Norway’s Geographic Position and Significance in Europe
Related Articles: Norway’s Geographic Position and Significance in Europe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Norway’s Geographic Position and Significance in Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Norway’s Geographic Position and Significance in Europe

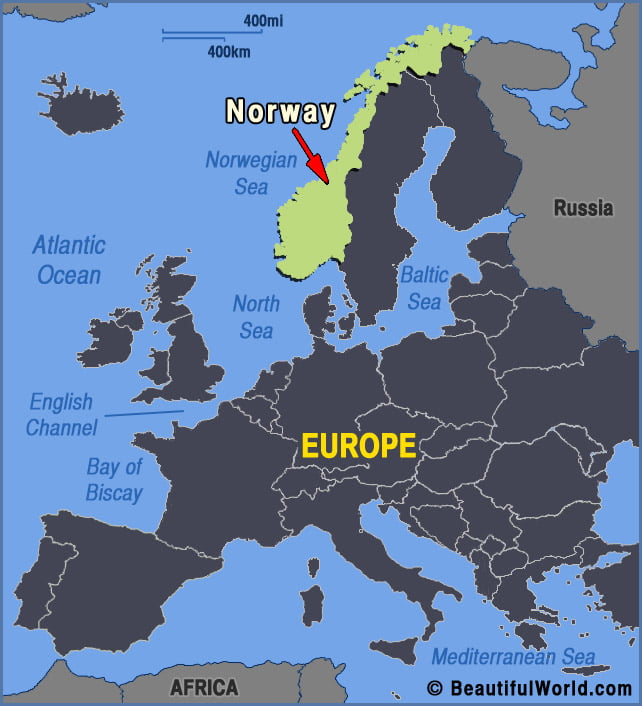
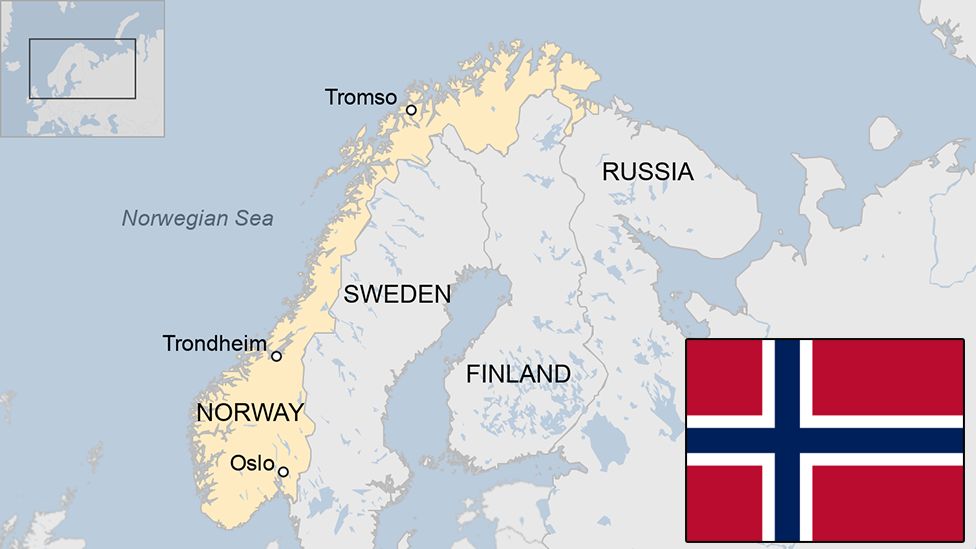
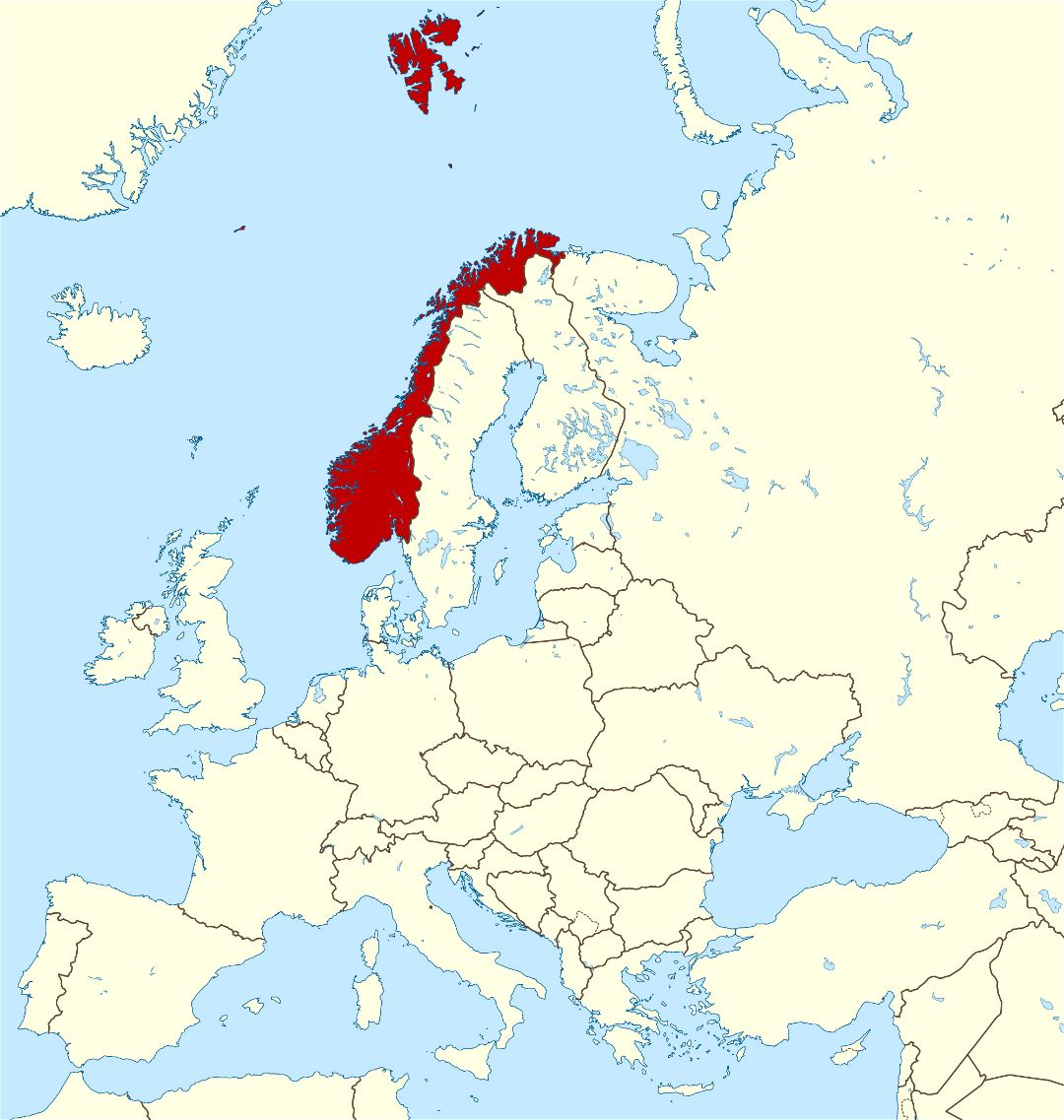
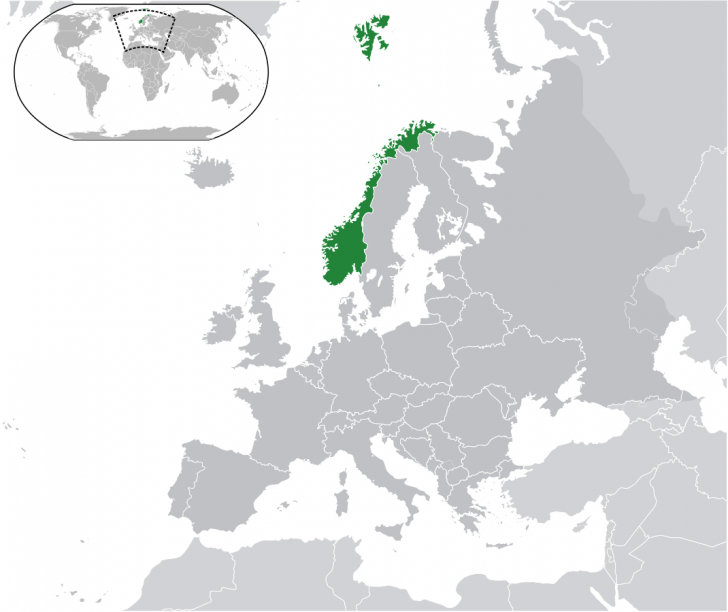
Norway occupies a unique and strategically important location on the European map. Extending along the western edge of the Scandinavian Peninsula, it shares land borders with Sweden, Finland, and Russia, while its extensive coastline faces the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. This geographical configuration significantly influences its history, culture, economy, and geopolitical role.
The country’s elongated shape, stretching approximately 1,750 kilometers (1,090 miles) north-south, results in considerable climatic variation. Southern Norway experiences a relatively temperate climate, influenced by the North Atlantic Current, while northern Norway endures long, dark winters and short, cool summers. This diverse climate supports a range of ecosystems, from lush forests in the south to arctic tundra in the north. This dramatic north-south variation is readily apparent on any European map displaying the country’s full extent.
Norway’s position on the Scandinavian Peninsula places it at a crossroads between Western and Eastern Europe. Historically, this has contributed to both cultural exchange and periods of conflict. The country’s relative isolation, particularly in its northern regions, has fostered a strong sense of national identity, while its proximity to major European powers has necessitated careful navigation of international relations. Its location also played a vital role during the Cold War, with the country serving as a buffer zone between East and West.
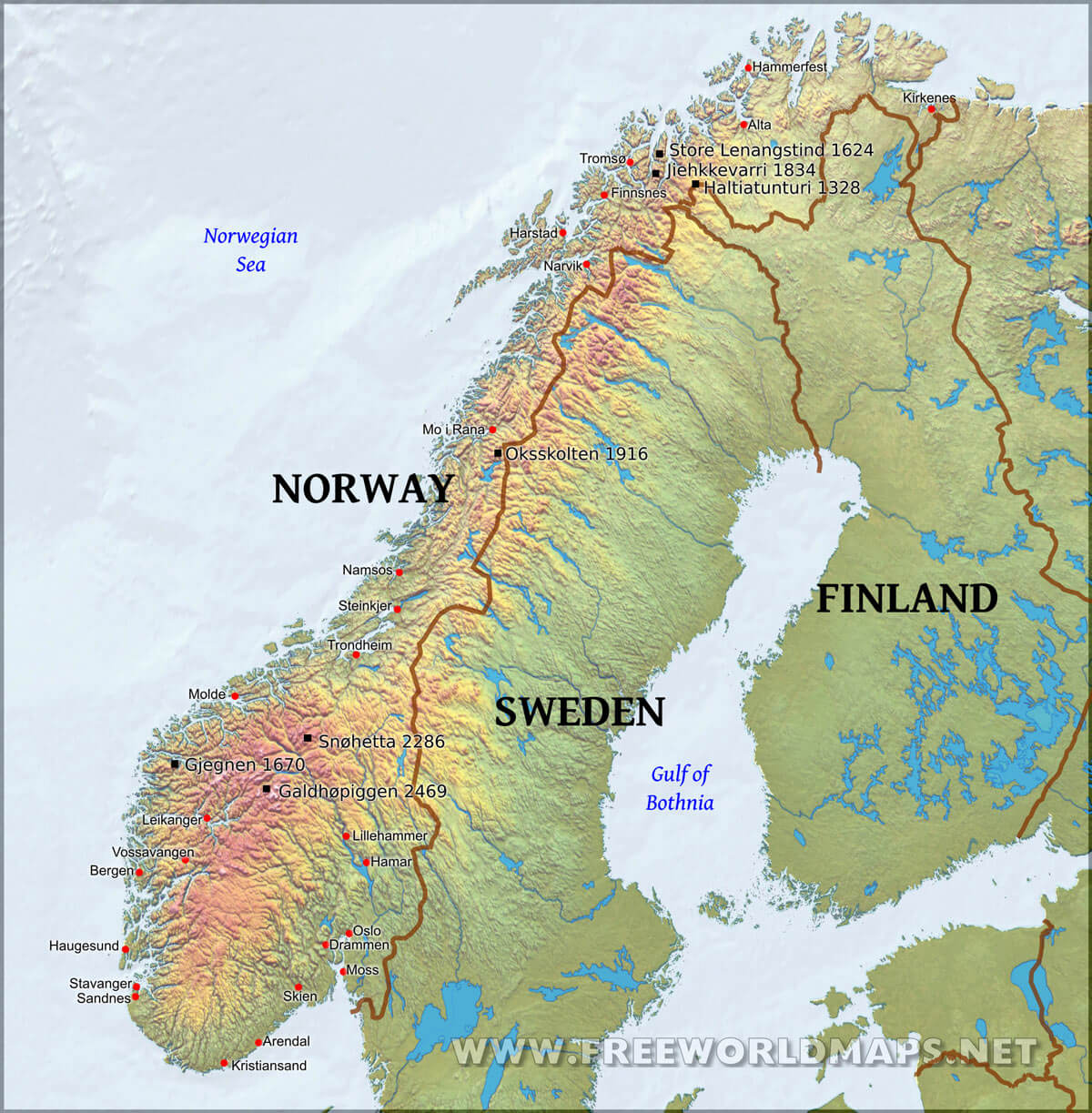
The nation’s extensive coastline, featuring a complex network of fjords, islands, and skerries, is a defining geographical feature. These intricate waterways have historically shaped Norwegian livelihoods, supporting fishing, maritime trade, and coastal communities. The sheer length of the coastline, far exceeding that of many larger nations, is readily apparent when examining the country’s cartographic representation. This maritime heritage continues to be a significant factor in Norway’s economy and national identity.
Norway’s abundant natural resources are directly linked to its geographical location. The country possesses substantial reserves of oil and natural gas, primarily located in the North Sea, off its western coast. Exploitation of these resources has transformed Norway’s economy, creating a significant source of wealth and contributing to its high standard of living. The location of these reserves, clearly visible on maps illustrating offshore resources, is fundamental to understanding Norway’s economic prosperity. Furthermore, the country’s abundant hydropower resources, derived from its numerous rivers and mountainous terrain, provide a clean and sustainable energy source.
The country’s mountainous terrain also influences its infrastructure development. Building and maintaining transportation networks presents significant challenges, impacting connectivity within the country and with neighboring nations. This is clearly reflected in the relatively low population density in many parts of the country, particularly in the mountainous interior. Understanding the topography, as depicted on a map, is crucial to comprehending the challenges and opportunities associated with Norway’s development.
Norway’s strategic geographic location also extends to its Arctic territories. The country possesses significant land area within the Arctic Circle, encompassing Svalbard and Jan Mayen, which hold geopolitical and economic significance in the context of increasing Arctic exploration and resource development. These territories are often highlighted on specialized maps focusing on the Arctic region, illustrating Norway’s unique position in this increasingly important area.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Norway’s approximate area? Norway covers approximately 385,207 square kilometers (148,729 square miles).
-
Which countries border Norway? Norway shares land borders with Sweden, Finland, and Russia.
-
What is the significance of Norway’s coastline? Its extensive and complex coastline is crucial for fishing, maritime trade, and shaping its national identity.
-
What are Norway’s major natural resources? Oil, natural gas, and hydropower are significant natural resources.
-
How does Norway’s geography influence its climate? The country’s elongated shape and proximity to the North Atlantic Current create significant climatic variation.
-
What is the impact of Norway’s mountainous terrain on its infrastructure? The mountainous terrain presents significant challenges for transportation network development.
-
What is the geopolitical significance of Norway’s Arctic territories? Svalbard and Jan Mayen hold significant geopolitical and economic importance in the context of increasing Arctic exploration.
Tips for Understanding Norway’s Geographic Context
-
Utilize detailed maps showing both physical and political features. These should include topographic maps illustrating elevation and relief, and political maps showing borders and administrative divisions.
-
Consider maps showcasing Norway’s offshore resources, particularly oil and gas fields in the North Sea.
-
Examine maps that highlight the Arctic region, paying particular attention to Norway’s territorial claims and presence in Svalbard and Jan Mayen.
-
Analyze maps illustrating population density, to understand how the geographical features influence population distribution.
-
Consult climate maps to appreciate the significant variation in climate across the country’s length.
Conclusion
Norway’s position on the European map is not merely a geographical fact; it is a fundamental element shaping its history, culture, economy, and international relations. The country’s unique combination of a long, indented coastline, mountainous terrain, and significant natural resources, coupled with its strategic location at the intersection of Western and Eastern Europe and its presence in the Arctic, creates a complex and fascinating geographical entity. A thorough understanding of this geographical context is essential for comprehending Norway’s past, present, and future role in the European and global landscape.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Norway’s Geographic Position and Significance in Europe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!