Navigating Europe’s Diverse Climates: A Comprehensive Overview of Weather Patterns Across the Continent
Related Articles: Navigating Europe’s Diverse Climates: A Comprehensive Overview of Weather Patterns Across the Continent
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Europe’s Diverse Climates: A Comprehensive Overview of Weather Patterns Across the Continent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Europe’s Diverse Climates: A Comprehensive Overview of Weather Patterns Across the Continent

Europe’s geographical diversity translates into a complex and varied tapestry of weather patterns. Understanding these patterns is crucial for numerous sectors, from agriculture and tourism to transportation and energy production. This analysis explores the key climatic influences shaping weather across the continent, examining regional variations and highlighting the significance of accurate weather forecasting.
Major Climatic Influences:
Several significant factors contribute to the continent’s diverse weather systems. The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), a climate pattern characterized by fluctuating atmospheric pressure differences between the Azores high and the Icelandic low, exerts a profound influence. A positive NAO generally brings milder, wetter conditions to northern Europe and drier conditions to southern Europe. Conversely, a negative NAO can lead to colder, drier weather in the north and wetter weather in the south.
The location of the jet stream, a fast-flowing, narrow air current in the upper atmosphere, significantly impacts weather systems. Its position and strength influence the movement of weather fronts, determining the frequency and intensity of storms, rainfall, and temperature fluctuations across the continent. A northward shift of the jet stream tends to bring colder air southward, while a southward shift can lead to milder conditions in northern latitudes.
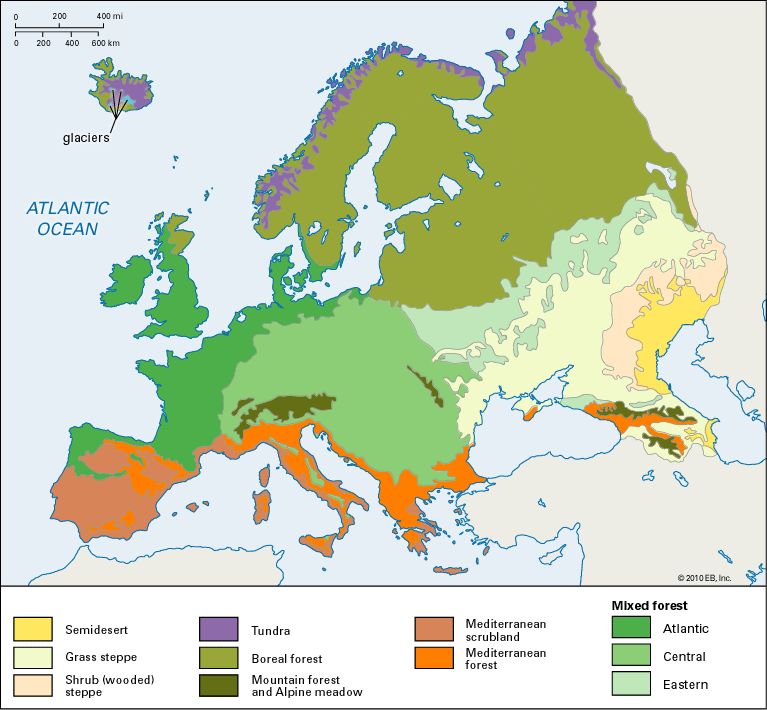
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining temperature variations. Southern Europe experiences a Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Northern Europe, by contrast, experiences a more temperate climate, with cooler summers and colder, often snowy winters. The influence of large bodies of water, such as the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, is also substantial. Ocean currents, like the Gulf Stream, moderate temperatures, particularly along western European coastlines, resulting in milder winters than would otherwise be expected at those latitudes. The proximity to these bodies of water also affects precipitation patterns, leading to higher rainfall in coastal regions.
Elevation further complicates the weather picture. Mountain ranges, such as the Alps and the Pyrenees, act as significant barriers, influencing precipitation and temperature gradients. Orographic rainfall, caused by air rising and cooling as it passes over mountains, results in higher precipitation on windward slopes and drier conditions on leeward slopes (rain shadow effect). Higher altitudes generally experience lower temperatures, even in relatively low latitudes.
Regional Weather Variations:
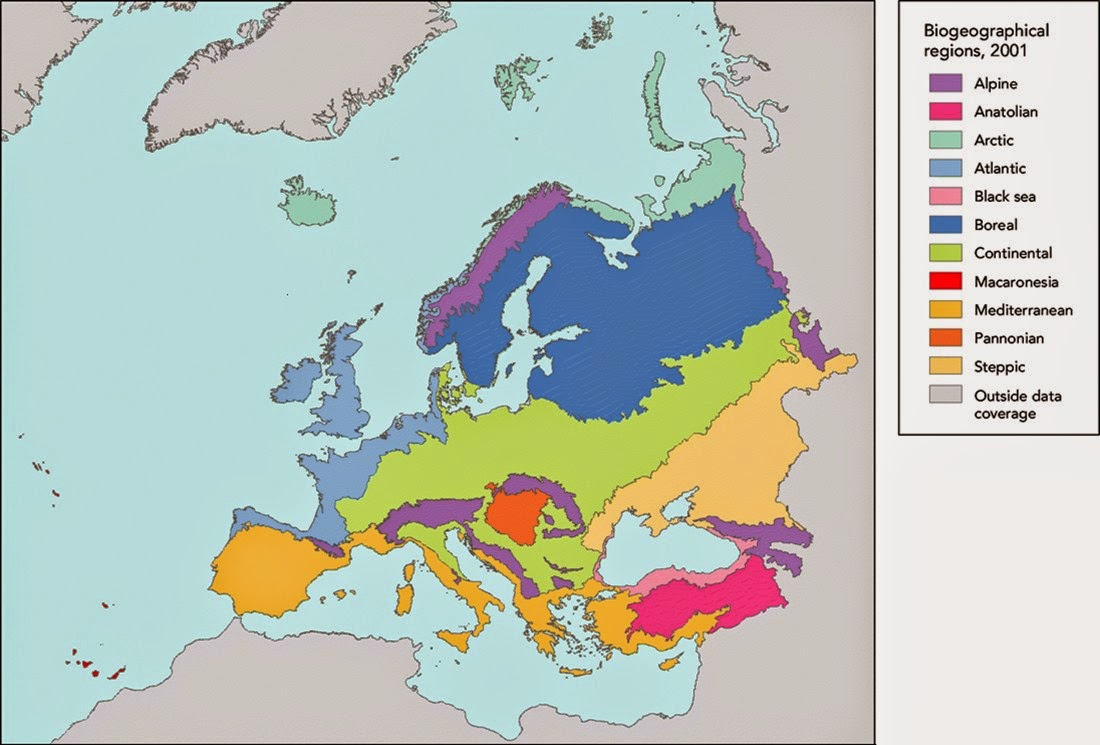
The intricate interplay of these factors produces distinct regional weather characteristics. Western Europe, influenced by the Gulf Stream and the prevailing westerly winds, generally enjoys a milder, wetter climate than eastern Europe, which experiences a more continental climate with greater temperature extremes and lower precipitation. Scandinavia experiences long, cold winters and short, cool summers, while the Mediterranean region enjoys warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Central Europe exhibits a transitional climate, with characteristics blending those of western and eastern Europe.
The Importance of Accurate Forecasting:
Accurate weather forecasting is paramount for various sectors across Europe. Agriculture relies heavily on weather predictions for optimal planting and harvesting times, pest control, and irrigation management. The tourism industry utilizes weather forecasts to help travelers plan their activities and minimize disruptions. Transportation systems depend on accurate weather information to ensure safety and efficiency, particularly in aviation and maritime sectors. The energy sector, especially renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, requires precise forecasts to optimize energy production and distribution. Furthermore, accurate weather prediction plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response, enabling timely warnings and effective mitigation strategies for extreme weather events such as floods, heatwaves, and storms.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: How accurate are European weather forecasts? A: The accuracy of weather forecasts varies depending on the forecast timeframe and the specific location. Generally, short-range forecasts (1-3 days) are highly accurate, while long-range forecasts (beyond 7 days) become progressively less precise. Advances in meteorological technology and modeling continually improve forecast accuracy.
-
Q: What are the most common weather hazards in Europe? A: Europe experiences a range of weather hazards, including floods, heatwaves, droughts, storms, and blizzards. The specific hazards vary geographically and seasonally.
-
Q: How does climate change affect European weather patterns? A: Climate change is already impacting European weather patterns, leading to more frequent and intense heatwaves, changes in precipitation patterns (including more intense rainfall and increased drought risk), and a greater frequency of extreme weather events.
-
Q: Where can reliable weather information for Europe be found? A: Reliable weather information can be obtained from national meteorological services across Europe, as well as from reputable international organizations such as the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
Tips for Utilizing Weather Information:
- Regularly consult reliable weather sources for up-to-date information.
- Pay attention to weather warnings and advisories issued by official agencies.
- Plan activities considering the forecast, particularly when engaging in outdoor pursuits.
- Prepare for potential weather hazards by having appropriate clothing and equipment.
- Stay informed about long-range weather trends to anticipate potential impacts on various sectors.
Conclusion:
Understanding the diverse weather patterns across Europe requires considering the complex interplay of geographical, atmospheric, and oceanic influences. Accurate weather forecasting is crucial for numerous sectors, enabling effective planning, risk management, and ultimately, contributing to societal well-being and economic prosperity. Continued investment in meteorological research and technology will be essential to enhancing forecast accuracy and improving preparedness for the increasingly variable weather conditions anticipated in the future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Europe’s Diverse Climates: A Comprehensive Overview of Weather Patterns Across the Continent. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!