Navigating the Architectural Marvel: A Comprehensive Guide to the Taj Mahal’s Spatial Layout
Related Articles: Navigating the Architectural Marvel: A Comprehensive Guide to the Taj Mahal’s Spatial Layout
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Architectural Marvel: A Comprehensive Guide to the Taj Mahal’s Spatial Layout. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Architectural Marvel: A Comprehensive Guide to the Taj Mahal’s Spatial Layout

The Taj Mahal, an iconic monument of Mughal architecture, transcends its aesthetic beauty to represent a sophisticated understanding of spatial planning and design. Understanding its layout, through various cartographic representations, provides invaluable insight into the monument’s historical significance, architectural intricacies, and the cultural context of its creation. This analysis explores the information conveyed through different types of visual representations of the complex, highlighting its importance for both scholarly research and visitor experience.
Spatial Organization and Key Features:
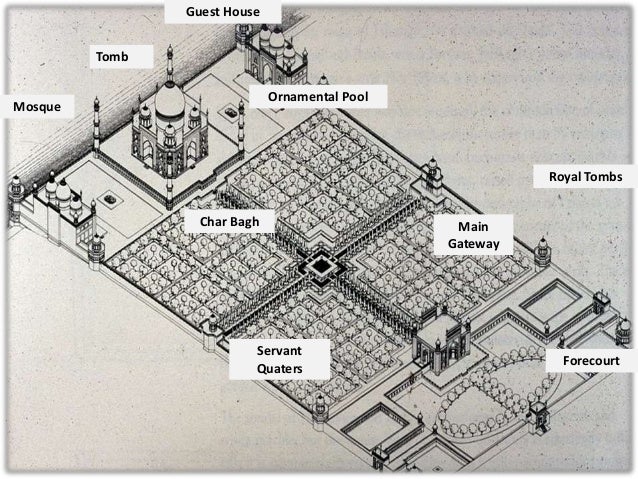
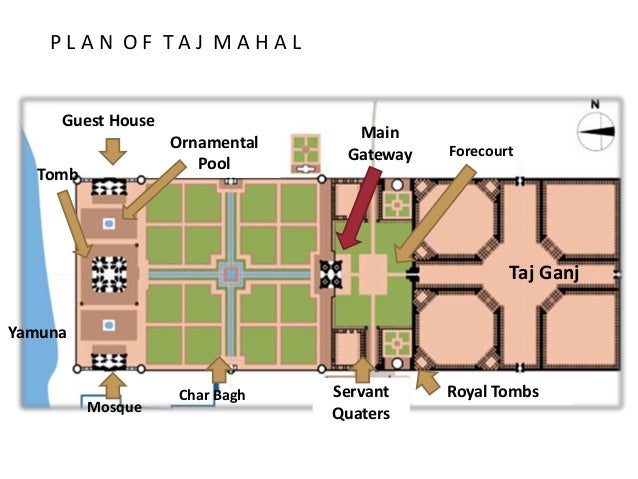
A detailed plan of the Taj Mahal complex reveals a meticulously organized arrangement of structures, gardens, and water features. The central axis, a defining characteristic of Mughal architecture, runs from the main gateway (the Darwaza) through the mosque, the Taj Mahal itself, and finally to the Yamuna River. This axial symmetry reflects a deep-seated cosmological belief system, emphasizing balance and harmony.
The main mausoleum, the Taj Mahal, stands as the focal point, its precise placement emphasizing its centrality within the entire composition. Surrounding the mausoleum are various structures, each serving a distinct purpose. The mosque, located on the west side, is a mirror image of a similar structure on the east, although the latter is now a guest house. These symmetrical elements underscore the planned and deliberate nature of the design.
The charbagh, or four-part garden, situated between the mausoleum and the main gateway, is an integral component. The garden’s layout, divided by pathways and water channels into four quadrants, symbolizes paradise in Persian garden design. This further reinforces the symbolic significance of the complex as a representation of earthly paradise. Detailed plans illustrate the precise dimensions of the garden, the placement of the water channels and fountains, and the arrangement of trees and flowerbeds.
Beyond the immediate vicinity of the mausoleum, the complex extends to include other structures, such as the main gateway, servants’ quarters, and other ancillary buildings. These elements, though less prominent, contribute to the overall functionality and aesthetic coherence of the complex. Detailed maps delineate the boundaries of the complex and show the relationship between these various structures.
The Value of Different Map Types:
Different types of cartographic representations serve distinct purposes in understanding the Taj Mahal’s layout. A simple site plan provides a general overview of the complex’s major structures and their relative positions. However, more detailed architectural drawings reveal the intricate details of individual buildings, including their dimensions, internal layouts, and decorative features.
Three-dimensional models, either physical or digital, offer a more immersive understanding of the spatial relationships between different elements. These models allow for a better visualization of the monument’s scale and its integration within its surroundings. Furthermore, historical maps, if available, can illustrate changes in the complex over time, providing valuable insights into its evolution and preservation.
Benefits of Cartographic Representation:
The use of various cartographic representations offers numerous benefits for scholars, architects, and visitors alike. For researchers, these tools provide crucial information for studying the monument’s architectural features, historical context, and cultural significance. Detailed plans facilitate the analysis of design principles, construction techniques, and the use of materials.
For architects and designers, the Taj Mahal’s layout serves as a valuable case study in spatial planning and design. The principles of symmetry, axial organization, and the integration of buildings and landscape offer lessons in creating harmonious and aesthetically pleasing environments.
For visitors, maps and plans enhance the experience by providing a framework for understanding the complex’s layout and the significance of its various components. Such information allows for a more informed and enriching visit, transforming a simple sightseeing trip into a journey of architectural and historical discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What is the overall size of the Taj Mahal complex? A: The complex covers a significant area, encompassing the mausoleum, gardens, mosque, guest house, and other structures. Precise dimensions vary depending on the boundaries included.
-
Q: What materials were used in the construction of the Taj Mahal? A: White marble was the primary material, supplemented by precious and semi-precious stones for intricate inlay work. Other materials included sandstone and mortar.
-
Q: How accurate are historical maps of the Taj Mahal complex? A: The accuracy of historical maps varies depending on the age and methodology of their creation. Modern surveys and digital mapping techniques provide more precise and detailed representations.
-
Q: Are there interactive maps available online? A: Yes, several websites and digital platforms offer interactive maps and virtual tours of the Taj Mahal complex, allowing for exploration from the convenience of a computer or mobile device.
-
Q: Can maps show the evolution of the complex over time? A: While detailed historical maps might be limited, comparative analysis of different maps across time can illustrate changes in the complex, perhaps due to renovations, extensions, or damage.
Tips for Utilizing Maps of the Taj Mahal:
- Consult multiple map types for a comprehensive understanding.
- Compare different maps to identify discrepancies and potential inaccuracies.
- Use maps in conjunction with other sources of information, such as historical accounts and architectural drawings.
- Consider the scale and projection of the map when interpreting distances and proportions.
- Utilize interactive maps and virtual tours to enhance the learning experience.
Conclusion:
The Taj Mahal’s spatial layout, as revealed through various cartographic representations, is a testament to the ingenuity and sophistication of Mughal architecture and planning. These visual aids are not merely tools for navigation but rather essential resources for understanding the monument’s historical context, architectural design, and symbolic meaning. The continued development and accessibility of these resources are crucial for scholarly research, architectural study, and the appreciation of this globally significant landmark. Through a deeper understanding of its spatial organization, the Taj Mahal’s enduring appeal and profound cultural significance become even more apparent.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Architectural Marvel: A Comprehensive Guide to the Taj Mahal’s Spatial Layout. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!