Lake Victoria: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Hub of East Africa
Related Articles: Lake Victoria: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Hub of East Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Lake Victoria: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Hub of East Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Lake Victoria: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Hub of East Africa

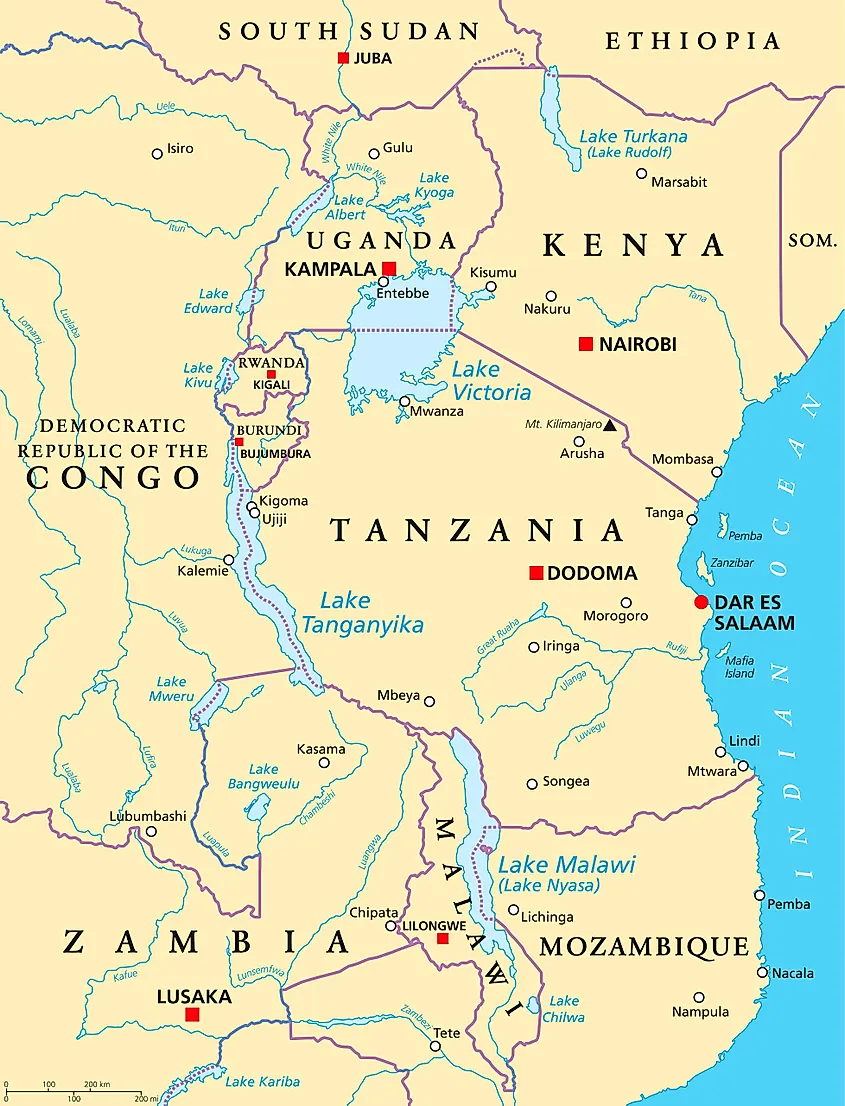
Lake Victoria, situated in East Africa, is the largest tropical lake globally, holding immense significance for the region’s geography, ecology, and human populations. Its vast expanse covers portions of three countries – Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda – creating a shared resource with complex political and economic implications. Understanding its geographical location, ecological importance, and socioeconomic impact requires a multifaceted approach.
Geographical Context:
The lake’s location within the East African Rift Valley system significantly influences its morphology and hydrology. Nestled at an elevation of approximately 1,134 meters above sea level, the lake’s basin is characterized by a relatively flat, gently sloping topography. This contributes to its vast surface area of approximately 69,485 square kilometers, exceeding the combined surface area of many smaller lakes worldwide. Its irregular shoreline is punctuated by numerous bays, inlets, and islands, adding to its complex hydrological dynamics. The Kagera River, the longest river feeding the lake, flows into the northern region, while other significant tributaries contribute to its water volume. The outflow, the Victoria Nile, forms the primary source of the White Nile, eventually feeding into the Nile River system.
The geological history of the region played a crucial role in the lake’s formation. The tectonic forces that created the East African Rift Valley also shaped the basin that now holds Lake Victoria. The lake’s depth varies considerably, with some areas exceeding 80 meters. This depth variation, combined with its vast size, creates diverse aquatic habitats that support a remarkable biodiversity.
Ecological Significance:
Lake Victoria’s biodiversity is exceptionally rich, supporting a wide array of aquatic life. The lake is renowned for its cichlid fish species, a group known for its remarkable adaptive radiation. Thousands of cichlid species have evolved within the lake, exhibiting a diverse range of morphologies and ecological niches. However, the introduction of the Nile perch in the 20th century significantly altered the lake’s ecosystem, leading to the decline of many native cichlid species and impacting the overall biodiversity.
Beyond the fish population, the lake supports a diverse array of other aquatic organisms, including invertebrates, amphibians, reptiles, and birds. The surrounding wetlands and riparian ecosystems provide crucial habitats for many terrestrial species as well. The lake’s ecological health is vital not only for its intrinsic biodiversity but also for the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on its resources.
Socioeconomic Impact:
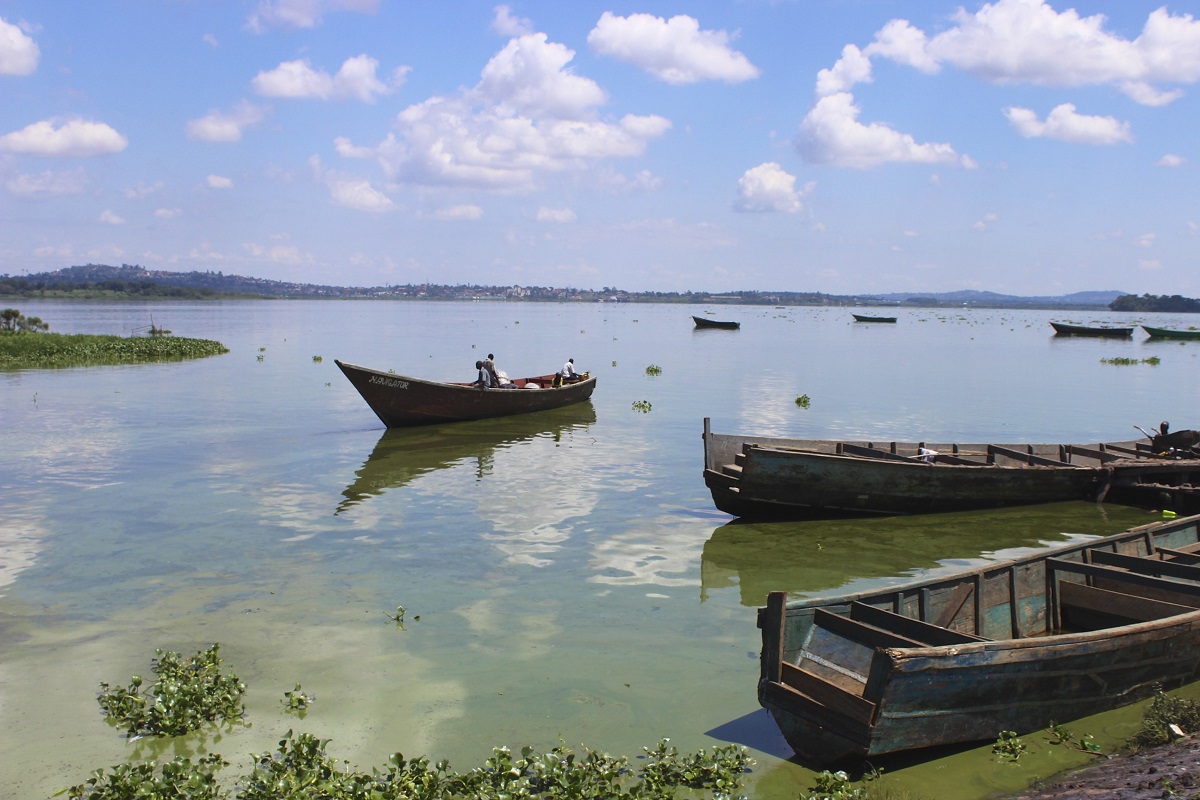
Lake Victoria plays a crucial role in the economies of the three countries that share its waters. Fisheries provide a significant source of protein and income for numerous communities. The lake also serves as a vital transportation route, facilitating trade and communication between different regions. Hydroelectric power generation from the lake’s outflow contributes to electricity supply in several areas. Furthermore, the lake’s basin supports extensive agricultural activities, contributing significantly to food production in the region.
However, the lake faces numerous challenges. Overfishing, pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial discharge, and the encroachment of human settlements threaten its ecological integrity and the livelihoods of those who depend on it. Water hyacinth infestation has also posed significant problems in recent years, impacting navigation and fishing activities. Effective management and sustainable resource utilization are crucial for safeguarding the lake’s long-term ecological and socioeconomic benefits.
FAQs:
- What are the main tributaries of Lake Victoria? The Kagera River is the largest tributary, but numerous smaller rivers and streams contribute to the lake’s water inflow.
- What is the primary outflow of Lake Victoria? The Victoria Nile is the principal outflow, forming the source of the White Nile.
- What are the major environmental challenges facing Lake Victoria? Overfishing, pollution, water hyacinth infestation, and habitat loss are significant threats.
- How does Lake Victoria impact the economies of the surrounding countries? It provides resources for fishing, transportation, hydropower, and agriculture, contributing substantially to regional economies.
- What is the significance of the cichlid fish species in Lake Victoria? They represent a remarkable example of adaptive radiation and are crucial to the lake’s biodiversity, although many species have been impacted by introduced species.
Tips for Sustainable Management:
- Implement stricter fishing regulations: Sustainable fishing practices are essential to prevent overexploitation and maintain fish stocks.
- Improve water quality management: Reducing pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial discharge is crucial for protecting the lake’s ecosystem.
- Control invasive species: Efforts to control the spread of invasive species like water hyacinth are necessary to minimize their negative impacts.
- Promote sustainable agriculture: Sustainable agricultural practices can help reduce pollution and protect the lake’s water quality.
- Foster regional cooperation: Collaboration among the three riparian countries is crucial for effective management of the shared resource.
Conclusion:
Lake Victoria represents a vital resource for East Africa, providing ecological, economic, and social benefits to millions of people. Its vast size and unique biodiversity make it a globally significant ecosystem. However, the numerous environmental and socioeconomic challenges facing the lake demand concerted efforts for sustainable management. Regional cooperation, integrated resource management, and community involvement are critical to ensuring the long-term health and productivity of this crucial freshwater resource, safeguarding its future for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Lake Victoria: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Hub of East Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!