Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Examination of Map-Based Pinning
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Examination of Map-Based Pinning
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Examination of Map-Based Pinning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Examination of Map-Based Pinning

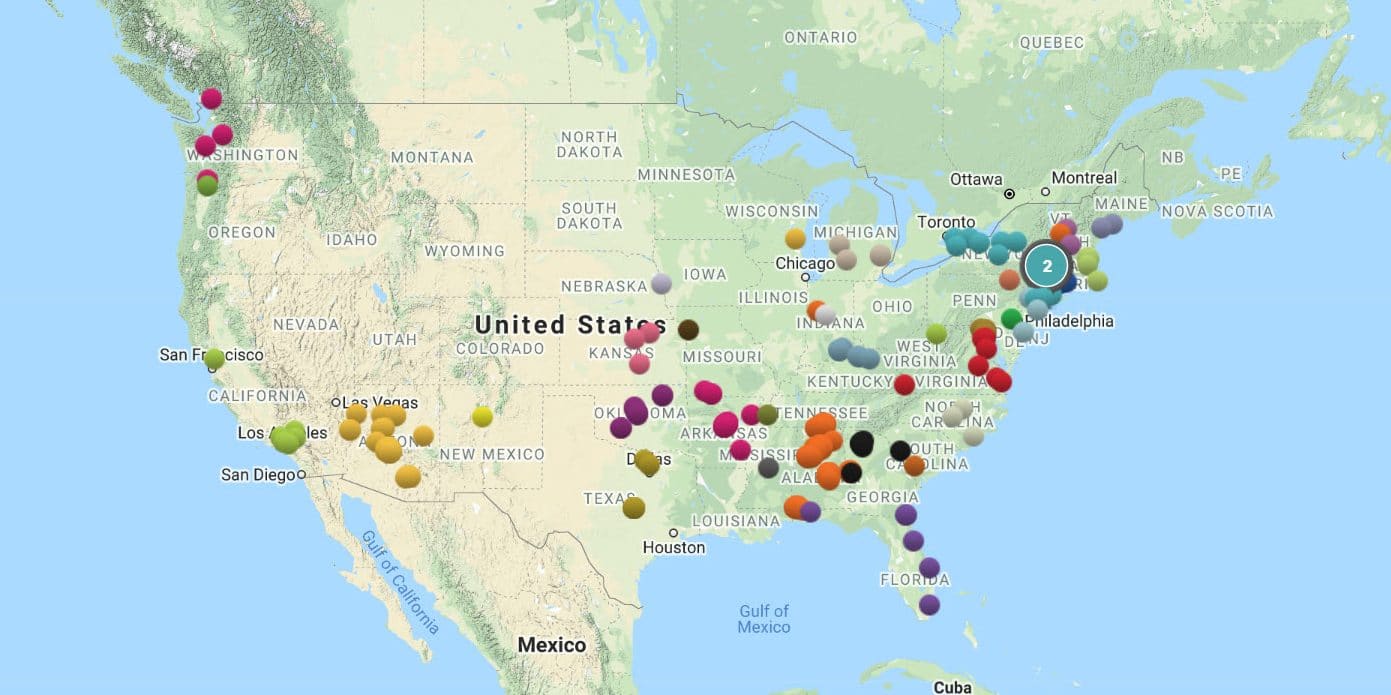
Map-based pinning, the act of placing markers onto a geographical representation to denote specific locations or points of interest, is a fundamental tool with applications spanning numerous fields. Its simplicity belies a profound impact on efficiency, communication, and data organization across various sectors. This analysis explores the mechanics, applications, and significance of this seemingly straightforward process.
The Mechanics of Location Marking
The core functionality involves overlaying digital or physical markers onto a map. Digital implementations utilize software applications, websites, or embedded systems that allow users to select a location on a map interface and add a visual indicator, often a pin or icon. These digital pins frequently incorporate additional data, such as textual descriptions, images, hyperlinks, or timestamps. Physical implementations, while less common in the digital age, involve placing pins, flags, or other markers directly onto a physical map. Regardless of the method, the underlying principle remains consistent: precise location identification and annotation.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
The utility of location marking transcends geographical limitations and extends to various sectors. In logistics and transportation, it streamlines route planning, tracks shipments, and manages fleets. Delivery services rely heavily on this technology to optimize delivery routes and provide real-time tracking information. Similarly, ride-sharing platforms utilize location marking to connect drivers with passengers and monitor vehicle locations.
Within the realm of urban planning and resource management, this methodology proves invaluable. Municipalities use location marking to map infrastructure, track utility services, and manage public resources effectively. Emergency response services leverage this capability for efficient dispatching and resource allocation during critical incidents. Environmental monitoring initiatives also employ it to track wildlife populations, record pollution levels, and manage protected areas.
Real estate applications are equally significant. Property listings frequently incorporate location markers to showcase property locations and their proximity to amenities. Construction projects use this method to track progress, manage resources, and coordinate activities. Furthermore, tourism and travel planning benefit significantly from location marking. Interactive maps highlight points of interest, allowing users to plan itineraries and explore destinations virtually.
The Significance of Precise Location Identification
The accuracy of location marking is paramount. Inaccurate placement can lead to significant inefficiencies, miscommunications, and even safety hazards. The reliability of the underlying map data and the precision of the pinning mechanism are critical factors. Advanced mapping technologies, such as GPS and GIS (Geographic Information Systems), play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy. These technologies provide highly precise location data, allowing for more effective location marking and subsequent analysis.
Data Organization and Analysis
Beyond simple location identification, location marking facilitates data organization and analysis. The ability to associate data with specific locations allows for the creation of comprehensive datasets that can be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and insights. This capability is particularly valuable in research, environmental studies, and public health initiatives. For example, mapping disease outbreaks allows for the identification of hotspots and facilitates targeted interventions.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations
While location marking offers numerous advantages, certain challenges exist. Data privacy concerns arise when personal location data is involved. Ensuring data security and adhering to relevant privacy regulations are crucial. Furthermore, the accuracy of location data can be affected by factors such as GPS signal interference or outdated map data. Regular updates and validation of map data are essential to maintain accuracy and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What types of maps are compatible with location marking? Most digital maps and many physical maps are compatible. The specific functionality depends on the map’s platform and features.
-
What data can be associated with a location marker? A wide range of data can be associated, including text, images, hyperlinks, and timestamps. The specific capabilities depend on the software or system used.
-
How is the accuracy of location marking ensured? Accuracy relies on the precision of the underlying mapping technology (e.g., GPS, GIS) and the accuracy of the data input.
-
What are the security implications of location marking? Data privacy and security are crucial concerns, especially when dealing with personal location data. Appropriate security measures and adherence to privacy regulations are essential.
-
What are the limitations of location marking? Limitations include potential inaccuracies due to outdated map data or GPS signal interference, and the potential for data privacy breaches.
Tips for Effective Location Marking
-
Use clear and concise labels: Ensure location markers are clearly labeled with descriptive and accurate information.
-
Maintain data consistency: Use a standardized format for data entry to ensure consistency across datasets.
-
Regularly update map data: Ensure that the underlying map data is up-to-date to maintain accuracy.
-
Implement appropriate security measures: Protect location data from unauthorized access and ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations.
-
Choose appropriate map scales: Select a map scale that is appropriate for the level of detail required.
Conclusion
Location marking represents a powerful and versatile tool with far-reaching implications across diverse sectors. Its ability to precisely identify, annotate, and analyze geographical locations facilitates efficiency, improves communication, and unlocks valuable insights from spatial data. However, responsible implementation requires careful consideration of data accuracy, security, and privacy. By addressing these challenges and leveraging the capabilities of advanced mapping technologies, location marking will continue to play a crucial role in shaping how we interact with and understand the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Examination of Map-Based Pinning. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!