Lake Winnebago: A Geographic and Ecological Overview
Related Articles: Lake Winnebago: A Geographic and Ecological Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Lake Winnebago: A Geographic and Ecological Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Lake Winnebago: A Geographic and Ecological Overview
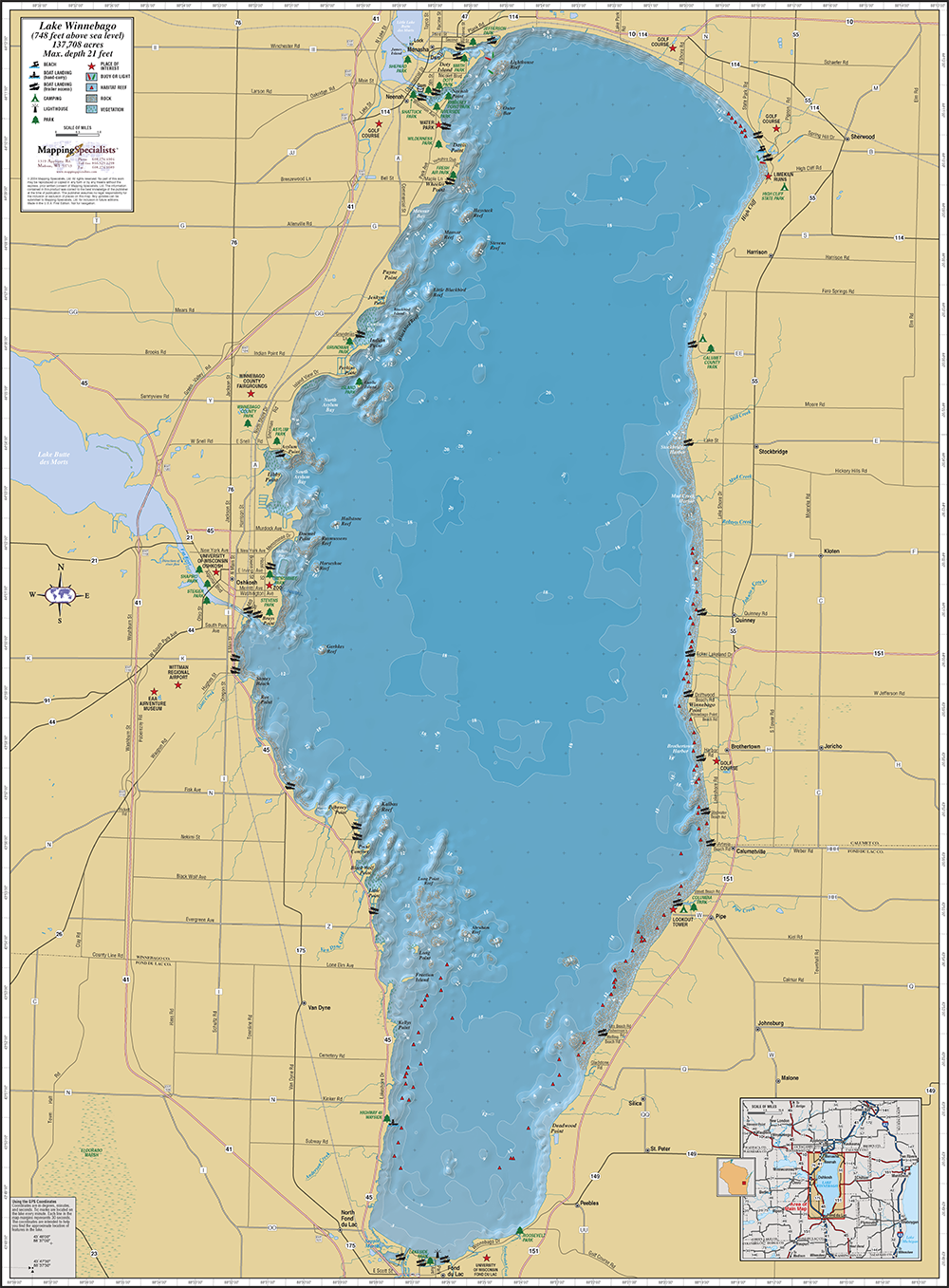
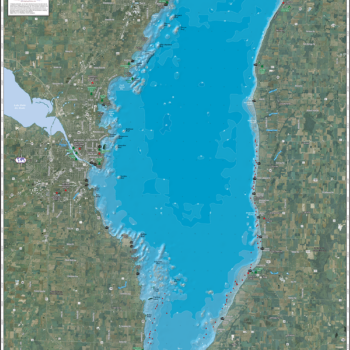
Lake Winnebago, situated in east-central Wisconsin, is a significant natural feature with profound ecological, economic, and cultural importance. Its shallow depth, expansive surface area, and unique geological history contribute to a diverse ecosystem and a rich human history interwoven with the lake’s rhythms. Understanding the lake’s geography, hydrology, and ecology reveals its vital role within the larger Wisconsin landscape.
Geographic Context and Formation:
The lake occupies a broad, shallow basin carved by glacial activity during the Wisconsin glaciation. The retreating glaciers left behind a vast expanse of meltwater, eventually forming the lake within the valley created by the scouring action of the ice sheets. Its irregular shoreline, characterized by numerous bays and inlets, reflects the underlying glacial topography. The lake’s relatively shallow depth, averaging approximately 15 feet, contributes to its susceptibility to wind-driven currents and rapid temperature fluctuations. These factors significantly influence the lake’s ecology and the activities conducted upon its waters. Surrounding the lake are diverse landforms, including gently rolling hills, agricultural fields, and urban areas, all interconnected through a complex hydrological system that feeds into and drains from the lake. The Fox River, a major tributary, plays a crucial role in the lake’s water balance, transporting both water and sediment.
Hydrology and Water Quality:
The lake’s hydrology is dynamic, influenced by precipitation, runoff from the surrounding watershed, and the inflow and outflow of the Fox River. Seasonal variations in water levels are common, with higher levels typically observed during spring snowmelt and periods of heavy rainfall. Water quality is a critical concern, affected by agricultural runoff, urban stormwater, and industrial discharges. Nutrient pollution, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, can lead to algal blooms, impacting water clarity and oxygen levels, posing threats to aquatic life. Ongoing monitoring and management efforts aim to mitigate these impacts and maintain a healthy lake ecosystem. The shallow depth contributes to rapid temperature changes, impacting both aquatic life and recreational activities. The lake’s relatively low water volume also makes it more vulnerable to pollution events.
Ecological Significance and Biodiversity:
Lake Winnebago supports a diverse array of aquatic life, including numerous fish species, waterfowl, and other wildlife. The lake is particularly renowned for its sturgeon population, a species of significant ecological and cultural importance. The annual sturgeon spearing season is a unique cultural event reflecting the deep-rooted connection between the community and the lake’s resources. The lake’s shallow waters and abundant nutrients provide a productive habitat for various species, including walleye, perch, and muskie. The extensive wetlands and marshes surrounding the lake further enhance biodiversity, providing critical habitat for migratory birds and other wildlife. The interplay between the lake and its surrounding ecosystems highlights the interconnectedness of the natural world and the importance of maintaining ecological integrity.
Economic and Cultural Importance:
Lake Winnebago plays a significant role in the regional economy. Fishing, tourism, and recreation generate substantial revenue, supporting local businesses and employment. The annual sturgeon spearing season is a major economic driver, attracting visitors and generating income through tourism and related activities. The lake also serves as a source of drinking water for some communities, highlighting its importance as a resource for human consumption. Beyond its economic contributions, the lake holds significant cultural value for the region’s inhabitants. Native American tribes have a long history connected to the lake, and their traditions and cultural practices remain interwoven with the lake’s ecosystem. The lake serves as a focal point for community gatherings, recreational activities, and a source of pride for the surrounding communities.
FAQs:
-
What is the average depth of Lake Winnebago? The average depth is approximately 15 feet.
-
What are the major tributaries of Lake Winnebago? The Fox River is the primary tributary.
-
What are the main threats to Lake Winnebago’s water quality? Agricultural runoff, urban stormwater, and industrial discharges are primary concerns.
-
What species of fish are found in Lake Winnebago? Walleye, perch, muskie, and sturgeon are notable examples.
-
What is the significance of the annual sturgeon spearing season? It is a culturally significant event and a major economic driver for the region.
-
What are the primary recreational activities on Lake Winnebago? Boating, fishing, and ice fishing are popular activities.
Tips for Responsible Lake Use:
-
Minimize the use of fertilizers and pesticides: Proper land management practices in the surrounding watershed help reduce nutrient pollution entering the lake.
-
Properly dispose of waste: Avoid littering and ensure proper disposal of sewage and other waste to prevent water contamination.
-
Practice responsible boating: Adhere to boating regulations and operate vessels safely to prevent accidents and habitat damage.
-
Support conservation efforts: Participate in or support initiatives aimed at protecting the lake’s ecosystem and water quality.
-
Educate others: Share knowledge about the lake’s importance and the need for its conservation with others.
Conclusion:
Lake Winnebago represents a valuable natural resource with significant ecological, economic, and cultural importance for the region. Its unique formation, dynamic hydrology, and rich biodiversity contribute to its distinctive character. Continued efforts in water quality management, responsible resource utilization, and community engagement are crucial for safeguarding the lake’s health and ensuring its sustained contribution to the well-being of the surrounding communities for generations to come. The ongoing balance between human activities and environmental protection will determine the future of this vital ecosystem.
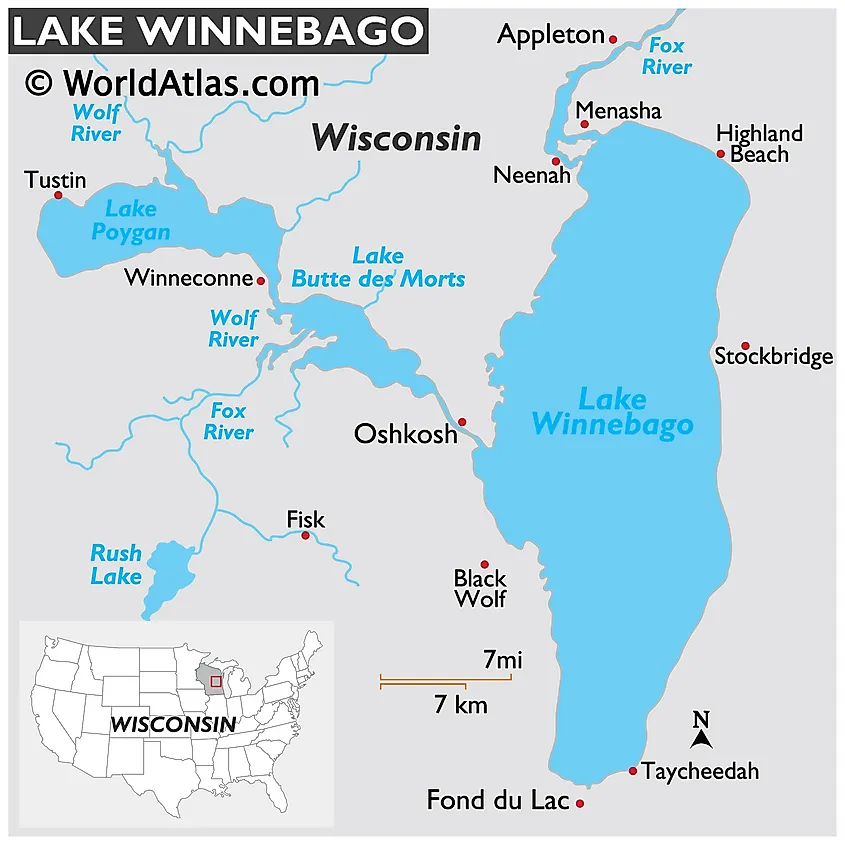


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Lake Winnebago: A Geographic and Ecological Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!