Navigating West Virginia’s Healthcare Landscape: An Examination of the DHHR’s Geographic Data
Related Articles: Navigating West Virginia’s Healthcare Landscape: An Examination of the DHHR’s Geographic Data
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating West Virginia’s Healthcare Landscape: An Examination of the DHHR’s Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating West Virginia’s Healthcare Landscape: An Examination of the DHHR’s Geographic Data

The West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources (DHHR) utilizes geographic information systems (GIS) technology to visualize and analyze a vast array of data related to the state’s healthcare infrastructure and population health. This spatial representation of crucial information provides valuable insights for policymakers, healthcare providers, and the public, facilitating improved resource allocation, program effectiveness, and ultimately, public health outcomes. This analysis explores the functionalities and significance of this data visualization tool.
Data Visualization and its Applications
The DHHR’s GIS platform integrates diverse datasets, creating a comprehensive picture of West Virginia’s healthcare landscape. This includes, but is not limited to, the locations of healthcare facilities – hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and long-term care centers – overlaid with demographic data such as population density, income levels, and prevalence of specific diseases or health conditions. This layered approach allows for sophisticated analysis, identifying areas with healthcare deserts, disparities in access to care, and potential health risks within specific communities.
For instance, mapping the distribution of healthcare providers against population density reveals areas with insufficient medical personnel, prompting targeted interventions to recruit and retain healthcare professionals in underserved regions. Similarly, overlaying disease prevalence data with socioeconomic factors can highlight health disparities and inform the development of culturally sensitive and effective public health initiatives.
The system’s capacity extends beyond static mapping. Dynamic visualizations can track the spread of infectious diseases in real-time, aiding in rapid response and containment efforts. Further, it allows for the analysis of healthcare utilization patterns, identifying trends and informing resource allocation decisions. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are directed to areas of greatest need, optimizing the efficiency and impact of healthcare programs.
Data Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of the geographic data are paramount. The DHHR employs rigorous data collection and validation methods to ensure the integrity of the information presented. Data sources include various state and federal agencies, healthcare providers, and public health surveys. Regular updates and quality control measures are implemented to maintain data currency and accuracy. Transparency in data sources and methodologies is crucial for building public trust and fostering informed decision-making.
Accessibility and User Friendliness
While the specific interface and accessibility of the DHHR’s GIS platform may vary, the aim is to provide a user-friendly platform accessible to a range of stakeholders. This includes healthcare professionals, public health officials, researchers, and even the general public, depending on the nature of the data released. Intuitive navigation and clear data presentation are essential for effective utilization of the information. The ability to download data in various formats further enhances accessibility for different analytical needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What types of data are included in the DHHR’s geographic information system? The system incorporates a wide range of data, including the location of healthcare facilities, demographic information, disease prevalence, socioeconomic indicators, and environmental factors.
-
How is the accuracy of the data ensured? Data accuracy is maintained through rigorous data collection, validation procedures, regular updates, and quality control measures. Multiple data sources are utilized and cross-referenced.
-
Is the data publicly accessible? The accessibility of specific data varies. Some data may be publicly available through the DHHR website, while other sensitive information is restricted to authorized users to protect patient privacy and confidentiality.
-
How is the information used to improve healthcare outcomes? The data informs resource allocation, identifies areas needing improvement, guides public health interventions, and supports the development of effective healthcare policies.
-
How is the system updated? The system is continuously updated to reflect changes in healthcare infrastructure, population demographics, and disease prevalence. The frequency of updates depends on the data source and its inherent dynamism.
Tips for Utilizing the Data
-
Understand the limitations of the data: Recognize that data may not be perfectly representative of the entire population or may contain inherent biases.
-
Consult multiple data sources: Cross-referencing information from various sources strengthens the validity of any conclusions drawn.
-
Focus on specific research questions: Clearly defined research questions guide the selection and analysis of relevant data.
-
Utilize appropriate analytical techniques: The choice of analytical methods should align with the research questions and data characteristics.
-
Consider the ethical implications: Data usage should always respect patient privacy and confidentiality.
Conclusion
The DHHR’s utilization of geographic information systems represents a significant advancement in West Virginia’s healthcare infrastructure. By visualizing complex data in a readily accessible and understandable format, this tool empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, improve resource allocation, and ultimately, enhance the health and well-being of West Virginia’s citizens. Continued investment in data quality, system accessibility, and analytical capacity will further strengthen the impact of this valuable resource. The ongoing development and refinement of this system are crucial for addressing present and future challenges in public health and healthcare delivery within the state.

![Welcome [www.dhhr.wv.gov]](http://www.dhhr.wv.gov/localhealth/newlocalsite/PublishingImages/map.gif)
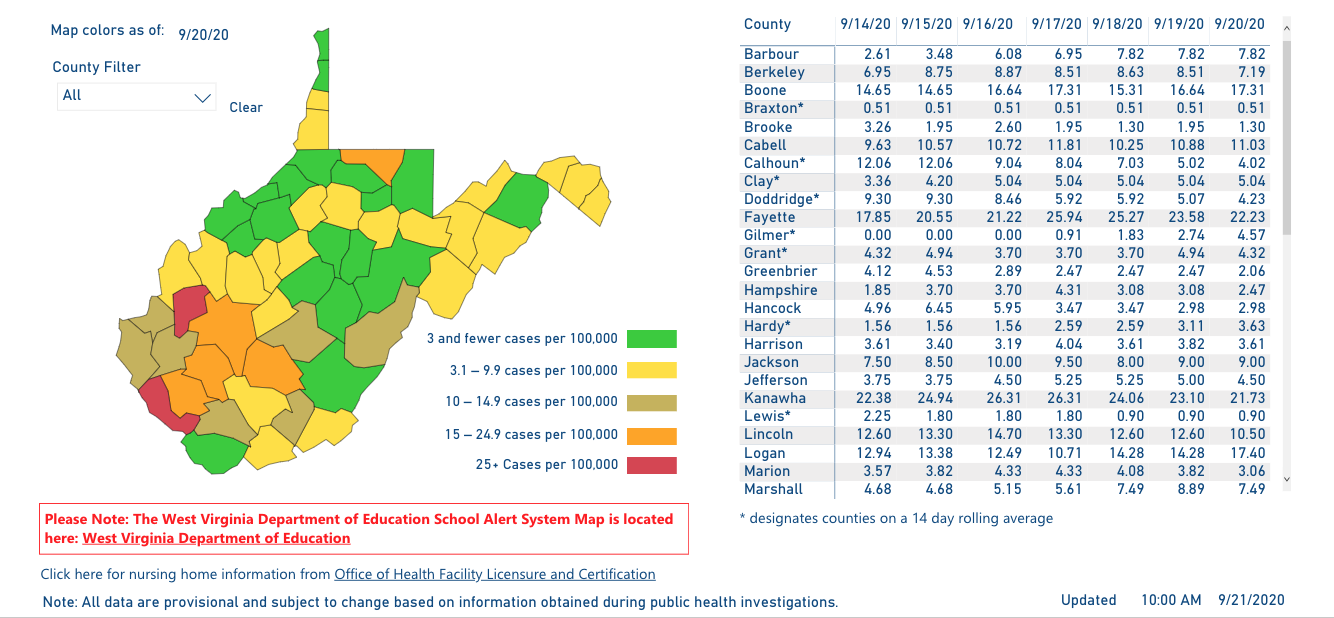

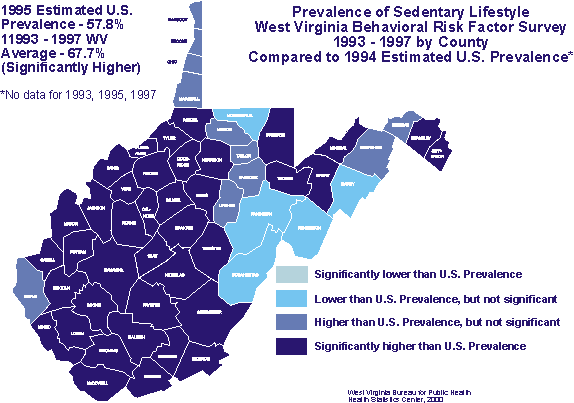
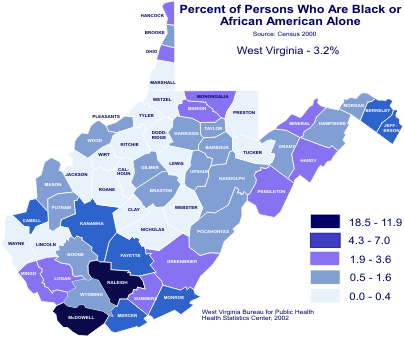
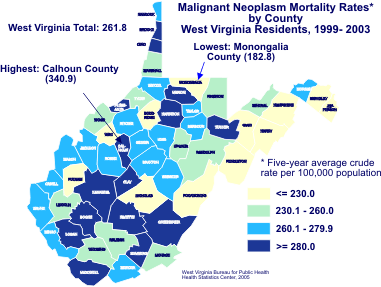
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating West Virginia’s Healthcare Landscape: An Examination of the DHHR’s Geographic Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
