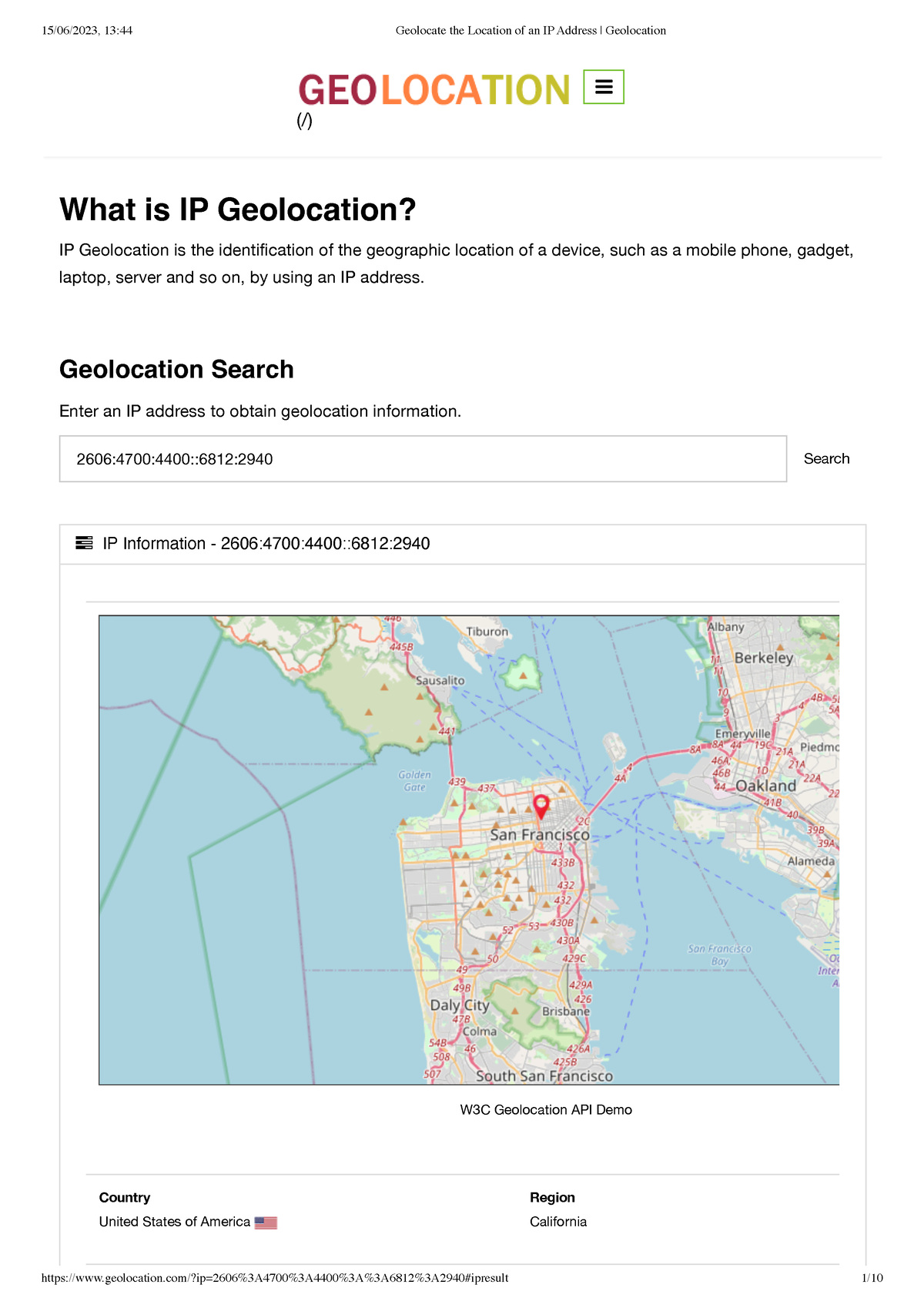
The ability to determine the geographical location associated with an internet protocol (IP) address is a crucial function with applications spanning numerous fields. This process, often referred to as IP geolocation, leverages various databases and techniques to approximate the physical location of a device connected to the internet based on its assigned IP address. Accuracy varies significantly depending on the method employed and the type of IP address involved.
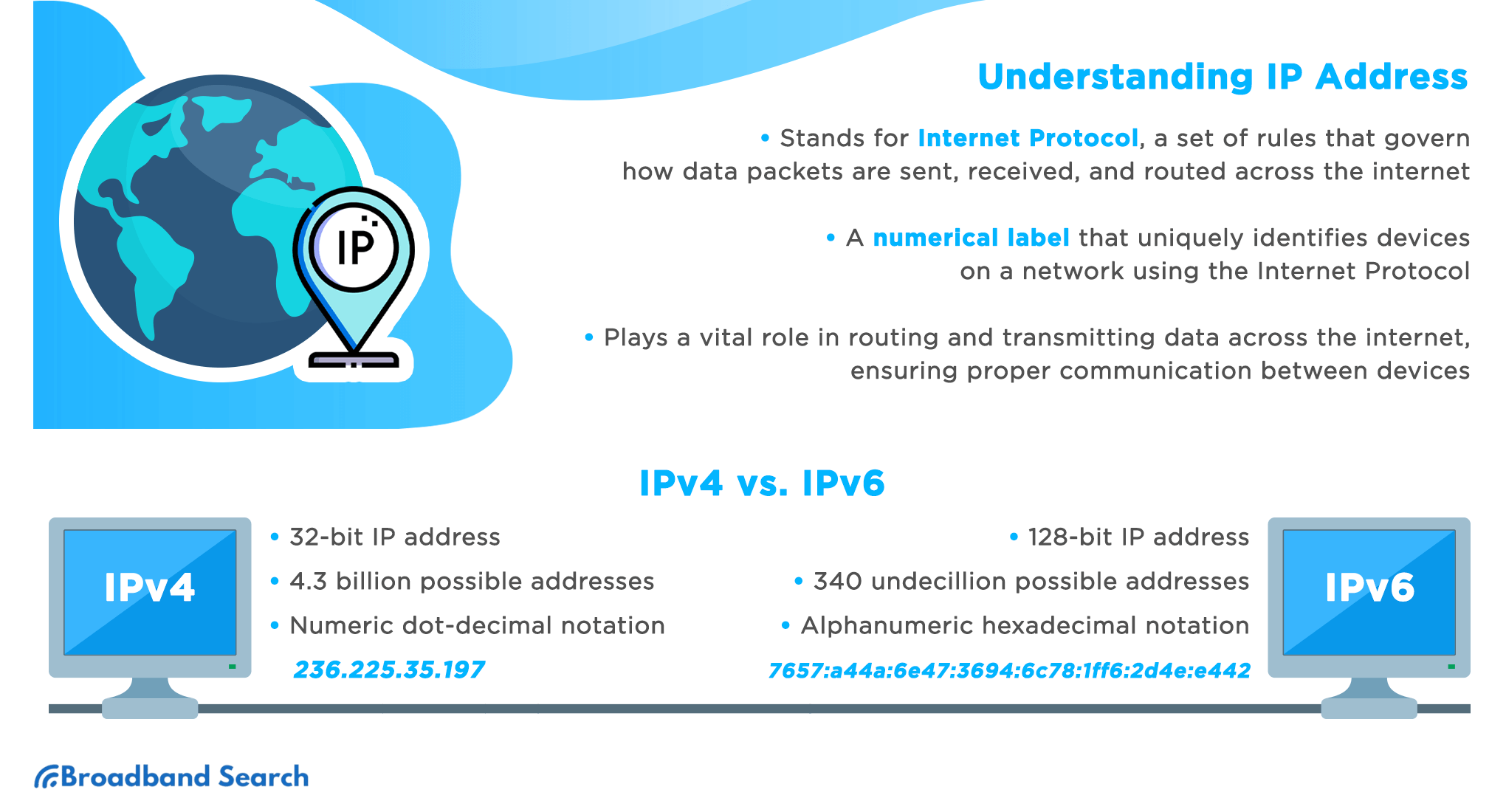
Understanding IP Addresses and their Relationship to Location
An IP address serves as a unique numerical identifier for every device participating in a network. These addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and are typically grouped into ranges associated with specific geographical regions. However, the relationship is not always precise. Several factors contribute to the complexities of this association.
-
IP Address Types: IPv4 addresses, the older standard, are 32-bit numbers, offering a limited number of unique addresses. IPv6 addresses, the newer standard, use 128 bits, providing a significantly larger address space. Geolocation accuracy tends to be higher with IPv4 addresses due to the historical structure of address allocation.
-
Network Address Translation (NAT): Many home and small business networks utilize NAT, a technique that allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address. This makes pinpointing the exact location of an individual device within the network challenging. Geolocation efforts in such cases will typically return the location of the network’s gateway, not the individual device.
-
Dynamic IP Addresses: Many ISPs assign dynamic IP addresses, meaning the address changes periodically. This necessitates frequent updates to geolocation databases to maintain accuracy. Static IP addresses, assigned permanently, offer greater consistency but are less common for residential users.
-
Data Centers and VPNs: The use of data centers and virtual private networks (VPNs) further complicates geolocation. Data centers often house numerous servers with IP addresses clustered within a specific geographic area. VPNs mask a device’s true IP address, making geolocation inaccurate or impossible. The geolocation service will likely identify the location of the VPN server, not the user’s actual location.
Methods for Determining Geographic Location
Several methods are used to determine geographic coordinates from an IP address. These methods vary in their accuracy and reliance on external data sources:
-
IP-to-Location Databases: These are commercial or publicly available databases mapping IP address ranges to geographical regions. These databases are regularly updated, but their accuracy depends on the frequency of updates and the completeness of the data. They are the most widely used method for IP geolocation.
-
Reverse DNS Lookup: This technique uses the IP address to query the Domain Name System (DNS) for associated domain names. While not directly providing geographic information, it can sometimes yield clues about the location through the domain name itself or associated DNS records. However, this method is limited in its accuracy and reliability.
-
Whois Databases: Whois databases contain registration information for domain names and IP addresses. While not directly providing geolocation data, they can sometimes provide contact information or organizational details that indirectly hint at the location. Again, this is not a primary method for precise geolocation.
-
Hybrid Approaches: Many services combine multiple data sources and techniques to improve accuracy. This approach leverages the strengths of different methods, mitigating the limitations of individual approaches.
Applications and Importance of Geolocation
The ability to associate an IP address with a geographic location is critical for various applications:
-
Cybersecurity: Identifying the geographic origin of cyber threats aids in threat analysis and incident response. Understanding the location of malicious actors can help in investigations and mitigation efforts.
-
Fraud Detection: Geolocation helps in detecting fraudulent activities by comparing the location inferred from the IP address with other information, such as the user’s claimed location. Discrepancies can flag suspicious activity.
-
Network Management: ISPs use geolocation to monitor network performance and troubleshoot issues. Identifying the geographic distribution of users helps optimize network infrastructure and resource allocation.
-
Targeted Advertising: Online advertising platforms leverage geolocation to target ads based on the user’s geographic location, improving ad relevance and effectiveness.
-
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs use geolocation to route users to the nearest server, minimizing latency and improving the speed of content delivery.
-
Market Research: Geolocation data aids in understanding user demographics and geographic distribution, providing valuable insights for market research and business planning.
-
Law Enforcement: Geolocation plays a role in investigations, assisting in identifying the location of individuals involved in criminal activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How accurate is IP geolocation? A: Accuracy varies significantly depending on the method used and the type of IP address. While geolocation can often provide a general region, precise location down to street address is rarely possible, especially with dynamic IP addresses or the use of VPNs.
-
Q: Are there any privacy concerns associated with IP geolocation? A: Yes, the ability to infer location from an IP address raises privacy concerns. Data protection regulations require transparency and user consent regarding the collection and use of geolocation data.
-
Q: Can IP geolocation be circumvented? A: Yes, using a VPN or proxy server can mask a user’s true IP address and make geolocation inaccurate.
-
Q: Is IP geolocation always reliable? A: No, various factors, including NAT, dynamic IP addresses, and the use of VPNs, can significantly impact the reliability and accuracy of geolocation.
Tips for Utilizing Geolocation Data
-
Understand limitations: Recognize that geolocation is an approximation, not an exact science. Accuracy varies based on several factors.
-
Cross-reference data: Combine geolocation data with other information to enhance accuracy and reliability.
-
Respect privacy: Adhere to relevant data protection regulations and ensure transparency regarding the collection and use of geolocation data.
-
Use reputable services: Choose reliable geolocation providers with accurate and up-to-date databases.
Conclusion
Geolocating IP addresses provides valuable insights for a wide range of applications. However, it’s crucial to understand the inherent limitations and potential inaccuracies. The accuracy of the process depends on various factors, including IP address type, network configurations, and the employed methodology. Responsible use of geolocation data, respecting privacy concerns and understanding its limitations, is paramount. As technology evolves, the techniques and accuracy of IP geolocation are expected to improve, expanding its applications further.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Geolocating IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!