Manitoba: A Geographic and Economic Overview
Related Articles: Manitoba: A Geographic and Economic Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Manitoba: A Geographic and Economic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Manitoba: A Geographic and Economic Overview
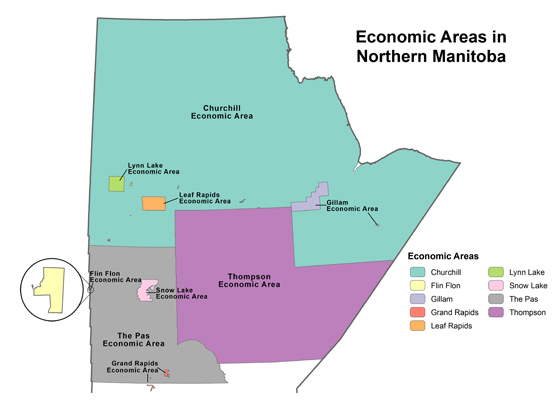
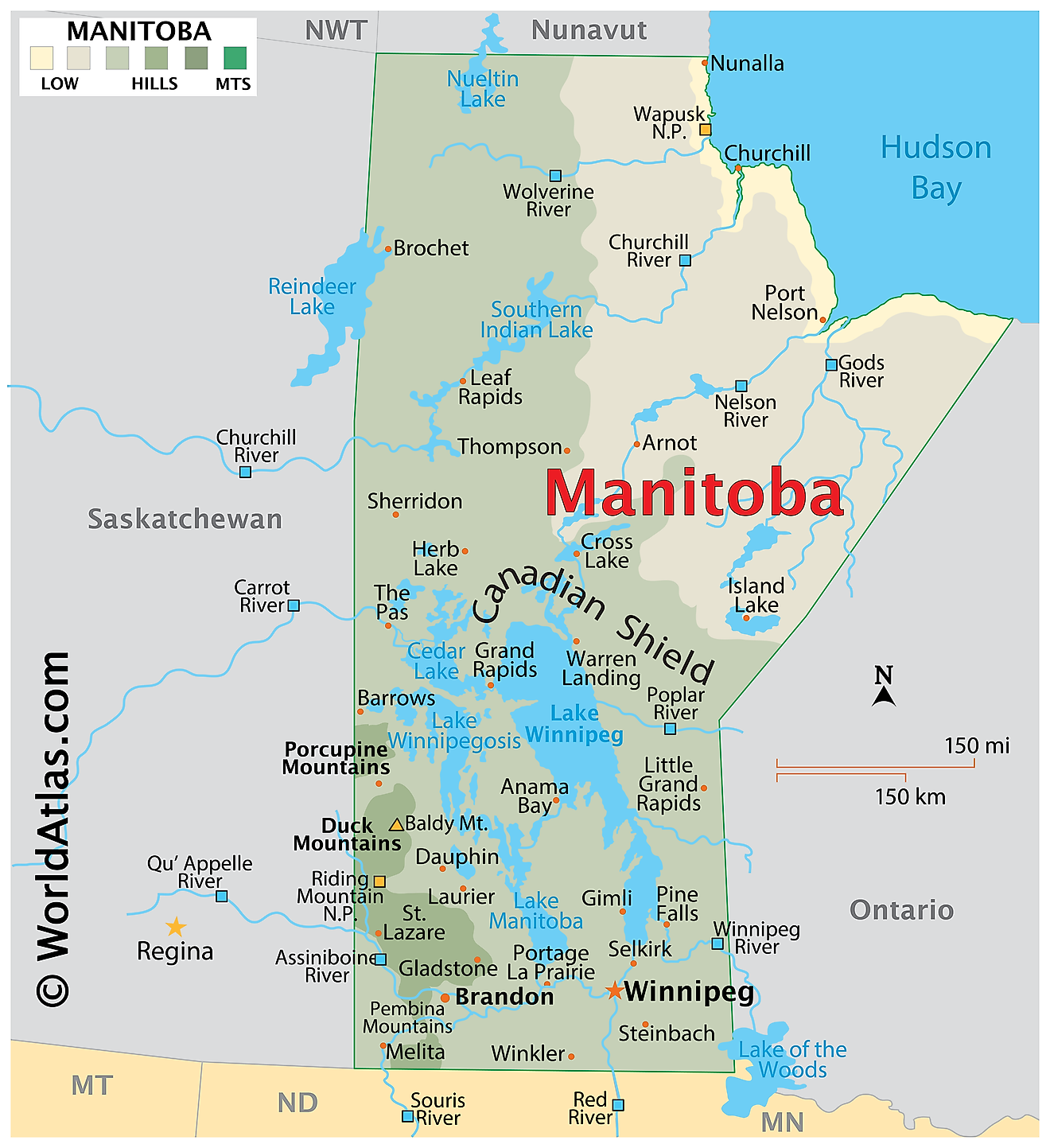
Manitoba, situated in the heart of Canada, occupies a significant portion of the central Canadian prairies and extends northward into the Canadian Shield. Its geographical location contributes significantly to its unique character and economic activities. The province’s position within the country facilitates trade and transportation links, while its diverse geography supports a range of industries.
Geographical Features and Their Influence:
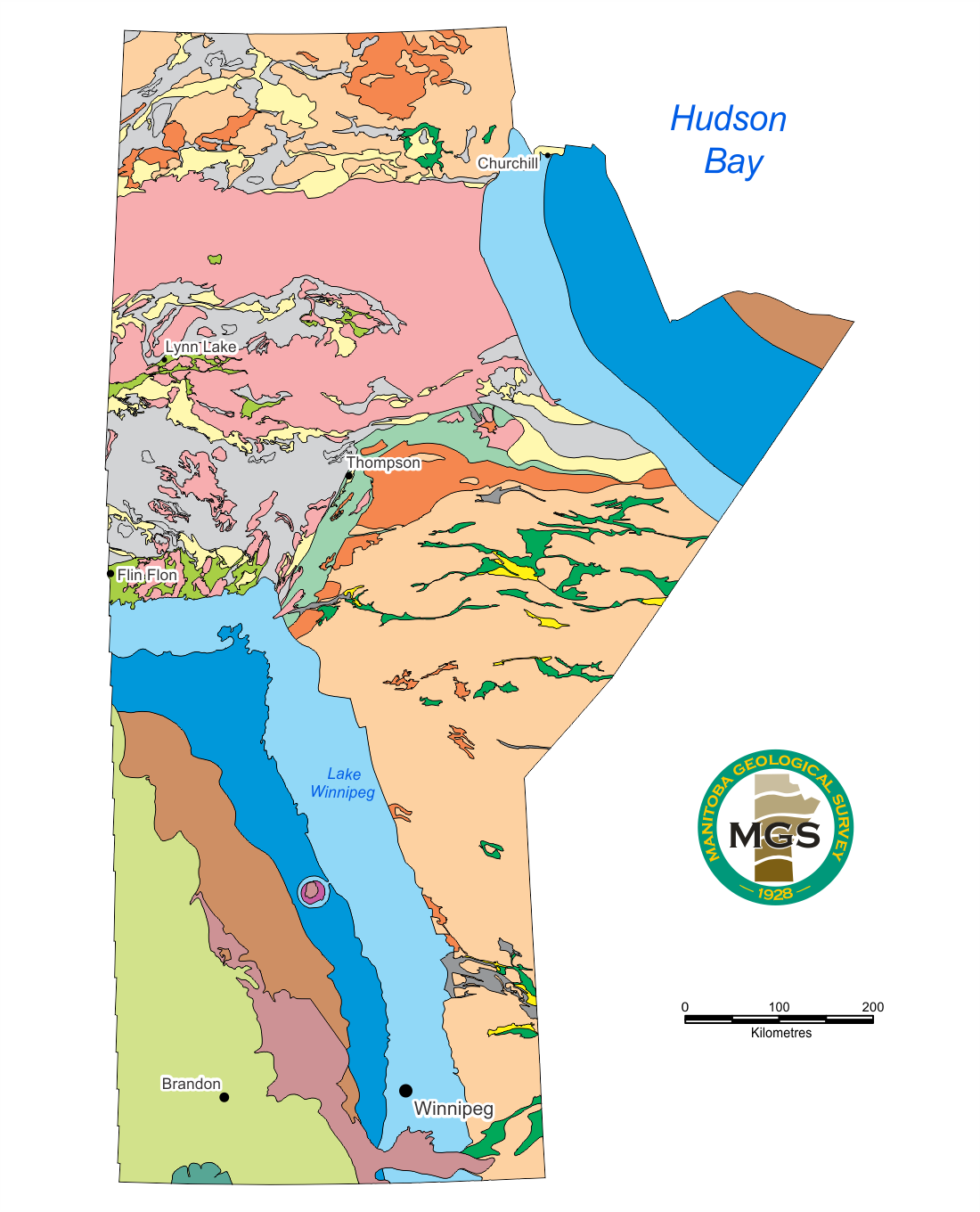
The province’s landscape is characterized by a striking diversity. The southern region comprises fertile prairies, ideal for agriculture, which forms the backbone of the provincial economy. This area is characterized by rolling hills and vast plains, traversed by major rivers such as the Red River and the Assiniboine River, which historically shaped settlement patterns and continue to play a crucial role in irrigation and transportation. The central region transitions into a mixed landscape of parkland and boreal forest, supporting forestry and resource extraction. Northern Manitoba is dominated by the Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of Precambrian rock, characterized by numerous lakes, rivers, and abundant mineral resources. This region supports mining, hydroelectric power generation, and tourism.
The presence of Lake Winnipeg, one of the largest freshwater lakes in the world, significantly impacts the province’s ecology and economy. It supports a substantial fishing industry and provides recreational opportunities, attracting tourists and contributing to the local economy. The numerous smaller lakes and rivers throughout the province contribute to biodiversity and provide essential resources for various industries.
Economic Activities and their Geographic Context:
Agriculture remains a cornerstone of Manitoba’s economy. The fertile prairies in the south produce a wide variety of crops, including wheat, canola, barley, and soybeans. Livestock farming, particularly cattle and hogs, also contributes significantly to agricultural output. The province’s strategic location within the North American grain belt facilitates efficient transportation and trade of agricultural products.
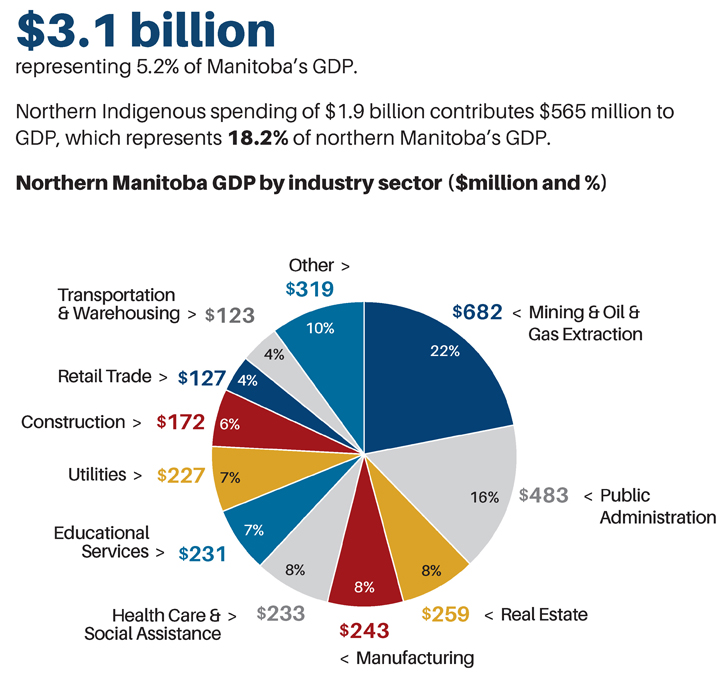
Natural resources play a crucial role in the provincial economy. Mining operations in northern Manitoba extract nickel, zinc, gold, and other minerals. Hydroelectric power generation, leveraging the province’s abundant water resources, provides a significant portion of Manitoba’s energy needs and contributes to the national energy grid. Forestry, concentrated in the central and northern regions, provides timber for lumber and pulp and paper production.
Manufacturing and processing industries are also important contributors to the economy. Food processing, particularly meat packing and grain processing, is closely linked to the agricultural sector. Other manufacturing activities include transportation equipment, machinery, and fabricated metal products.
The service sector, encompassing finance, healthcare, education, and retail, is increasingly significant. The provincial capital, Winnipeg, serves as the primary economic hub, concentrating a large portion of the service sector activities.
Transportation and Infrastructure:
Manitoba’s strategic location and extensive transportation network facilitate trade and economic activity. The province is served by major highways, railways, and waterways, connecting it to other parts of Canada and the United States. The Port of Churchill, on Hudson Bay, historically played a significant role in grain exports, although its operational status has fluctuated. Winnipeg’s James Armstrong Richardson International Airport serves as a major air transportation hub.
The development and maintenance of infrastructure, including transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems, are crucial for supporting economic growth and ensuring the well-being of the population. Investments in infrastructure are essential for attracting investment, fostering economic diversification, and enhancing the province’s competitiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the capital of Manitoba? The capital city is Winnipeg.
-
What are the major industries in Manitoba? Agriculture, mining, hydroelectric power generation, forestry, manufacturing, and services are all major contributors to the provincial economy.
-
What is the climate like in Manitoba? Manitoba experiences a continental climate, characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The climate varies across the province, with the southern region experiencing milder conditions than the northern regions.
-
What are the major cities in Manitoba besides Winnipeg? Brandon, Thompson, and Portage la Prairie are notable cities.
-
What natural resources are found in Manitoba? Manitoba possesses significant reserves of minerals, including nickel, zinc, gold, and others. It also has abundant water resources, forests, and fertile agricultural land.
Tips for Visiting or Relocating to Manitoba:
-
Research the climate: Be prepared for significant temperature variations throughout the year.
-
Consider transportation: Familiarize yourself with the transportation infrastructure and plan accordingly.
-
Explore the diverse landscapes: Manitoba offers a wide range of natural attractions, from prairies to boreal forests to the Canadian Shield.
-
Learn about the cultural heritage: Manitoba has a rich and diverse cultural heritage, reflecting its Indigenous populations and its history as part of both French and British North America.
-
Understand the economy: Research the economic opportunities available in the province, considering the various sectors and industries.
Conclusion:
Manitoba’s unique geography, encompassing prairies, forests, and the Canadian Shield, shapes its diverse economic activities and contributes to its distinctive identity. The province’s strategic location within Canada and its well-developed transportation infrastructure facilitate trade and economic interaction. Sustained investment in infrastructure, diversification of the economy, and responsible management of natural resources are crucial for ensuring the continued prosperity and well-being of Manitoba. Understanding the interplay between geography, resources, and economic activities provides a comprehensive perspective on this important Canadian province.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Manitoba: A Geographic and Economic Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!