Navigating the Boston Green Line: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Boston Green Line: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Boston Green Line: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Boston Green Line: A Comprehensive Guide

The Boston Green Line, a vital component of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) rapid transit system, serves as a crucial artery for commuters and visitors navigating the city and its surrounding areas. Understanding its layout, branching routes, and operational nuances is essential for efficient travel within Greater Boston. This article provides a detailed examination of the Green Line’s network, highlighting its significance in the region’s transportation infrastructure.
The Green Line’s Geographic Reach and Branches:
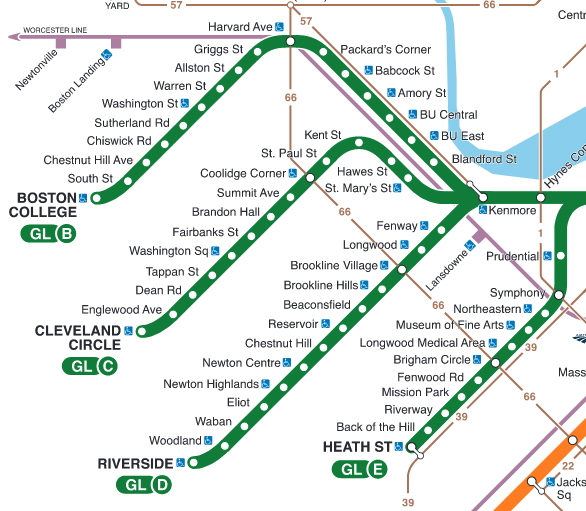
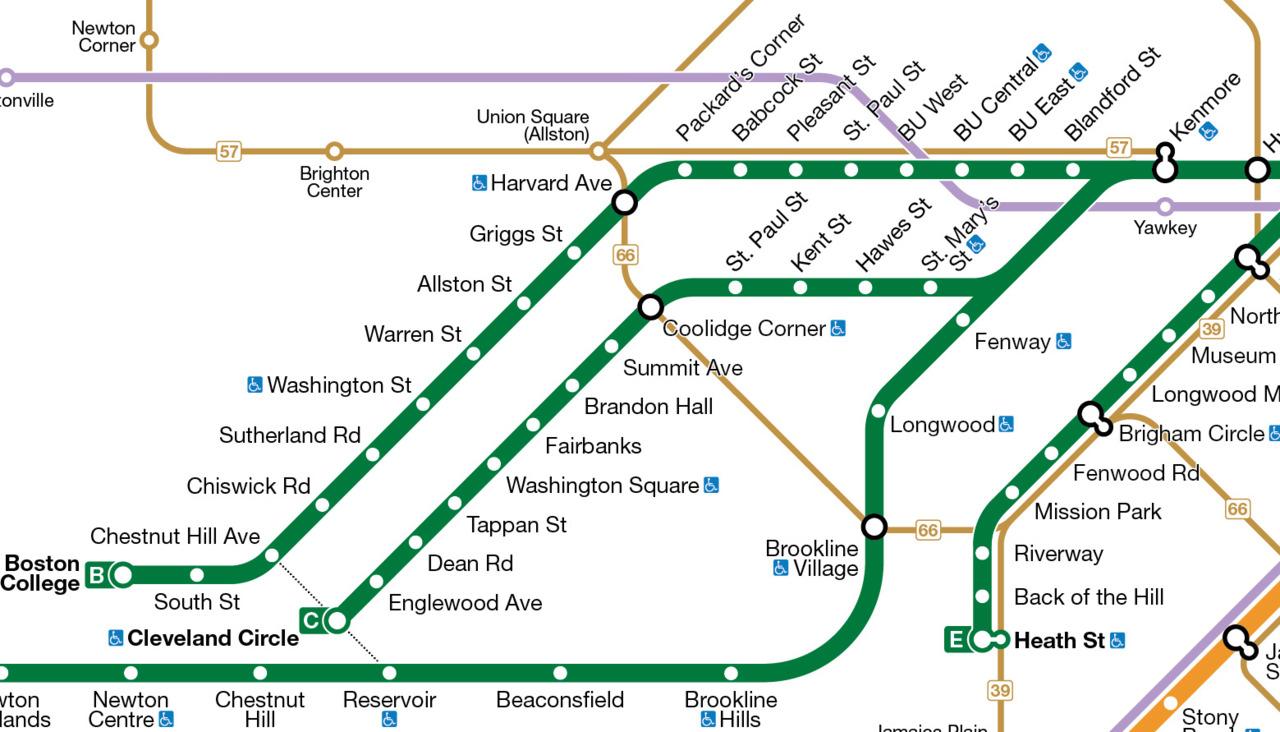
The Green Line’s distinctive characteristic is its branching structure. Unlike many other subway systems with predominantly linear routes, the Green Line comprises three distinct branches: the B, C, and D branches. Each branch serves a unique geographic area, offering access to diverse neighborhoods and points of interest.
The B branch, running largely underground, connects Boston College in Newton with Government Center in downtown Boston. This branch serves several key neighborhoods, including Kenmore Square, Fenway, and Back Bay, providing convenient access to Fenway Park, Boston University, and numerous cultural institutions.
The C branch, also largely subterranean, follows a similar path to the B branch until Kenmore Square, where it diverges, traveling above ground through Brookline and ending at Cleveland Circle. This branch provides access to residential areas in Brookline and offers a scenic above-ground route through the city’s western suburbs.
The D branch, initially sharing track with the C branch, separates near Kenmore Square, traveling above ground through the Fenway-Kenmore area before transitioning underground, ultimately terminating at Government Center. This branch provides an alternative route to downtown Boston from the western suburbs, offering a different perspective on the city’s landscape compared to the B and C branches.
Understanding the Map’s Key Features:
Effective navigation relies on understanding the map’s visual cues. The color-coding (green) immediately identifies the Green Line. Stations are clearly marked, with their names displayed prominently. Transfer points to other MBTA lines, such as the Red Line or Orange Line, are indicated, facilitating seamless travel between different modes of transportation. The map usually distinguishes between underground and above-ground sections, allowing users to anticipate the type of travel experience. Detailed maps often include information on accessibility features at each station, such as elevator access for individuals with mobility challenges. Furthermore, the map often integrates surrounding geographical landmarks, helping users contextualize their location and plan their journey effectively.
The Green Line’s Significance in the Boston Transportation Ecosystem:
The Green Line’s importance extends beyond simply connecting points A and B. It plays a crucial role in relieving traffic congestion, providing a viable alternative to driving, particularly during peak hours. This contributes to reduced carbon emissions and improved air quality within the city. Its accessibility to various residential areas, educational institutions, and employment centers makes it a vital component of the daily commute for a substantial portion of the Greater Boston population. Furthermore, the Green Line’s extensive network supports the city’s thriving tourism industry, providing convenient access to major attractions and facilitating exploration of diverse neighborhoods. The system’s accessibility also benefits residents and visitors with mobility challenges, promoting inclusivity and accessibility in urban transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What are the operating hours of the Green Line? A: The Green Line operates on a schedule that generally extends from early morning until late evening, with variations on weekends and holidays. Specific schedules are available on the MBTA website.
-
Q: How can I purchase a ticket for the Green Line? A: Various fare options are available, including CharlieCards, CharlieTickets, and mobile payment systems. Information on fare purchasing and payment methods is accessible on the MBTA website.
-
Q: Are there accessibility features on the Green Line? A: Many stations offer accessibility features, such as elevators and ramps. However, accessibility varies across stations, and it’s advisable to check the MBTA website for specific details on individual stations.
-
Q: How frequent is the service on the Green Line? A: Service frequency varies depending on the time of day and the specific branch. Generally, service is more frequent during peak hours. Real-time information on train arrival times is available through the MBTA’s mobile app.
-
Q: Are there any planned service disruptions or closures? A: The MBTA website provides up-to-date information on service alerts, planned maintenance, and any potential disruptions to service.
Tips for Efficient Green Line Travel:
- Utilize the MBTA’s real-time tracking app to monitor train arrival times and plan your journey accordingly.
- Familiarize oneself with the map’s layout and identify transfer points in advance to streamline travel between different lines.
- Allow extra time for travel, especially during peak hours or periods of expected service disruptions.
- Check the MBTA website for any service alerts or planned closures before commencing travel.
- Consider purchasing a CharlieCard for convenient and cost-effective fare payment.
Conclusion:
The Boston Green Line stands as a critical component of the city’s public transportation network. Its extensive reach, multiple branches, and integration with other transit lines provide essential connectivity for residents, commuters, and visitors. Understanding its layout, utilizing available resources for real-time information, and employing efficient travel strategies are key to maximizing the benefits of this vital transportation system. Continued investment and improvements in infrastructure and service will further enhance its role in supporting Boston’s economic and social vitality.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Boston Green Line: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!