Mapping Louisiana’s Plantation Legacy: A Geographic and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Mapping Louisiana’s Plantation Legacy: A Geographic and Historical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Louisiana’s Plantation Legacy: A Geographic and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Louisiana’s Plantation Legacy: A Geographic and Historical Exploration

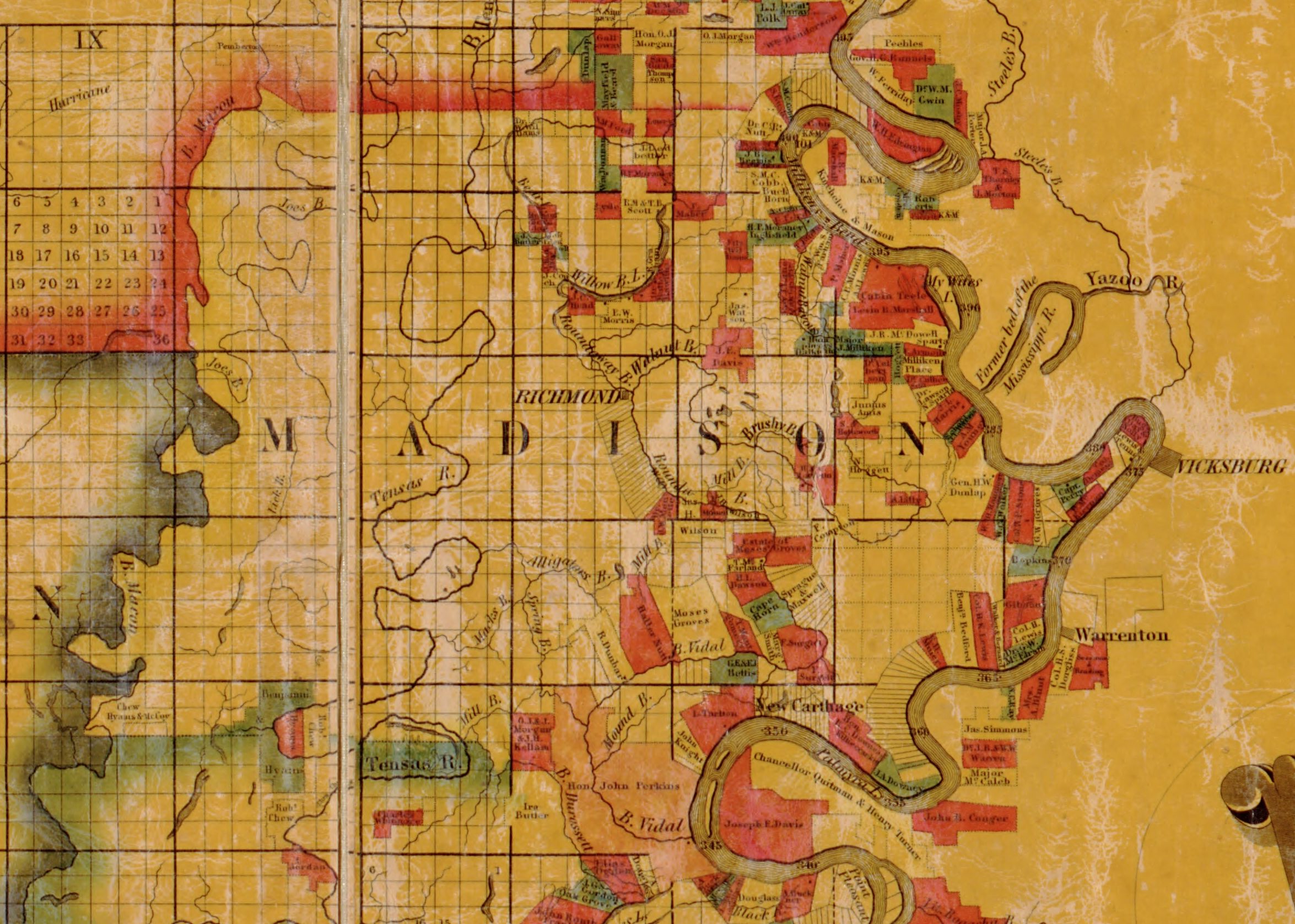
Louisiana’s history is inextricably linked to its plantation system. A geographical examination of these estates reveals a complex interplay of environmental factors, economic forces, and social structures that shaped the state’s development. Understanding the spatial distribution of these properties provides crucial insights into the state’s past and its enduring legacy. This analysis explores the geographic patterns of these historical sites, their significance, and the information they convey about Louisiana’s history.
The distribution of plantations across Louisiana was heavily influenced by the natural environment. The fertile alluvial soils of the Mississippi River delta and its tributaries provided ideal conditions for the cultivation of cash crops like sugar cane, cotton, and indigo. Consequently, a high concentration of plantations developed along these waterways, facilitating transportation of goods to market. Parishes like Iberville, St. James, St. John the Baptist, and Ascension, situated along the Mississippi River and its bayous, became centers of plantation agriculture. This riparian concentration is readily apparent on any historical map depicting these properties.
However, the landscape was not uniformly suitable for plantation agriculture. The northern and western regions of the state, characterized by less fertile soils and different climatic conditions, saw a less dense concentration of large-scale plantations. These areas often supported smaller farms and different agricultural practices. This variation in geographical distribution reflects the specific environmental requirements of different crops and the economic viability of plantation agriculture in various locations.
Mapping these historical sites reveals more than just geographical patterns; it also illustrates the evolution of the plantation system over time. Early plantations, often smaller in size, were established closer to existing settlements and transportation routes. As the demand for cash crops increased, larger plantations emerged, extending further into the interior along navigable waterways. This expansion is reflected in the increasing density of plantation markers on historical maps over time. The maps also show the shifting boundaries of plantation holdings, reflecting land acquisition, inheritance patterns, and economic fluctuations.
Furthermore, cartographic representation of these historical sites allows for analysis of the social and political structures that underpinned the plantation system. The spatial proximity of plantations often reflected social connections and power dynamics among plantation owners. Neighboring estates frequently belonged to families with established relationships, illustrating the importance of kinship and social networks in the functioning of the plantation economy. The size and location of slave quarters, often depicted on detailed maps, reveal aspects of the enslaved population’s living conditions and their relationship to the plantation’s overall structure.
Examining the historical maps also highlights the impact of infrastructure on the plantation system. The development of roads, canals, and railroads facilitated the transportation of goods and the movement of people, influencing the location and growth of plantations. The strategic placement of plantations along these transportation networks enhanced their economic viability and contributed to the overall success of the plantation economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What types of information can be gleaned from maps depicting historical Louisiana plantations? Maps provide insights into the geographical distribution of plantations, their size and layout, proximity to waterways and transportation routes, and the potential relationships between neighboring estates. They also offer clues about the social and economic structures of the plantation system.
-
How did environmental factors influence the location of plantations? Fertile alluvial soils along the Mississippi River and its tributaries were crucial for the success of plantation agriculture, leading to a high concentration of plantations in these areas. Less fertile regions saw fewer and smaller plantations.
-
What role did transportation networks play in the development of the plantation system? Rivers, canals, and later railroads played a vital role in transporting crops to market and connecting plantations to urban centers. Plantations strategically located along these routes enjoyed greater economic success.
-
How do maps reflect the social structure of the plantation system? The proximity of plantations can indicate social connections between owners. The location and size of slave quarters, when depicted, provide insights into the lives of the enslaved population.
Tips for Researching Louisiana Plantations using Maps
-
Utilize multiple map sources: Consult various historical maps, including cadastral maps, land ownership records, and thematic maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of plantation distribution.
-
Correlate map data with other historical sources: Combine map information with written documents, such as plantation records, diaries, and census data, to create a richer historical narrative.
-
Pay attention to scale and detail: Different maps offer varying levels of detail. Examine maps with appropriate scales to accurately assess plantation size and location.
-
Consider the limitations of historical maps: Recognize that historical maps may contain inaccuracies or omissions. Cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
A geographical analysis of Louisiana’s plantation system, facilitated by the use of historical maps, provides a powerful tool for understanding the state’s complex history. The spatial distribution of these estates reflects the interplay of environmental factors, economic forces, and social structures that shaped Louisiana’s development. By critically examining these maps and correlating the information with other historical sources, a more complete and nuanced understanding of the plantation system’s impact on Louisiana’s landscape and society can be achieved. This interdisciplinary approach enhances historical scholarship and facilitates a deeper engagement with the state’s past.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Louisiana’s Plantation Legacy: A Geographic and Historical Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!