Navigating North Carolina: A Regional Geographic Overview
Related Articles: Navigating North Carolina: A Regional Geographic Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating North Carolina: A Regional Geographic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating North Carolina: A Regional Geographic Overview
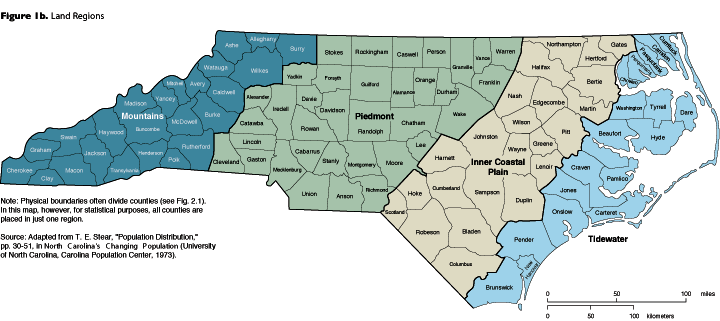
North Carolina’s diverse geography and history have led to the development of distinct regional identities. Understanding these regions requires a spatial understanding, often facilitated by cartographic representation. Such representations highlight not only the physical boundaries but also the cultural, economic, and political nuances that define each area. This analysis explores these regional divisions, examining their characteristics and the value of their geographic delineation.
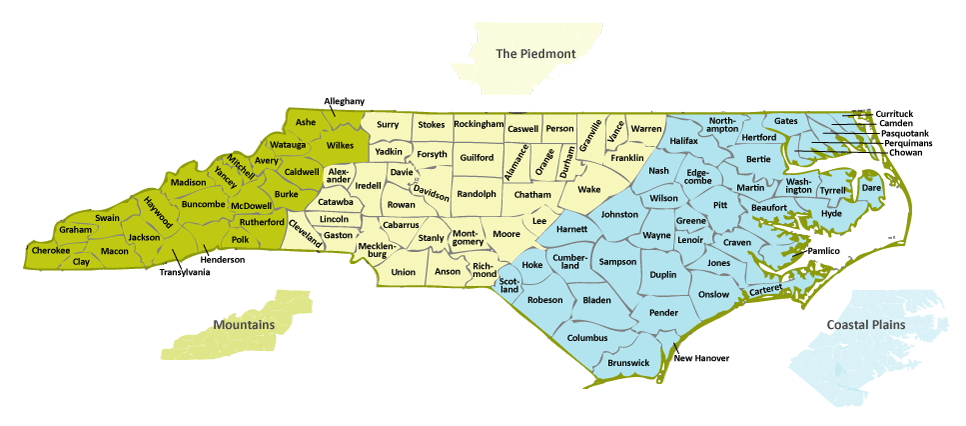
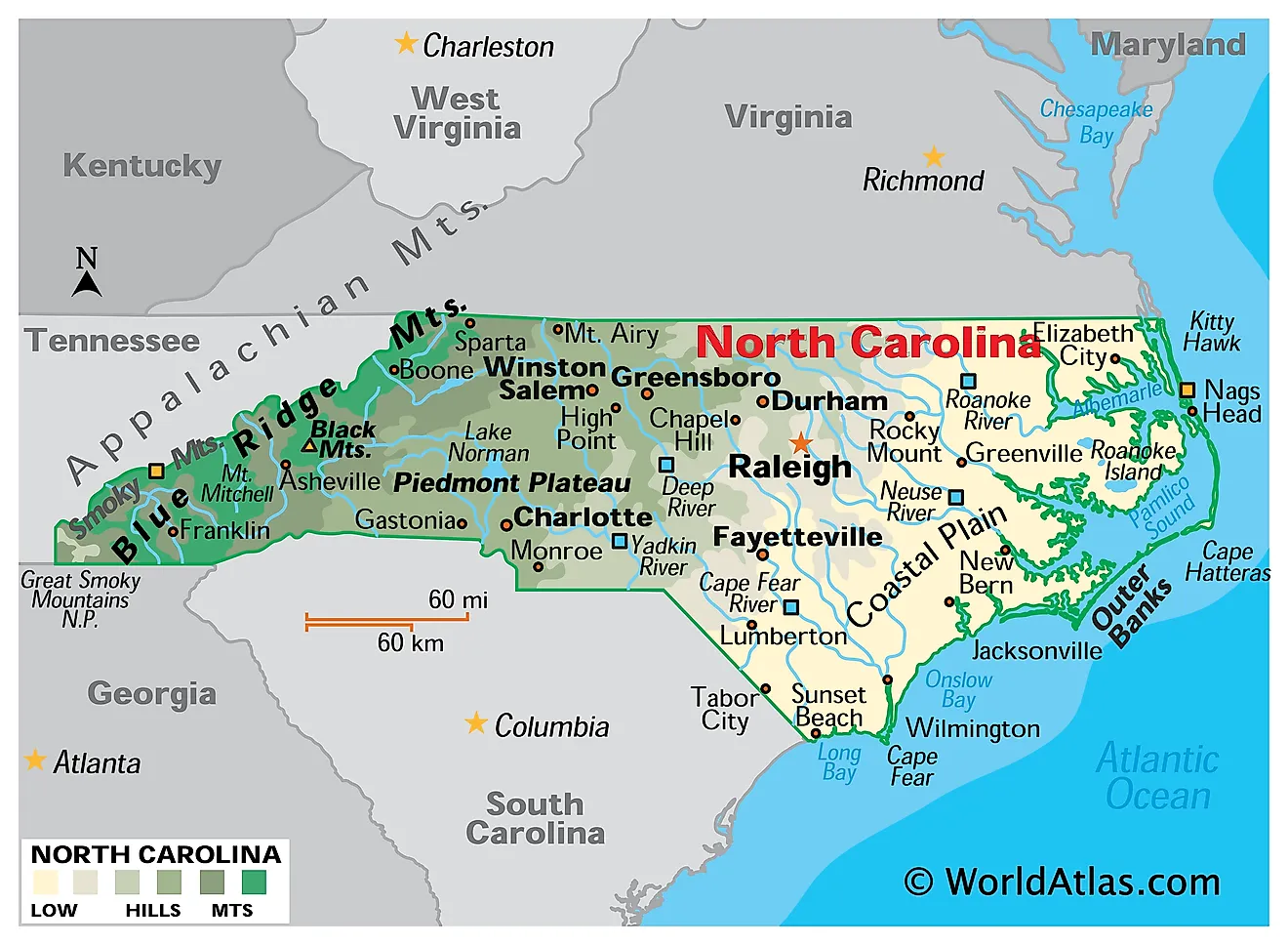
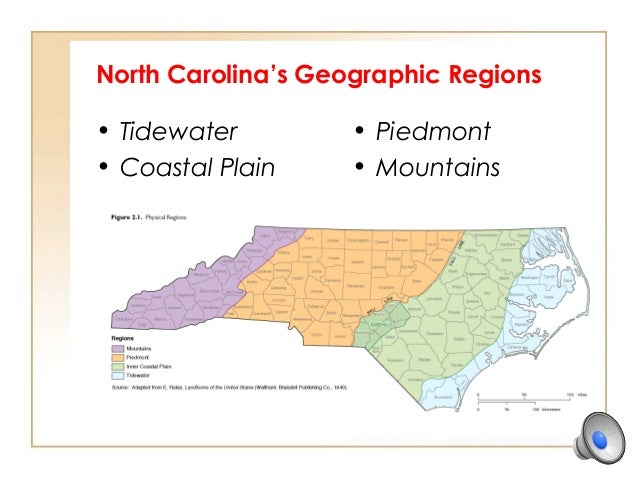
Several methods exist for dividing North Carolina into regions, each with its own merits and limitations. Some common approaches utilize physiographic features, such as the Coastal Plain, Piedmont, and Mountains. This division reflects the significant geological differences across the state, impacting agriculture, settlement patterns, and infrastructure development. The Coastal Plain, a low-lying area extending from the Atlantic coast westward, features fertile soils suitable for agriculture, particularly tobacco and cotton historically, and now a variety of crops and aquaculture. The Piedmont, a rolling upland region, boasts a more varied topography and historically supported a diverse range of industries, including textiles and furniture manufacturing. Finally, the mountainous west is characterized by rugged terrain, impacting transportation and economic activity, but also offering opportunities in tourism and forestry.
Other regional classifications consider cultural and historical factors. For example, one might distinguish between the eastern, central, and western parts of the state, reflecting differences in population density, political affiliation, and cultural traditions. The eastern region, heavily influenced by its coastal location, maintains a strong connection to maritime industries and a distinct cultural heritage. The central region, encompassing much of the Piedmont, represents a more diverse economic base and a blend of urban and rural communities. The western region, encompassing the Appalachian Mountains, is characterized by a strong sense of community, a focus on outdoor recreation, and a history rooted in Appalachian culture.
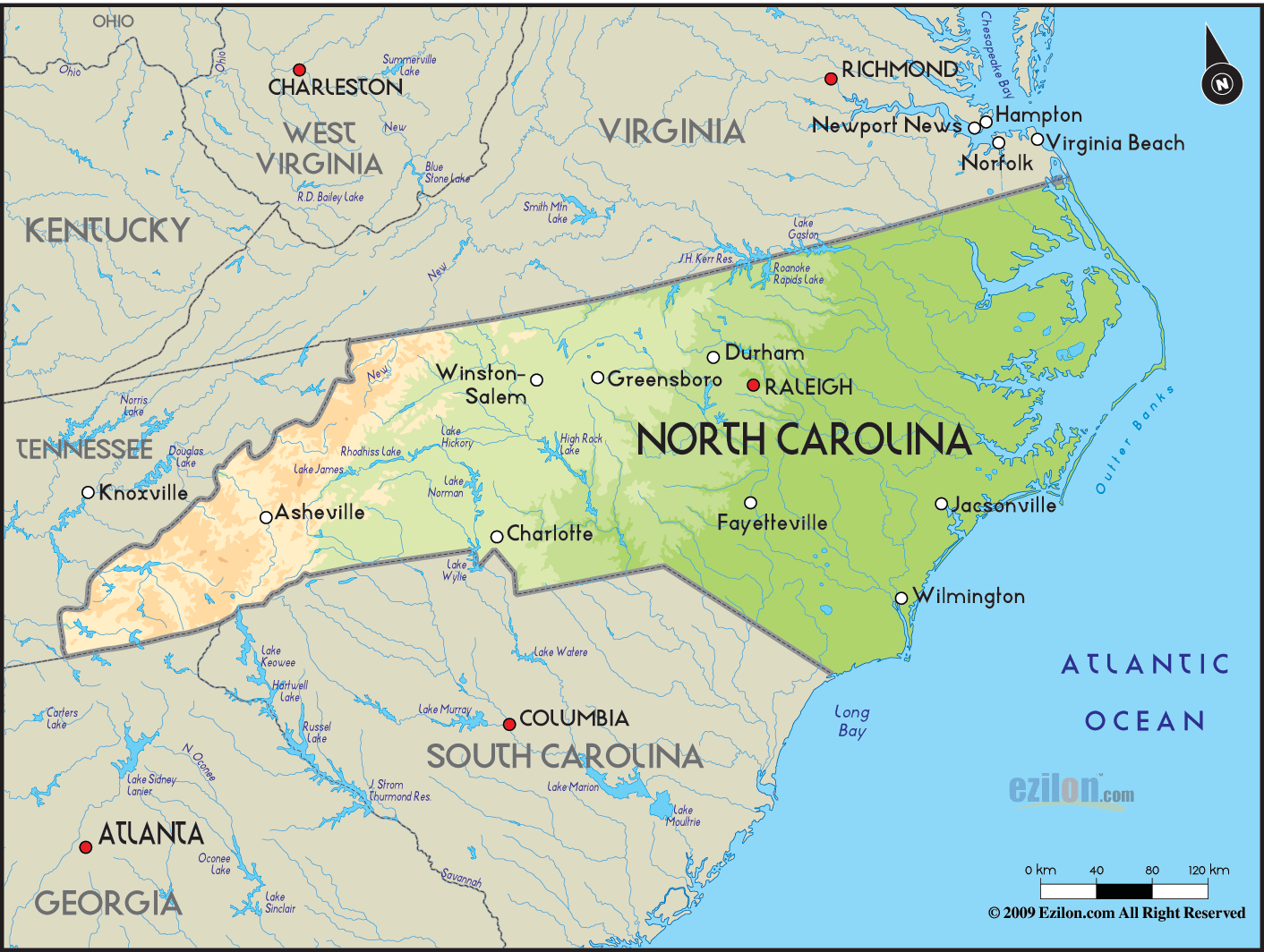
Still other approaches incorporate economic factors. For instance, regions might be defined based on metropolitan areas, reflecting the concentration of economic activity and population around major urban centers like Charlotte, Raleigh-Durham, and Greensboro. This approach highlights the importance of these urban areas as engines of economic growth and centers of innovation. Conversely, a focus on rural areas might illuminate the challenges faced by communities with limited access to resources and opportunities. This approach helps to understand the disparities in economic development across the state.
The representation of these regions on a map offers several significant advantages. First, it provides a visual summary of the state’s geographic complexity, allowing for quick comprehension of the spatial distribution of various characteristics. Secondly, such a representation facilitates comparative analysis, enabling researchers and policymakers to identify regional disparities in areas such as income, education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Thirdly, a well-designed map can serve as a powerful communication tool, enabling effective dissemination of information to the public and stakeholders.
For example, a map highlighting regional variations in economic activity can inform economic development strategies, allowing for targeted investments and interventions. Similarly, a map illustrating disparities in healthcare access can guide the allocation of resources to improve health outcomes across the state. Maps depicting population density can inform decisions related to infrastructure development, ensuring adequate provision of services to all communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the most commonly used methods for defining North Carolina’s regions? The most common methods rely on physiographic features (Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Mountains), broad geographic divisions (East, Central, West), and metropolitan areas. Each offers a different perspective on the state’s regional diversity.
-
How do these regional divisions impact policymaking? Understanding regional differences is crucial for effective policymaking. Policies need to be tailored to address specific regional needs and challenges, considering factors such as economic conditions, infrastructure, and access to services.
-
What are some limitations of using regional divisions? Regional divisions are inherently simplifications of a complex reality. Boundaries between regions are often not sharply defined, and the characteristics of a region can vary within its boundaries. Furthermore, the chosen method of division influences the results, highlighting the need for multiple perspectives.
-
How can access to regional maps be improved? Increased access to high-quality, easily interpretable maps, through online platforms and public institutions, is crucial. This requires investment in geographic information systems (GIS) and data visualization techniques.
Tips for Utilizing Regional Maps of North Carolina
-
Consider the purpose: The choice of map should align with the specific research question or policy challenge being addressed. Different mapping techniques highlight different aspects of regional variation.
-
Examine the data source: The reliability of the map depends on the quality and accuracy of the underlying data. Understanding the data source is essential for proper interpretation.
-
Pay attention to scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail visible. Maps at different scales can provide different insights into regional variations.
-
Integrate multiple data layers: Combining multiple data layers, such as population density, income levels, and infrastructure, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of regional characteristics.
Conclusion
Regional divisions provide a valuable framework for understanding the complex geographic, economic, and cultural landscape of North Carolina. Utilizing cartographic representations of these regions allows for a more nuanced and informed approach to research, policymaking, and public discourse. The continued development and accessibility of high-quality regional maps are essential for promoting effective governance and equitable resource allocation across the state. Further research into the evolving nature of these regions and their interactions is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities facing North Carolina in the future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating North Carolina: A Regional Geographic Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!