Mauritius: A Geographic and Strategic Overview
Related Articles: Mauritius: A Geographic and Strategic Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mauritius: A Geographic and Strategic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mauritius: A Geographic and Strategic Overview
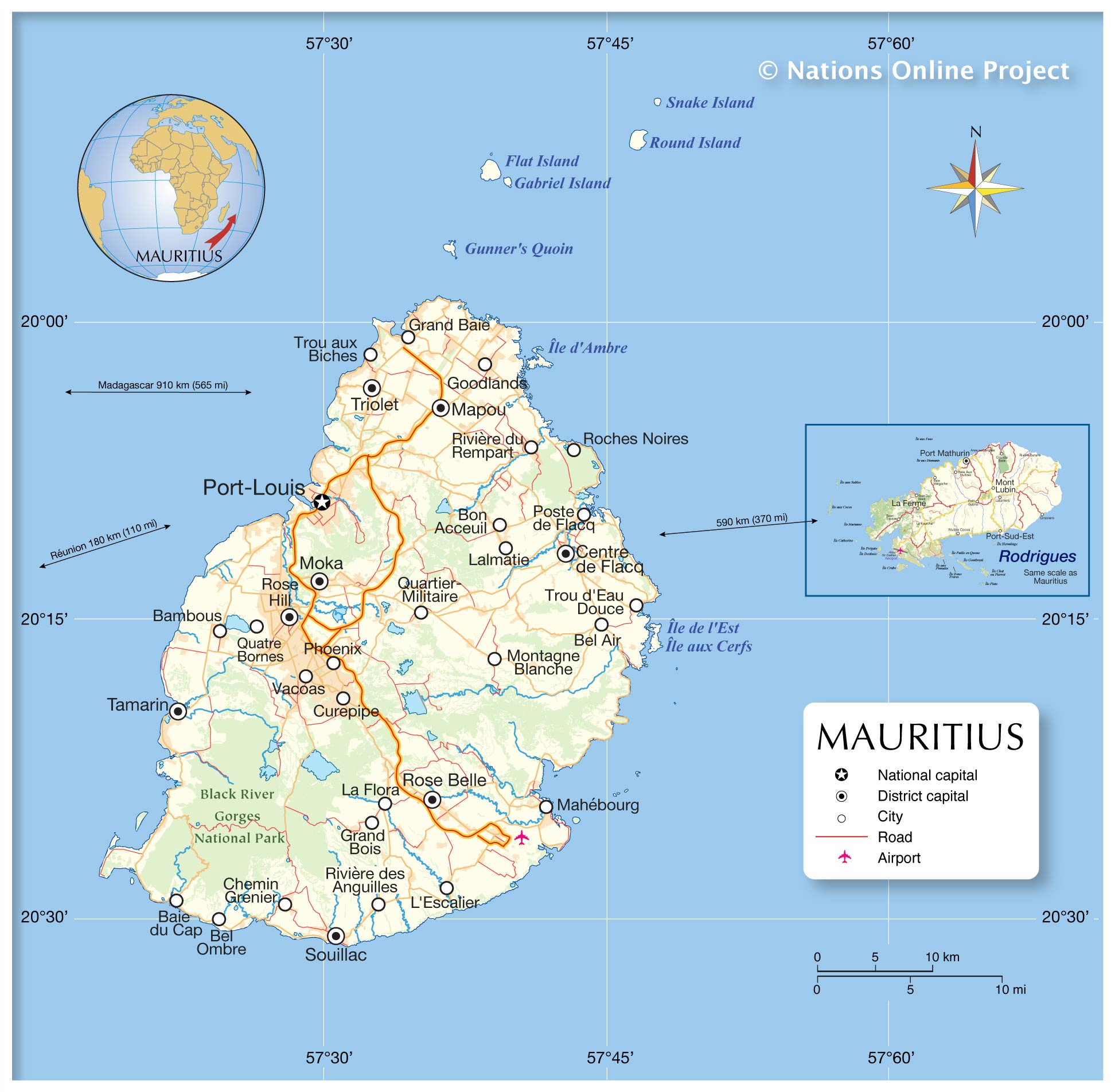
Mauritius, an island nation in the Indian Ocean, holds a significant position geographically and strategically. Its location contributes to its unique biodiversity, economic opportunities, and geopolitical importance. Understanding its precise location requires examining its relationship to larger landmasses and ocean currents.
Geographical Context:
The island of Mauritius, along with Rodrigues, Agaléga, and Saint Brandon, constitutes the Republic of Mauritius. This archipelago lies approximately 2,000 kilometers (1,200 miles) east of Madagascar and 800 kilometers (500 miles) east of the Seychelles. Its position in the southwestern Indian Ocean places it within the tropics, influencing its climate and biodiversity. The island’s proximity to Madagascar and the African continent is significant, impacting trade routes and historical connections. More precisely, Mauritius is located between latitudes 19°50′ and 20°30′ South and longitudes 57°15′ and 57°45′ East. This precise positioning within the southwestern Indian Ocean places it within a region of considerable maritime traffic and ecological significance.
Regional Significance:
Mauritius’s location within the Indian Ocean places it at a crucial juncture of maritime trade routes. Historically, it served as an important port of call for ships traversing the Indian Ocean, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between Africa, Asia, and Europe. This strategic position continues to be relevant in contemporary times, with the island playing a role in regional and international shipping. The country’s well-developed port infrastructure supports significant trade volumes, contributing substantially to its economy. Furthermore, the surrounding waters are rich in marine resources, supporting both fishing industries and tourism.
Ecological Importance:
The island’s isolation and tropical climate have contributed to the development of unique flora and fauna. Many endemic species, found nowhere else on Earth, call Mauritius home. The island’s coral reefs are also exceptionally diverse, contributing to the overall ecological richness of the region. This unique biodiversity is a significant draw for eco-tourism, contributing to the island’s economic development while simultaneously highlighting the importance of conservation efforts. The surrounding waters also form part of a larger marine ecosystem, playing a role in the health of the Indian Ocean as a whole.
Geopolitical Considerations:
Mauritius’s location contributes to its geopolitical significance. The island’s relative isolation, coupled with its economic strength and commitment to international cooperation, has allowed it to develop a substantial role in regional diplomacy and international organizations. Its participation in various international forums reflects its commitment to global issues, including climate change, sustainable development, and maritime security. The island’s strategic location also necessitates ongoing engagement with neighboring countries and international partners to ensure regional stability and economic prosperity.
FAQs:
-
Q: What is the closest continent to Mauritius? A: Africa, specifically Madagascar, is the geographically closest continent.
-
Q: In which hemisphere is Mauritius located? A: Mauritius is located in the Southern Hemisphere.
-
Q: What ocean surrounds Mauritius? A: The Indian Ocean surrounds Mauritius.
-
Q: What is the significance of Mauritius’s location in relation to major shipping lanes? A: Its location places it within key maritime trade routes connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe, making it a significant hub for shipping and commerce.
-
Q: How does Mauritius’s location affect its climate? A: Its tropical location in the Southern Hemisphere results in a warm, tropical climate.
Tips for Locating Mauritius on a World Map:
- Start with Africa: Locate the African continent.
- Focus on Madagascar: Identify Madagascar, the large island off the southeast coast of Africa.
- Look East: Mauritius lies east of Madagascar, approximately 2,000 kilometers away.
- Use Coordinates: The coordinates (19°50’S, 57°30’E) can be used for precise location.
- Utilize Online Mapping Tools: Interactive maps offer the most accurate and detailed visualization.
Conclusion:
Mauritius’s location in the southwestern Indian Ocean is far from arbitrary. Its position has profoundly shaped its natural environment, economic development, and geopolitical role. The island’s unique biodiversity, strategic importance as a maritime hub, and active participation in international affairs all stem directly from its geographic context. Understanding this location provides a crucial framework for appreciating the island nation’s significance on the global stage. Further research into the region’s history, ecology, and economy will further illuminate the multifaceted impact of Mauritius’s geographical situation.

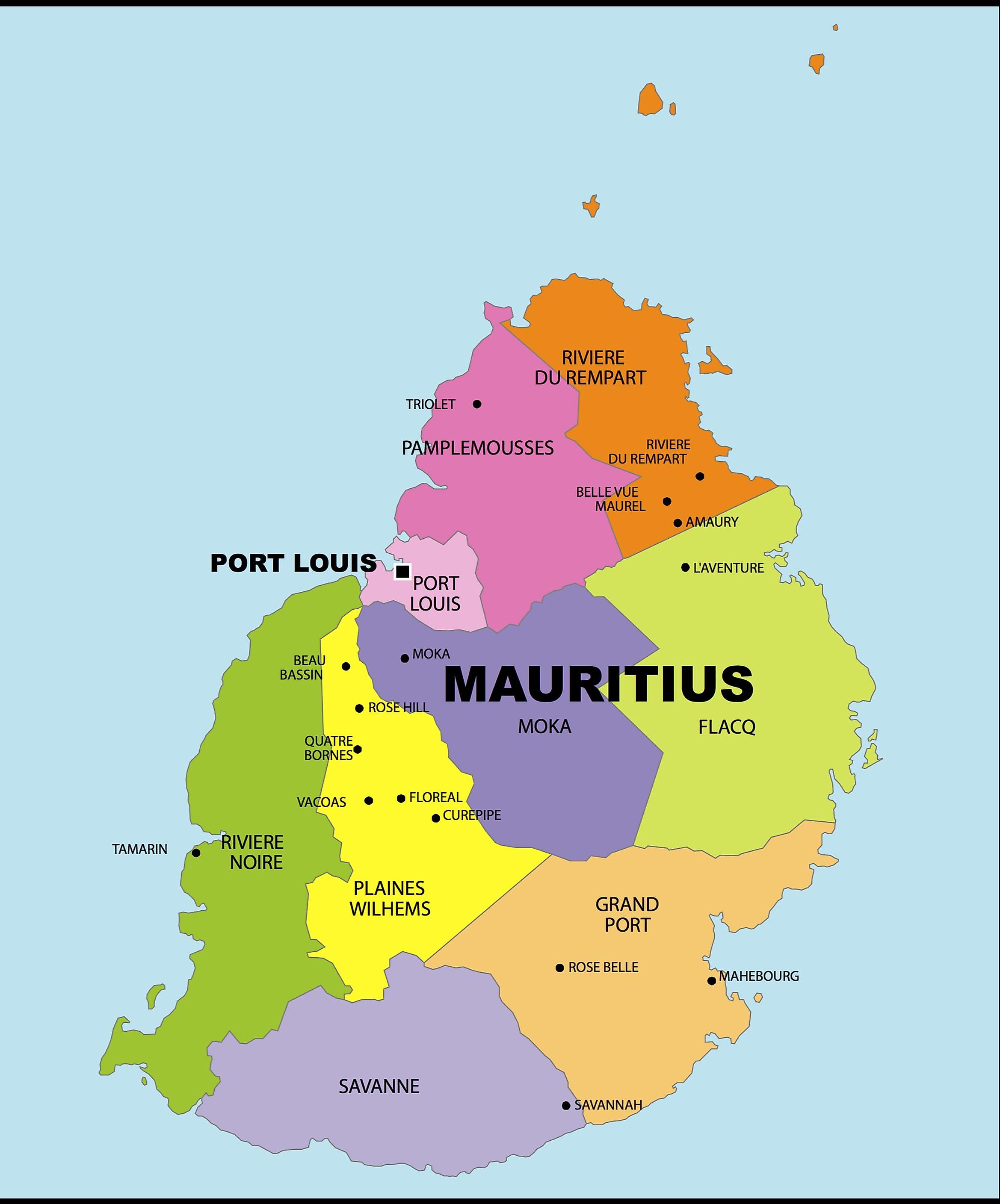


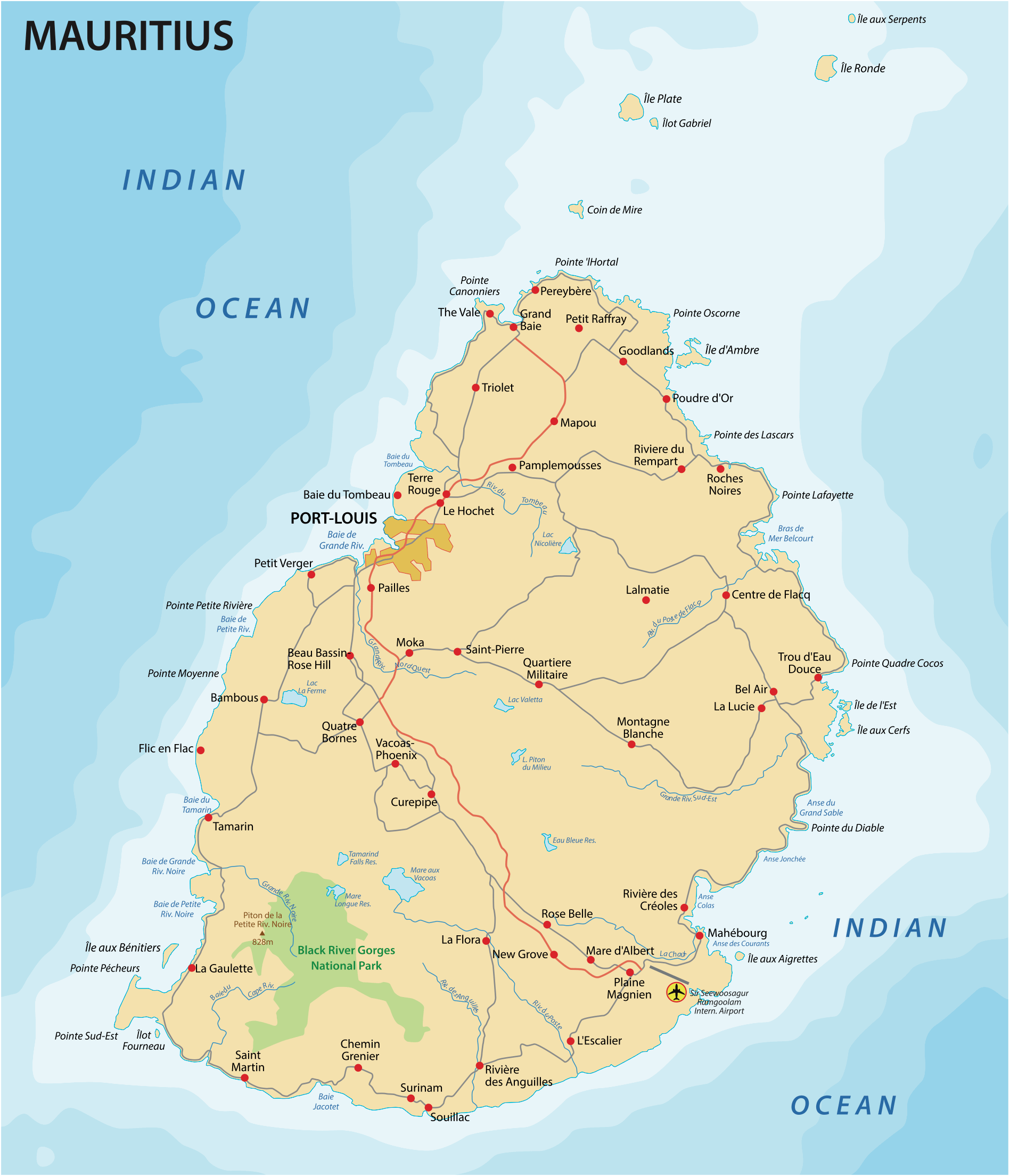

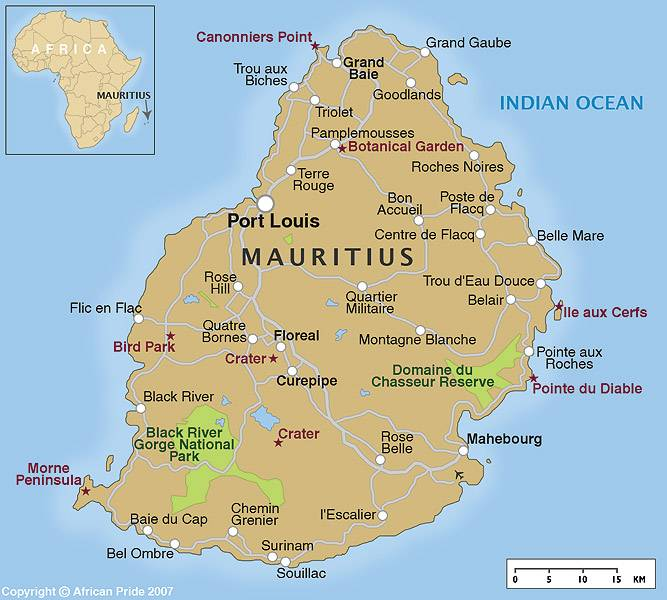

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mauritius: A Geographic and Strategic Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!