Navigating the World Digitally: A Comprehensive Look at Location-Based Applications
Related Articles: Navigating the World Digitally: A Comprehensive Look at Location-Based Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World Digitally: A Comprehensive Look at Location-Based Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World Digitally: A Comprehensive Look at Location-Based Applications
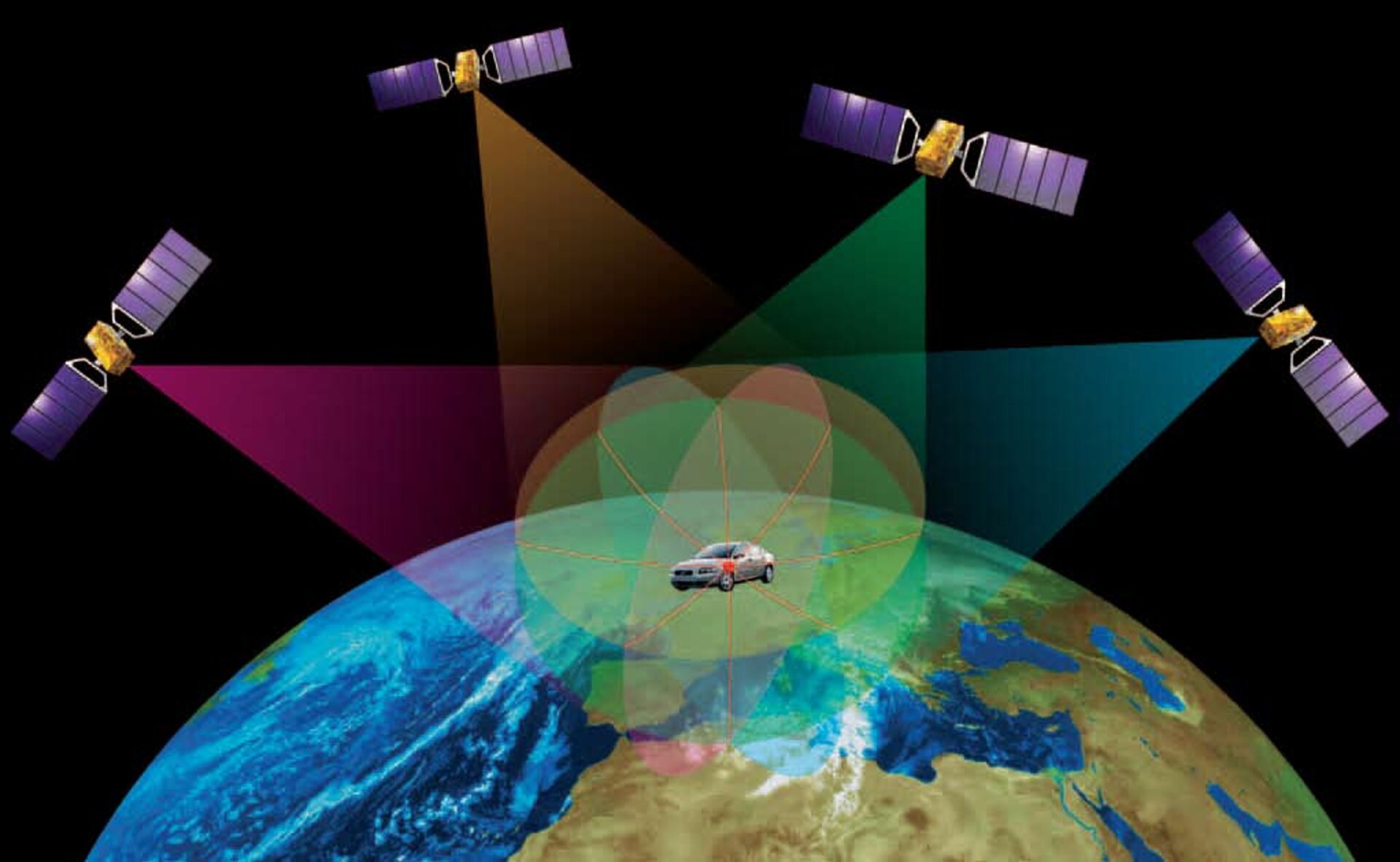

Location-based applications, commonly known as mapping apps, have revolutionized personal and professional navigation. These applications leverage Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, coupled with sophisticated mapping data and algorithms, to provide users with real-time location information and route guidance. Their impact extends far beyond simple directions, permeating various aspects of modern life.
The Foundation: GPS Technology and Mapping Data
The core functionality of these applications relies on the precise positioning provided by GPS satellites. These satellites transmit signals that are received by GPS-enabled devices, such as smartphones. By triangulating these signals, the device determines its location with remarkable accuracy. This raw location data is then integrated with extensive map databases. These databases contain a wealth of geographical information, including roads, buildings, points of interest (POIs), and topographical features. The data is constantly updated, ensuring the accuracy and relevance of the information presented to users.
Beyond Navigation: Diverse Applications and Features
The capabilities of these applications extend far beyond simple route planning. Modern applications offer a diverse range of features designed to enhance user experience and provide valuable information. Some of these include:
-
Real-time Traffic Updates: These applications often integrate real-time traffic data from various sources, enabling users to avoid congested areas and optimize their travel time. Algorithms analyze traffic flow and suggest alternative routes based on current conditions.
-
Public Transportation Integration: Many applications seamlessly integrate with public transportation schedules and routes. Users can plan journeys using multiple modes of transport, including buses, trains, and subways, with real-time updates on arrival times and potential delays.
-
Point-of-Interest Search and Discovery: These applications offer comprehensive search functionality, allowing users to locate specific points of interest, such as restaurants, shops, hospitals, or tourist attractions. User reviews and ratings can further inform decision-making.
-
Offline Map Access: Many applications allow for downloading map data for offline use, a crucial feature for areas with limited or no internet connectivity. This ensures continued navigation capabilities even in remote locations.
-
Augmented Reality Navigation: Some advanced applications incorporate augmented reality (AR) features, overlaying digital information onto the real-world view through a smartphone camera. This can enhance navigation by providing clear visual guidance, particularly in unfamiliar environments.
-
Street View and 360° Imagery: Users can explore locations virtually using street view imagery and 360° panoramas, providing a visual preview of destinations before arriving.
-
Sharing Location: Many applications allow users to share their real-time location with others, facilitating coordination and safety, particularly useful for meeting up with friends or family.
-
Speed Limit and Safety Features: Some applications provide real-time speed limit information and alerts, helping users to drive safely and avoid speeding tickets. Advanced features may include warnings about nearby accidents or hazards.
The Importance of Accuracy and Data Privacy
The accuracy of the location information and map data is paramount to the functionality of these applications. Continuous updates and rigorous data validation are essential to ensure reliable navigation. Furthermore, data privacy is a significant consideration. Users should be aware of the data collected by these applications and the privacy policies governing its use.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How accurate are these applications? Accuracy varies depending on several factors, including GPS signal strength, satellite availability, and the accuracy of the underlying map data. Generally, accuracy is high in urban areas with good GPS reception.
-
What happens if there is no internet connection? Many applications allow for offline map access, but the extent of functionality may be limited. Real-time traffic and other data-dependent features may be unavailable.
-
Are these applications safe to use? Security features vary across applications. Users should choose reputable applications from trusted developers and be mindful of the permissions granted.
-
What data is collected by these applications? Applications typically collect location data, search history, and usage patterns. Users should review the privacy policies of the application before use.
-
Can these applications be used for navigation in remote areas? While functionality may be limited in remote areas due to poor GPS signal strength or lack of map data, offline maps can often provide basic navigation capabilities.
Tips for Effective Use
-
Ensure GPS is enabled: Verify that the location services are activated on the device before using the application.
-
Check for updates: Regularly check for application updates to ensure access to the latest map data and features.
-
Plan routes in advance: Planning routes beforehand, especially for longer journeys, can help to identify potential delays or issues.
-
Allow for unexpected delays: Real-time traffic updates can help, but unforeseen circumstances can still cause delays. Allow extra time for travel, especially during peak hours.
-
Review privacy settings: Familiarize oneself with the application’s privacy settings and adjust them according to personal preferences.
Conclusion
Location-based applications have become indispensable tools for navigation and location-based services. Their integration of GPS technology, comprehensive mapping data, and sophisticated algorithms provides users with powerful tools for planning journeys, exploring new places, and staying connected. However, responsible use requires awareness of accuracy limitations, data privacy concerns, and the need to supplement technological guidance with common sense and situational awareness. As technology continues to evolve, these applications will undoubtedly continue to enhance and expand their capabilities, further integrating into the fabric of daily life.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World Digitally: A Comprehensive Look at Location-Based Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!