Mapping the Maya: Unveiling a Lost Civilization Through Cartography
Related Articles: Mapping the Maya: Unveiling a Lost Civilization Through Cartography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Maya: Unveiling a Lost Civilization Through Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Maya: Unveiling a Lost Civilization Through Cartography
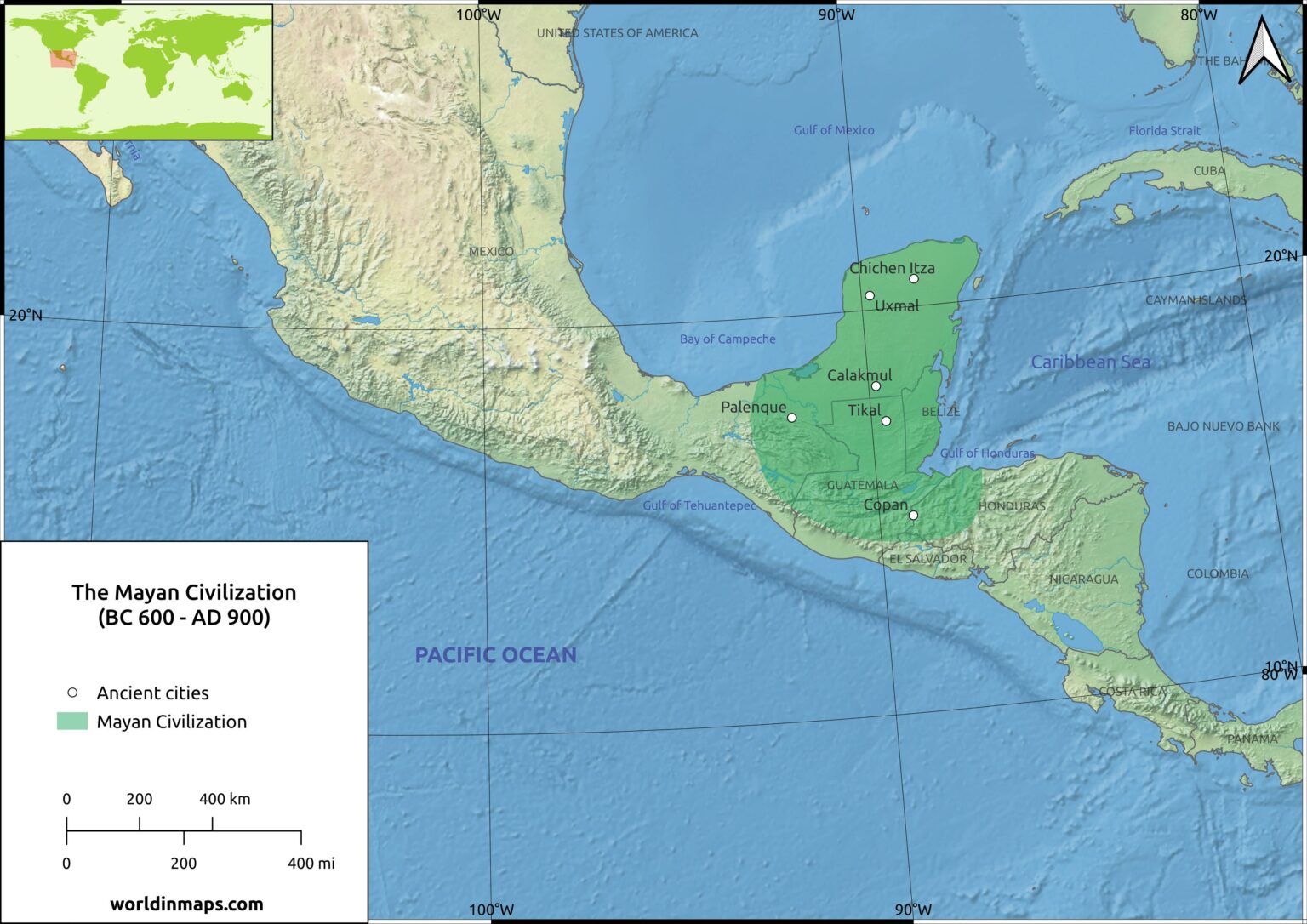
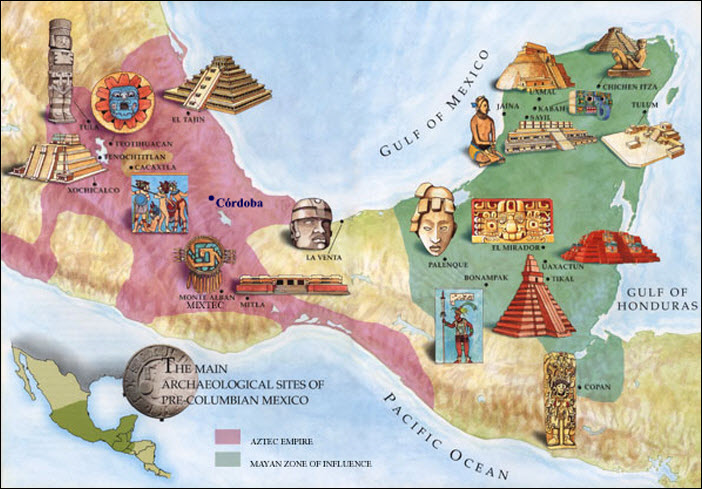
The Maya civilization, renowned for its sophisticated calendar system, advanced mathematics, and intricate artistry, left behind a remarkable legacy scattered across present-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador. Understanding the spatial distribution of this civilization’s urban centers, ceremonial sites, and agricultural landscapes requires a detailed cartographic approach. Mapping these ruins provides invaluable insights into the Maya’s social organization, political structures, economic systems, and environmental adaptations. The resulting geographical data allows for a more comprehensive understanding of this complex society, its rise, and its eventual decline.
Spatial Distribution and Regional Variations:
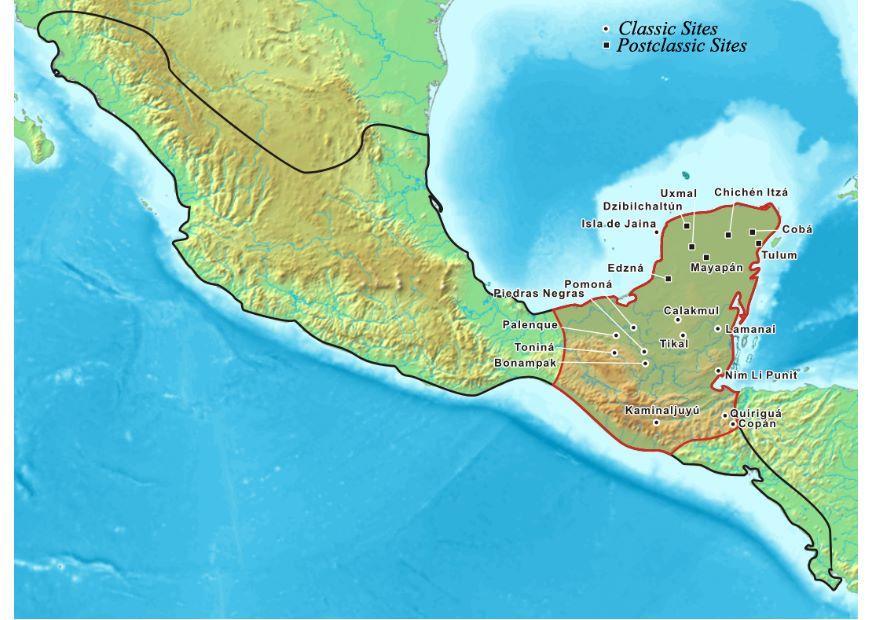
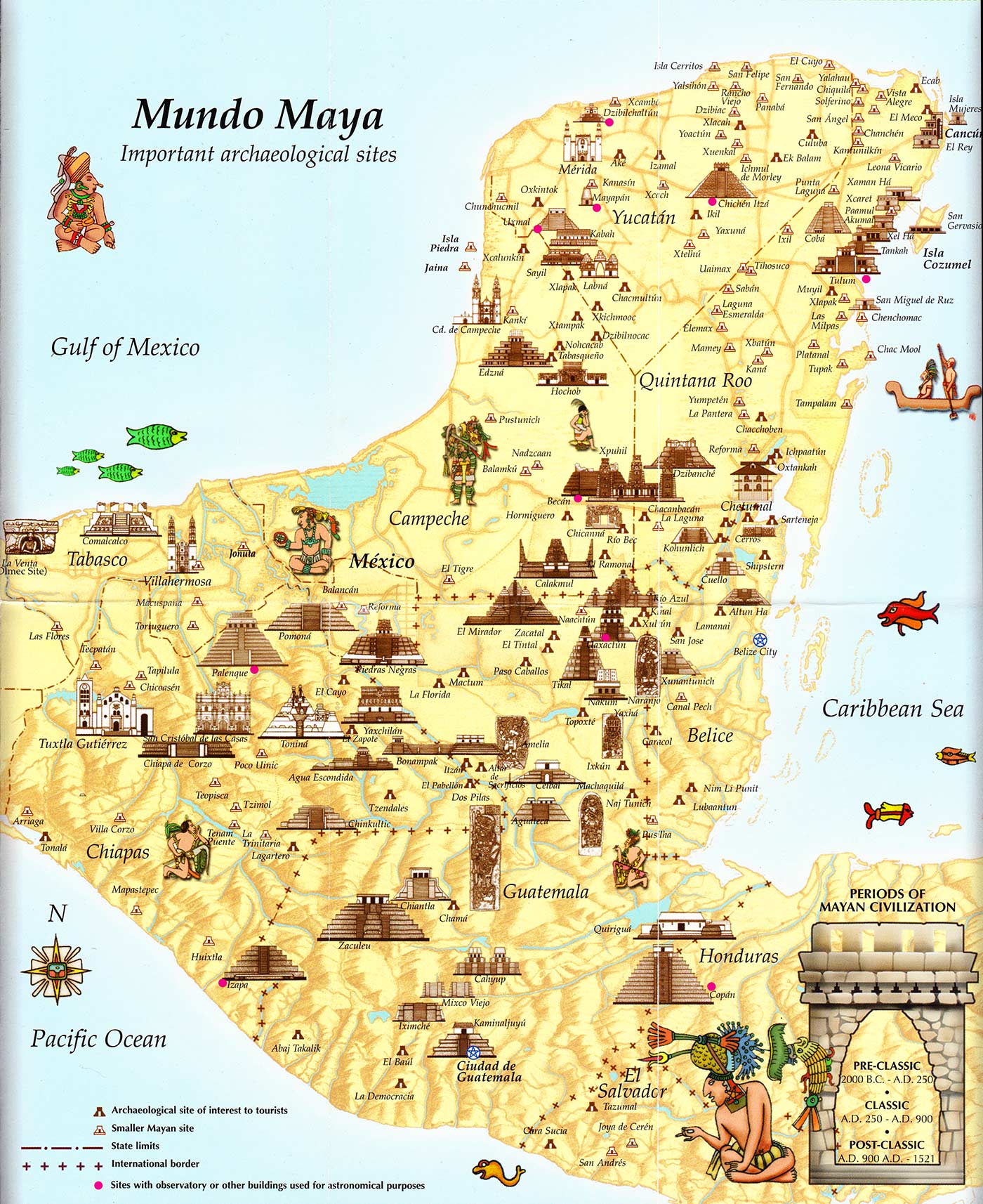
Archaeological mapping reveals a significant variation in the density and size of Maya settlements across the region. The northern Yucatán Peninsula, for example, features numerous smaller, dispersed sites, suggesting a less centralized political organization compared to the southern lowlands. Areas like the Petén Basin in Guatemala, however, boast large urban centers like Tikal and Calakmul, indicating a more hierarchical social structure with powerful ruling elites. This uneven distribution is linked to factors such as water availability, soil fertility, and proximity to trade routes. Detailed maps highlight the strategic location of cities near rivers and fertile valleys, reflecting the importance of agriculture and resource management.
Technological Advancements in Mapping:
Modern mapping techniques, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing (aerial photography, LiDAR), and ground-penetrating radar (GPR), have revolutionized the study of Maya ruins. LiDAR, in particular, penetrates the dense rainforest canopy, revealing previously unknown structures and settlement patterns hidden beneath the vegetation. This technology has dramatically increased the accuracy and detail of maps, allowing researchers to identify previously unseen features such as roads, canals, and agricultural terraces. GIS software facilitates the integration of diverse data sets, including archaeological findings, environmental data, and historical records, creating comprehensive spatial models of Maya civilization.
Insights into Social Organization and Political Structures:
The spatial arrangement of structures within Maya sites offers crucial insights into social organization and political power. Large palaces and temples, typically located in central areas, signify the power and prestige of ruling elites. Residential areas, often organized around plazas and courtyards, reflect the social stratification within the community. The size and complexity of these residential areas can indicate wealth and status. Mapping reveals the intricate network of relationships between different settlements, suggesting alliances, conflicts, and trade networks that shaped the political landscape of the Maya world. The strategic placement of fortifications and defensive structures further highlights the competitive dynamics between different Maya polities.
Economic Systems and Resource Management:
Mapping reveals the strategies employed by the Maya to manage resources and sustain their population. The location of agricultural fields, quarries, and trade routes provides evidence of their economic activities. The construction of extensive systems of raised fields and canals demonstrates their sophisticated understanding of water management in a tropical environment. The analysis of mapped data allows researchers to assess the carrying capacity of the environment and understand how the Maya adapted their economic strategies to fluctuating environmental conditions. Trade routes, often following rivers and natural pathways, reveal the extent of the Maya’s interaction with other cultures and the flow of goods across the region.
Environmental Adaptations and Sustainability:
The Maya were adept at adapting to their environment. Mapping reveals their strategies for managing resources in a challenging tropical climate. The construction of reservoirs and water management systems highlights their ability to cope with periods of drought. The location of settlements in relation to natural resources, such as limestone quarries and obsidian sources, provides insights into their material culture and technological advancements. Mapping allows researchers to analyze the impact of the Maya on their environment and assess the sustainability of their practices. Understanding the relationship between human activities and environmental change is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of Maya civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What is the significance of mapping Maya ruins?
- A: Mapping provides crucial data for understanding the spatial distribution of settlements, the organization of society, economic systems, and the interaction between the Maya and their environment. This allows for a more complete picture of their complex civilization.
-
Q: What technologies are used in mapping Maya ruins?
- A: Modern techniques include GIS, aerial photography, LiDAR, and GPR, significantly enhancing the accuracy and detail of the resulting maps.
-
Q: How does mapping contribute to our understanding of Maya social structures?
- A: The spatial arrangement of structures within sites reveals social hierarchies, political power dynamics, and the relationships between different settlements.
-
Q: What insights does mapping offer regarding Maya economic systems?
- A: Mapping helps identify agricultural fields, quarries, and trade routes, providing evidence of economic activities and resource management strategies.
-
Q: How does mapping contribute to understanding Maya environmental adaptations?
- A: Mapping reveals the strategies employed by the Maya to manage resources and adapt to environmental challenges, such as drought and resource scarcity.
Tips for Utilizing Maps of Maya Ruins:
- Consider the scale and resolution of the map when interpreting data. Different maps provide varying levels of detail.
- Examine the map legend carefully to understand the symbols and abbreviations used.
- Integrate the map data with other sources of information, such as archaeological reports and historical texts, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Analyze the spatial distribution of features to identify patterns and relationships.
- Compare maps from different time periods to observe changes in settlement patterns and land use.
Conclusion:
The cartographic study of Maya ruins is an ongoing process, constantly refined by technological advancements and new discoveries. The detailed maps produced through these efforts provide an invaluable resource for understanding the complex interplay of social, political, economic, and environmental factors that shaped Maya civilization. By integrating various data sources and employing advanced mapping techniques, researchers continue to unlock the secrets of this remarkable civilization, revealing a more nuanced and comprehensive picture of its past. The continuing development and refinement of these cartographic resources remain essential for future research and a deeper appreciation of the Maya legacy.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Maya: Unveiling a Lost Civilization Through Cartography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!