Navigating the Complexities of Electronic Toll Collection: A Comprehensive Overview of Automated Toll Booth Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Electronic Toll Collection: A Comprehensive Overview of Automated Toll Booth Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Electronic Toll Collection: A Comprehensive Overview of Automated Toll Booth Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of Electronic Toll Collection: A Comprehensive Overview of Automated Toll Booth Mapping
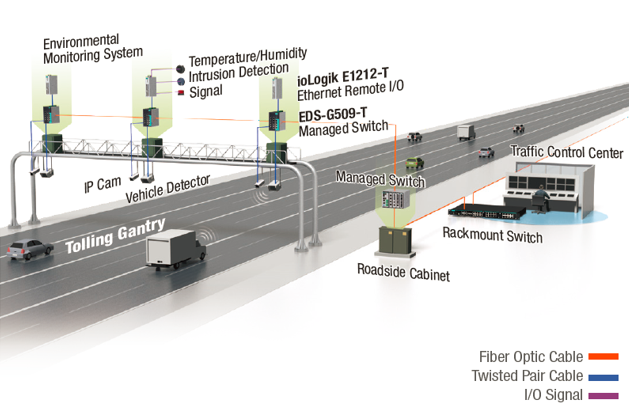
The proliferation of electronic toll collection (ETC) systems has revolutionized highway travel, offering smoother traffic flow and reduced congestion. However, this technological advancement presents a new challenge: the need for accurate and comprehensive mapping of toll locations. This mapping, often referred to implicitly as a "phantom tollbooth map," is crucial for efficient navigation and accurate toll calculation. Its absence or inaccuracy can lead to significant financial and logistical complications for drivers.
This article explores the intricacies of automated toll booth mapping, detailing its components, functionalities, and overall significance in the modern transportation landscape. The discussion will encompass various aspects, including data acquisition, map creation, integration with navigation systems, and the implications for both drivers and transportation authorities.
Data Acquisition and Map Creation:
The foundation of any effective automated toll booth map lies in the accurate acquisition and processing of relevant data. This involves collecting precise geographical coordinates of toll plazas, gantry locations, and associated infrastructure. Data sources may include government agencies, toll operators, and private mapping companies. High-resolution imagery from aerial photography, satellite imagery, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scanning are employed to create detailed three-dimensional models of the road network and toll locations.
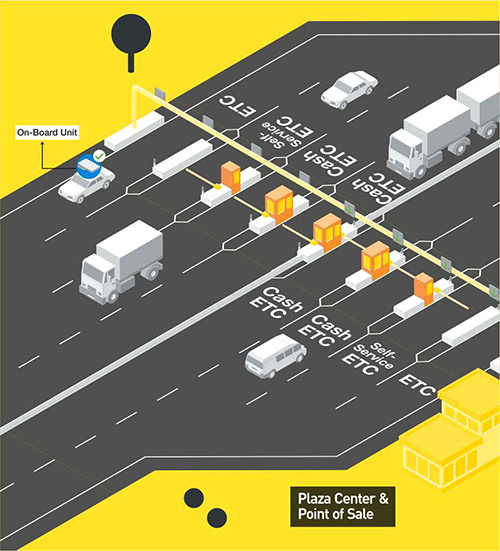
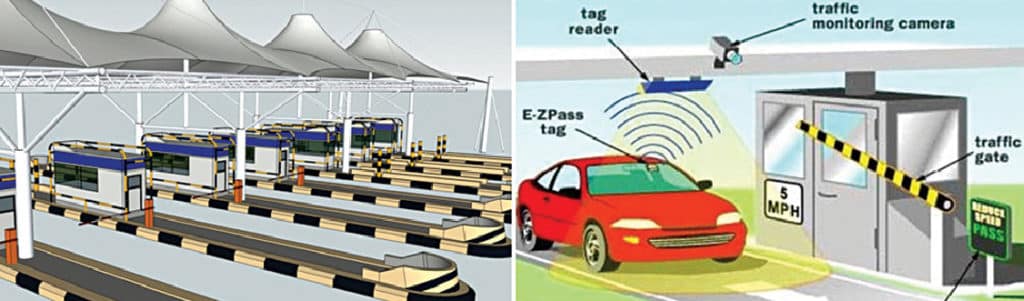
This raw data undergoes rigorous processing and validation to ensure accuracy and consistency. This process typically involves geometric correction, feature extraction, and data fusion techniques to integrate information from multiple sources. The resulting data is then used to generate a digital map representing the location and characteristics of each toll point. This map incorporates information such as the type of toll system used (e.g., transponder-based, video-based), toll rates, and any relevant restrictions or regulations.
Integration with Navigation Systems:
To maximize utility, the automated toll booth map must be seamlessly integrated with navigation systems used by drivers. Modern navigation applications utilize this data to provide real-time guidance, alerting drivers to upcoming tolls and providing options for toll avoidance where available. This integration typically involves employing application programming interfaces (APIs) to exchange data between the mapping system and the navigation application.
The level of integration varies across different navigation platforms. Some systems simply display the location of toll plazas on the map, while others provide more advanced features, such as calculating the total toll cost for a planned route and offering alternative routes that minimize or avoid tolls altogether. The accuracy and reliability of these navigation features are directly dependent on the quality and currency of the underlying automated toll booth map.
Benefits and Implications for Drivers and Transportation Authorities:
The accurate and up-to-date mapping of automated toll collection points offers numerous benefits for both drivers and transportation authorities. For drivers, it enhances convenience and reduces the risk of unexpected toll charges. Real-time information regarding toll locations and costs allows for better trip planning and budgeting. Accurate navigation aids in avoiding delays associated with toll plaza congestion.
For transportation authorities, comprehensive mapping facilitates efficient toll collection, monitoring, and management. This data supports the optimization of toll rates, the identification of areas requiring infrastructure improvements, and the effective enforcement of toll regulations. Accurate data also aids in traffic management and the planning of new road infrastructure. Furthermore, the data contributes to the development of more effective transportation policies and strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: How often is the automated toll booth map updated? A: The frequency of updates varies depending on factors such as the rate of infrastructure changes and the specific needs of the transportation authority. However, regular updates are crucial to maintain accuracy.
-
Q: What happens if the map is inaccurate? A: Inaccurate information can lead to incorrect toll calculations, resulting in unexpected charges or missed payments. It can also lead to inefficient routing and increased travel time.
-
Q: What data security measures are in place? A: The security of the data used to create and maintain these maps is a high priority. Robust security protocols are typically implemented to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
Q: How is the accuracy of the map verified? A: Accuracy verification involves a combination of techniques, including ground truthing, comparison with other data sources, and continuous monitoring for discrepancies.
Tips for Utilizing Automated Toll Booth Maps:
-
Verify map accuracy: Before embarking on a journey, it is advisable to confirm the accuracy of the toll information provided by the navigation system against official sources.
-
Plan routes in advance: Utilize the mapping features to plan routes that minimize or avoid tolls, depending on individual preferences and budgetary considerations.
-
Ensure adequate funds: Ensure that sufficient funds are available in any associated ETC account to cover anticipated toll charges.
-
Understand toll regulations: Familiarize oneself with the specific regulations and requirements of the toll system being used.
Conclusion:
The creation and maintenance of accurate and comprehensive automated toll booth maps are critical for the efficient operation of electronic toll collection systems. These maps play a vital role in enhancing driver experience, improving traffic flow, and supporting effective transportation management. Continuous investment in data acquisition, processing, and integration technologies is essential to ensure the long-term effectiveness and reliability of these systems, promoting smoother and more efficient highway travel for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Electronic Toll Collection: A Comprehensive Overview of Automated Toll Booth Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!