Namibia’s Geographic Context within Southern Africa
Related Articles: Namibia’s Geographic Context within Southern Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Namibia’s Geographic Context within Southern Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Namibia’s Geographic Context within Southern Africa

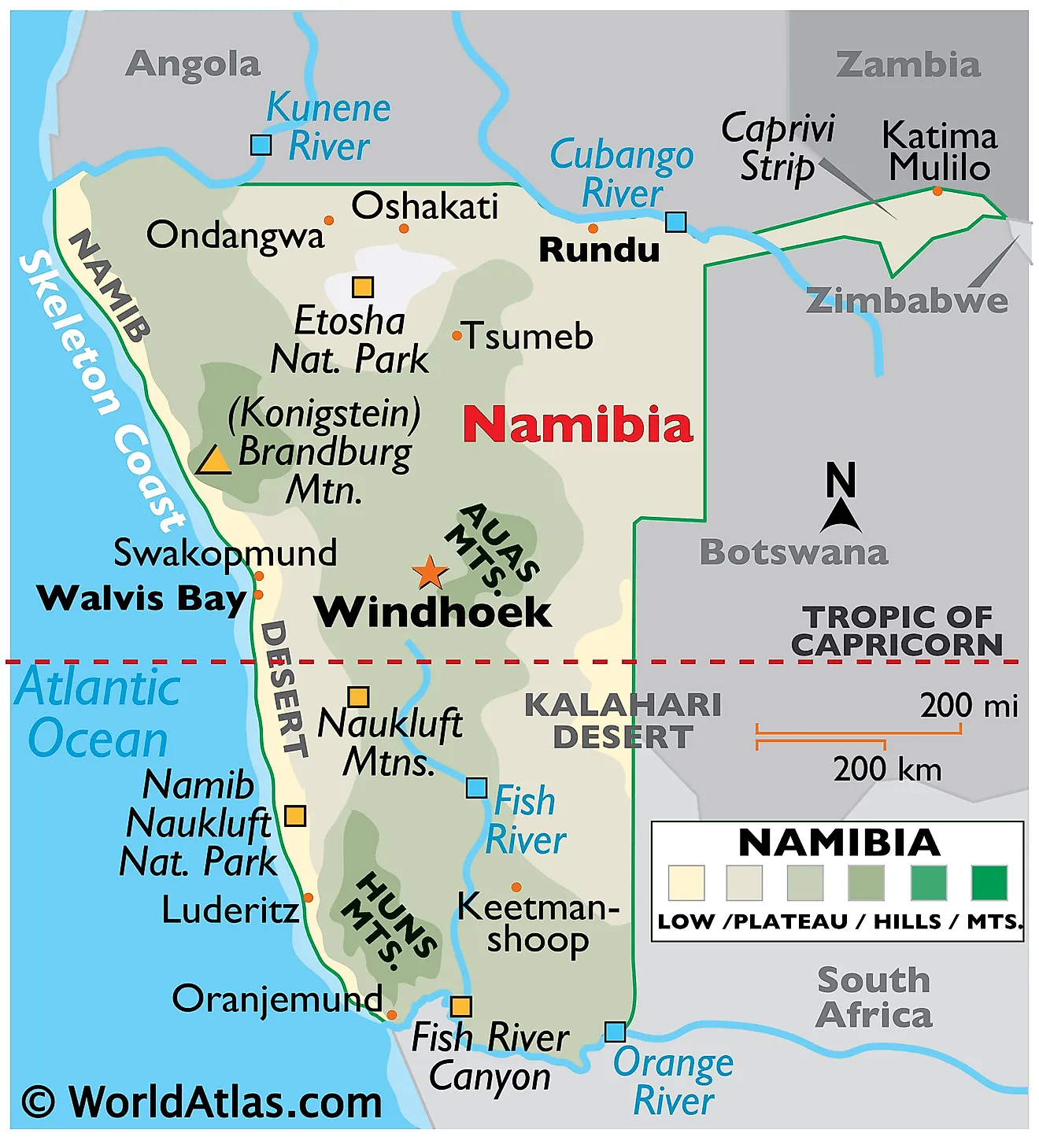
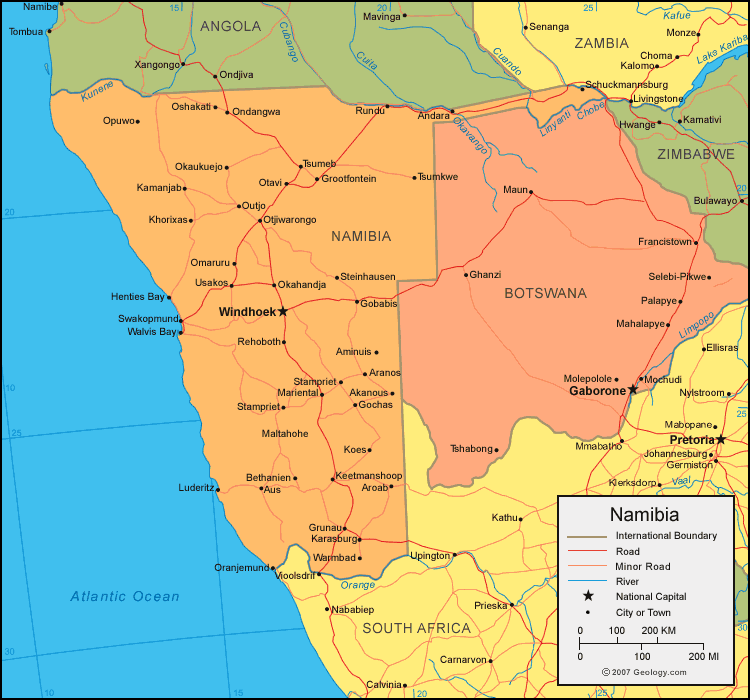
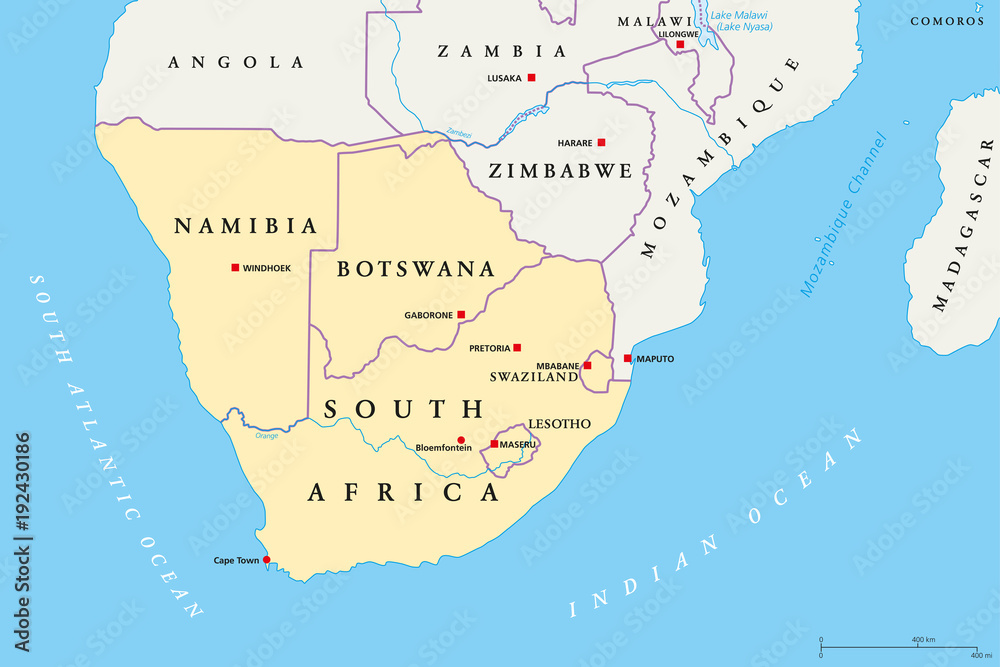
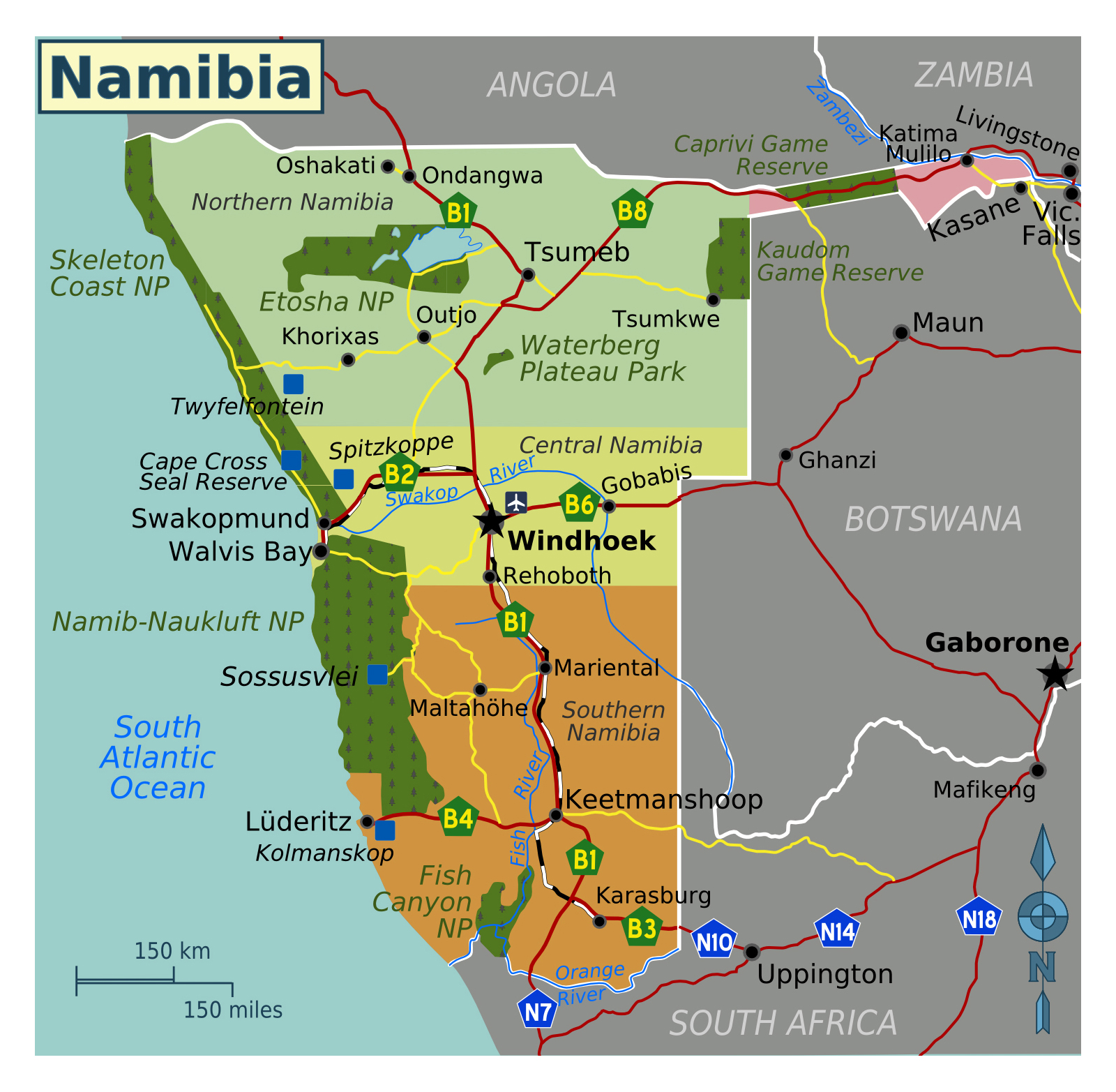
Namibia, a country on the southwestern coast of Africa, occupies a unique geographical position. Its location significantly shapes its climate, biodiversity, and geopolitical relationships. Understanding its spatial context within the broader African landscape requires examination of its borders, topography, and relationship to neighboring states.
Namibia’s borders are relatively straightforward. To the north lies Angola, to the east Botswana and Zambia, and to the south South Africa. The Atlantic Ocean forms its western boundary, a coastline extending approximately 1,570 kilometers. This extensive coastline, characterized by the cold Benguela Current, influences the country’s arid climate and supports unique marine ecosystems. The country’s shape is roughly rectangular, with a relatively narrow coastal strip broadening significantly towards the interior. This inland expansion encompasses diverse landscapes, ranging from the coastal desert to the higher elevations of the central plateau and the northern savannahs.
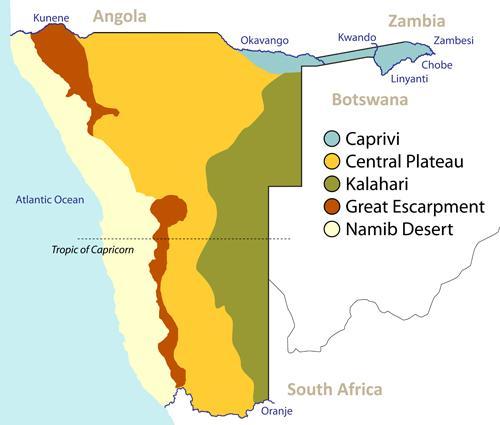
The Namib Desert, a hyper-arid region known for its ancient sand dunes and unique flora and fauna, dominates the western portion. This desert extends inland, gradually transitioning into the Namibian interior. The central plateau, characterized by a more temperate climate, supports a wider range of vegetation and is crucial for agriculture and livestock farming. The northern regions of the country are characterized by savannas, receiving more rainfall and exhibiting greater biodiversity. This variation in topography and climate creates distinct ecological zones, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. The presence of the Orange River in the south also plays a significant role in shaping the landscape and providing a vital water resource.
The country’s geographical features significantly influence its economic activities. The coastal areas, while arid, support fishing industries, while the central plateau is suitable for livestock farming and some agriculture. The northern regions, with their more favorable climate, have greater agricultural potential. However, the aridity of much of the country presents significant challenges for water management and resource allocation. Understanding the spatial distribution of these resources is crucial for sustainable development planning.
The country’s location within Southern Africa also plays a key role in its geopolitical standing. Its proximity to South Africa, a major regional power, has historically influenced its political and economic trajectory. Its shared borders with Angola, Botswana, and Zambia facilitate regional trade and cooperation, although challenges relating to cross-border crime and resource management exist. Namibia’s strategic location along the Atlantic coast also has implications for maritime trade and security.
Understanding the Importance of Cartographic Representation
Accurate and detailed maps are indispensable tools for understanding Namibia’s geography. These maps provide a visual representation of the country’s physical features, its political boundaries, and the distribution of its resources. They facilitate effective planning for infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental conservation. Furthermore, detailed cartographic representations are crucial for disaster response and mitigation efforts, assisting in the identification of vulnerable areas and the efficient allocation of resources during emergencies. The use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology enhances the capabilities of these maps, allowing for sophisticated spatial analysis and modeling.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the total land area of Namibia? Namibia covers approximately 825,615 square kilometers.
-
What are the major geographical features of Namibia? The major features include the Namib Desert, the central plateau, and the northern savannas. The Orange River also represents a significant geographical feature.
-
What is the climate like in Namibia? Namibia has a predominantly arid climate, with significant variations across different regions. The coastal regions are influenced by the cold Benguela Current, while the interior experiences greater temperature fluctuations.
-
What are the major economic activities in Namibia? The economy relies on mining, fishing, tourism, and agriculture, although the latter is constrained by the arid climate.
-
What are the major challenges facing Namibia’s geography? Desertification, water scarcity, and the impacts of climate change pose significant challenges.
Tips for Utilizing Maps of Namibia
-
Select appropriate map scales: Different scales are appropriate for different purposes. Large-scale maps are suitable for detailed local planning, while small-scale maps are better for regional overviews.
-
Identify key features: Focus on understanding the location and significance of major geographical features, such as rivers, mountains, and deserts.
-
Consider thematic maps: Thematic maps highlighting specific aspects, such as population density, rainfall patterns, or mineral resources, provide valuable insights.
-
Utilize online mapping tools: Interactive online maps offer dynamic visualization and data analysis capabilities.
-
Cross-reference with other data sources: Combine map data with other sources, such as statistical reports and satellite imagery, for a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
Namibia’s geographical location and its diverse landscape are integral to its identity and development trajectory. The aridity of much of the country presents significant challenges, requiring careful planning and resource management. However, the country’s varied geography also presents opportunities, particularly in tourism and resource extraction. Accurate and detailed cartographic representations are vital tools for understanding and managing the complexities of Namibia’s physical environment, facilitating sustainable development and ensuring the country’s future prosperity. The effective use of maps, combined with other data sources, is crucial for informed decision-making across various sectors.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Namibia’s Geographic Context within Southern Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!