Navigating Time in Brazil: A Geographic and Practical Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Time in Brazil: A Geographic and Practical Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Time in Brazil: A Geographic and Practical Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Time in Brazil: A Geographic and Practical Guide
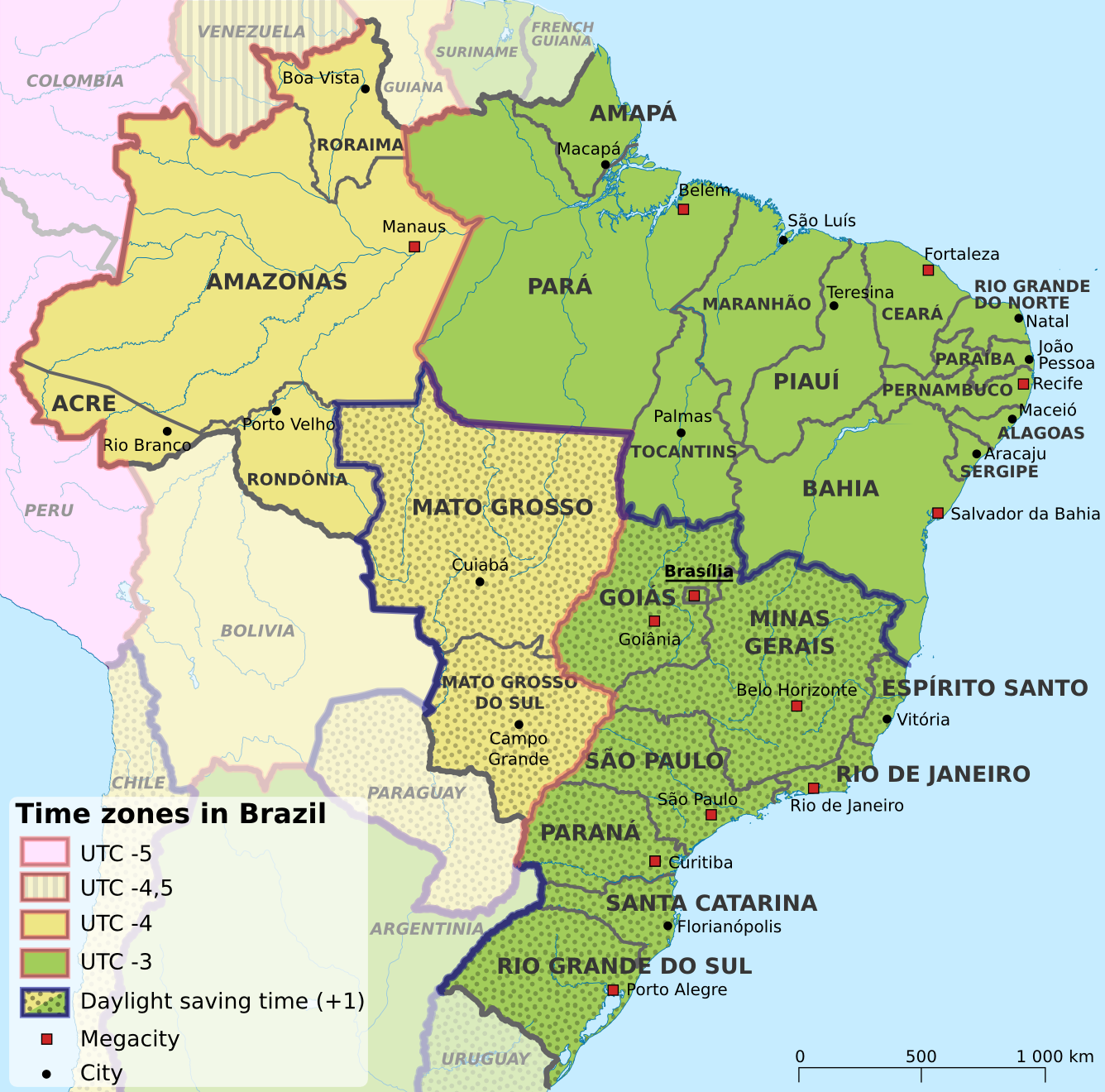
Brazil, a geographically vast nation extending across a significant portion of South America, presents a unique challenge regarding timekeeping: its sheer size necessitates the adoption of multiple time zones. Understanding these zones is crucial for efficient communication, scheduling, and logistical operations within the country and internationally. This exploration delves into the complexities of Brazilian time, offering a detailed analysis of its geographical distribution and practical implications.
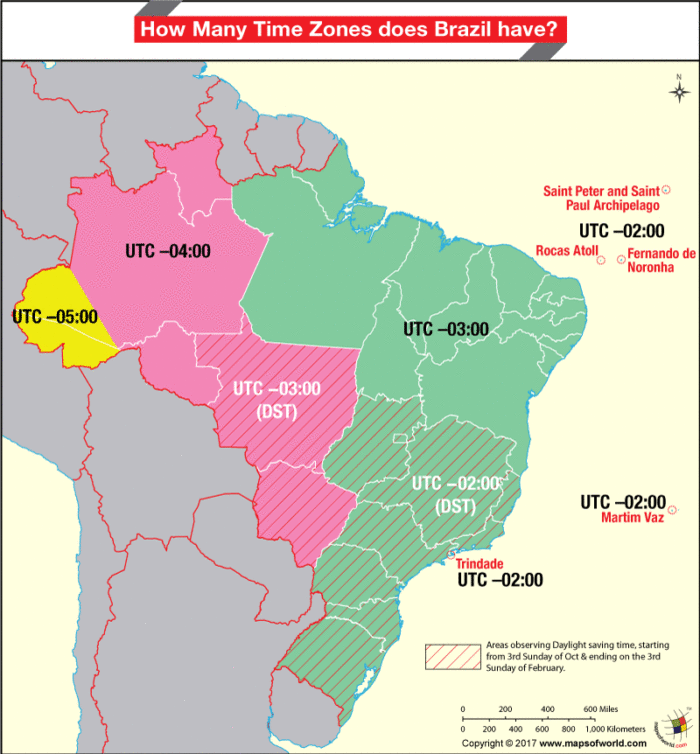
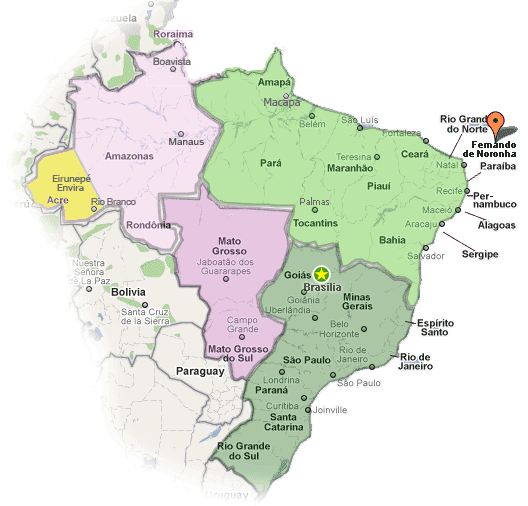
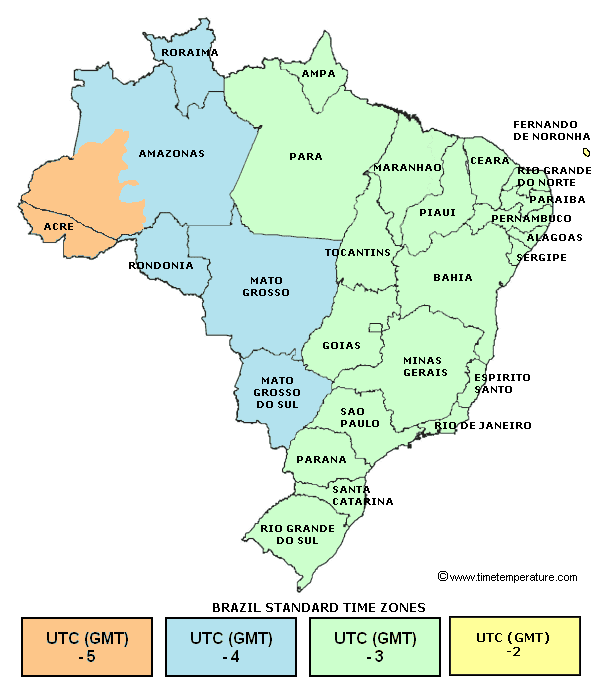
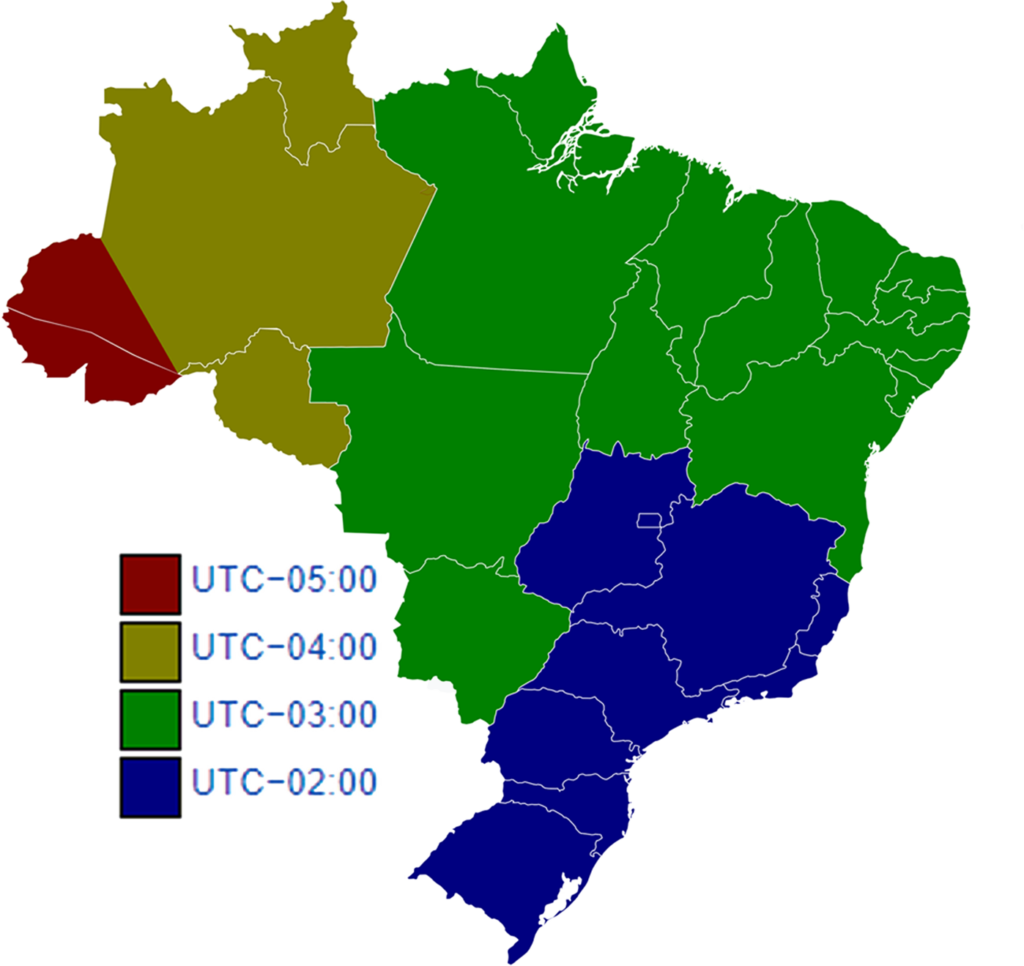
Brazil officially observes four time zones, although the colloquial usage and historical context occasionally blur the lines. These zones are defined in relation to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the primary international time standard. The most easterly zone, encompassing the states of Roraima, Amazonas, Acre, and Rondônia, observes Amazon Standard Time (AMT), which is UTC−4. This zone is strategically located to align with the sunrise and sunset patterns prevalent in the Amazon rainforest, maximizing daylight hours for the region’s inhabitants and activities.
Moving eastward, the vast majority of the country, including major metropolitan areas like São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Brasília, and Belo Horizonte, operates on Brasília Time (BRT), which is UTC−3. This is the country’s primary time zone and the one most frequently encountered in international contexts. The selection of Brasília as the reference point for the national time standard reflects the country’s geopolitical center and its importance as the seat of federal government. The concentration of population and economic activity within this time zone further underscores its significance.
A smaller eastern sliver of Brazil, comprising the states of Fernando de Noronha and the Rocas Atoll, utilizes Fernando de Noronha Time (FNT), which is UTC−2. This geographically isolated area observes a time zone distinct from the mainland, primarily due to its easterly location and the need to maintain a reasonable alignment with daylight hours. The limited population of this region means its unique time zone has minimal impact on broader national timekeeping practices.
Finally, the state of Pará, owing to its extensive geographical area, utilizes both BRT and AMT. This division within a single state illustrates the challenges inherent in assigning time zones to a country of Brazil’s size and diverse geography. The western portion of Pará, closer to the Amazon River basin, adheres to AMT, while the eastern portion aligns with BRT. This internal variation necessitates careful attention to detail when scheduling events or communicating across different parts of the state.
The adoption of these time zones is not merely a matter of convenience; it has profound implications for various sectors. The airline industry, for example, must meticulously coordinate flight schedules across different time zones to ensure on-time departures and arrivals. The financial sector relies on precise timekeeping for transactions and market operations, with the potential for significant losses due to time-related errors. International trade and commerce depend on clear communication and coordination across time zones, impacting efficiency and profitability. Even daily life is significantly affected, with work schedules, social events, and family interactions all influenced by the time zone in which individuals reside.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: Why does Brazil have multiple time zones?
-
A: Brazil’s vast geographical extent, spanning several degrees of longitude, necessitates the use of multiple time zones to optimize daylight hours and align with local sunrise and sunset times across different regions.
-
Q: What is the most commonly used time zone in Brazil?
-
A: Brasília Time (BRT), which is UTC−3, is the most widely used time zone in Brazil and the one typically referenced in international contexts.
-
Q: How do I determine the time zone for a specific location in Brazil?
-
A: Referencing a detailed map of Brazil’s time zones or using online time zone converters with specific location input provides the most accurate information.
-
Q: Does Brazil observe daylight saving time?
-
A: Brazil has historically observed daylight saving time, but its implementation has been inconsistent over the years, varying by region and time period. Currently, daylight saving time is not consistently observed nationwide.
-
Q: What are the potential consequences of not understanding Brazilian time zones?
-
A: Misunderstandings regarding time zones can lead to missed meetings, delayed flights, logistical errors, and communication breakdowns, impacting efficiency and potentially causing financial losses.
Tips for Navigating Brazilian Time Zones
-
Always verify the time zone: When scheduling meetings or communications with individuals or organizations in Brazil, always confirm the specific time zone being used.
-
Utilize online time zone converters: These tools allow for easy conversion between time zones, ensuring accurate scheduling and communication.
-
Be mindful of regional variations: Recognize that time zone divisions within states, like Pará, necessitate careful consideration when scheduling events or coordinating activities.
-
Account for time differences in international communication: When communicating with Brazil internationally, factor in the significant time difference to avoid scheduling conflicts and ensure timely responses.
-
Consult reliable sources: Official government websites and reputable travel guides offer the most accurate and up-to-date information on Brazilian time zones.
Conclusion
The implementation of multiple time zones in Brazil is a reflection of the country’s vast geography and diverse population. Understanding the nuances of these zones is essential for efficient communication, logistical planning, and successful interactions within and beyond the country’s borders. By carefully considering the specific time zone of a given location, individuals and organizations can avoid potential problems and ensure smooth operations across this geographically expansive nation. The importance of accurate timekeeping in Brazil extends beyond simple convenience; it is a critical element in maintaining efficient communication, economic activity, and overall societal functioning.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Time in Brazil: A Geographic and Practical Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!