OpenStreetMaps: A Collaborative Approach to Global Cartography
Related Articles: OpenStreetMaps: A Collaborative Approach to Global Cartography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to OpenStreetMaps: A Collaborative Approach to Global Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
OpenStreetMaps: A Collaborative Approach to Global Cartography
OpenStreetMap (OSM) represents a significant advancement in global mapping, offering a free and open-source alternative to proprietary map services. Unlike commercially driven platforms, this project relies on a collaborative effort from a worldwide community of mappers, contributing data to create a comprehensive and ever-evolving representation of the planet. This collaborative nature is fundamental to its success and differentiates it from traditional mapping methodologies. The data is available under an Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL), allowing for free use and redistribution, subject to certain conditions that ensure the continued openness of the project.
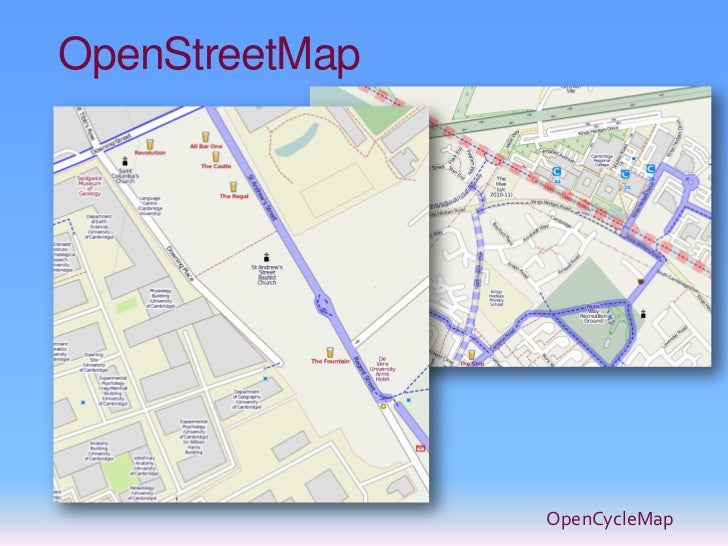
The core of the project is its reliance on volunteered geographic information (VGI). Individuals contribute data through various methods, including GPS traces from mobile devices, aerial imagery analysis, and on-the-ground surveys. This decentralized approach ensures a wider coverage and greater detail in areas often neglected by commercial map providers, particularly in developing countries or remote regions. The data encompasses a wide range of features, from roads and buildings to points of interest, administrative boundaries, and natural features. The level of detail varies geographically, reflecting the density of contributors in a particular area.
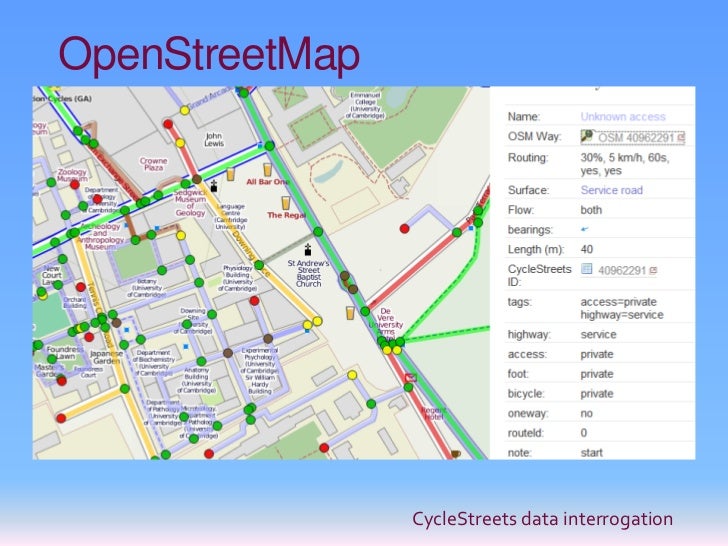
Data validation and quality control are crucial aspects of maintaining the accuracy and reliability of the maps. The community employs various mechanisms to ensure data integrity. These include mechanisms for flagging and correcting errors, peer review processes, and automated checks. The open nature of the project allows for transparency and facilitates the identification and resolution of inaccuracies. This continuous process of improvement ensures that the data remains current and reflects the dynamic nature of the world’s geography.
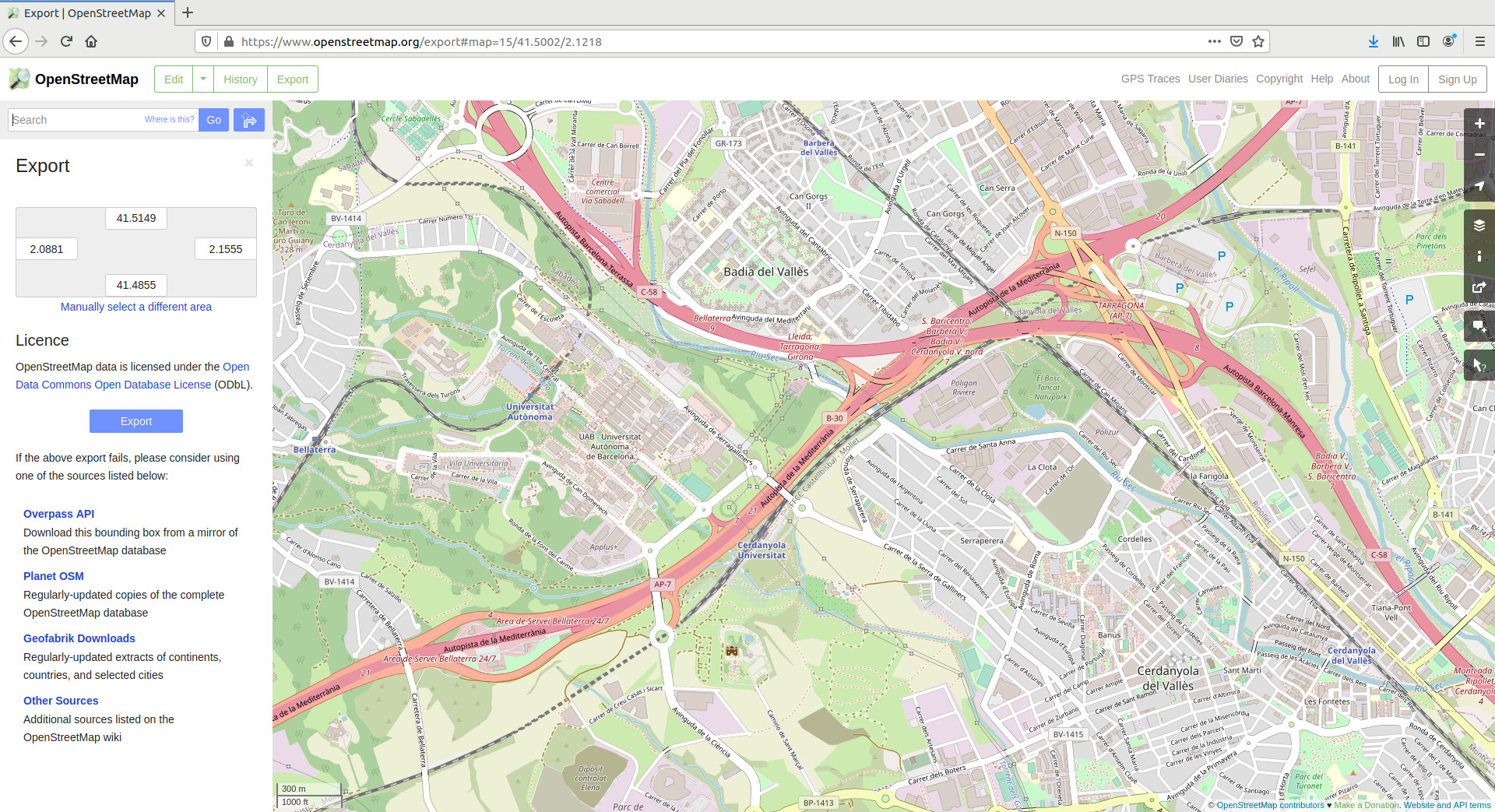
The availability of this openly licensed data has numerous applications across various sectors. Navigation applications leverage the data to provide routing services, while urban planning initiatives utilize it for infrastructure development and management. Emergency response teams can benefit from the detailed information for efficient disaster relief efforts. Researchers use the data for various analytical studies, including transportation modeling, environmental monitoring, and epidemiological research. Furthermore, the open nature of the project fosters innovation, allowing developers to create custom applications and tools tailored to specific needs.
The technical infrastructure supporting the project is equally important. The data is stored and managed using a sophisticated database system, optimized for handling large volumes of geospatial data. The project utilizes a variety of open-source software tools for data editing, visualization, and analysis. This commitment to open-source technologies ensures accessibility and promotes collaboration among developers. The platform’s API allows developers to integrate the map data into their applications, fostering innovation and expanding the reach of the project. Regular updates and improvements to the infrastructure ensure the project’s scalability and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the accuracy of OpenStreetMap data? The accuracy varies geographically, depending on the level of community involvement in a particular area. While generally reliable, it’s crucial to remember that the data is contributed by volunteers and may contain inaccuracies. Regular updates and community validation efforts aim to minimize these inaccuracies.
-
How can I contribute to OpenStreetMap? Contribution involves various methods, including tracing GPS tracks, adding points of interest, and editing existing data using the online editor or dedicated desktop applications. Detailed tutorials and guides are available on the project’s website.
-
Is OpenStreetMap suitable for professional applications? Yes, many organizations and businesses utilize the data for professional purposes, including navigation, urban planning, and disaster response. However, the accuracy should be verified for critical applications, and users should be aware of the potential for inaccuracies in certain areas.
-
How is the data licensed? The data is licensed under the Open Database License (ODbL), which permits free use and redistribution, subject to specific conditions designed to ensure the continued openness of the project.
-
How is OpenStreetMap funded? Funding primarily comes from donations and grants, supplemented by the work of volunteers.
Tips for Contributing to OpenStreetMap
-
Begin with smaller tasks: Start by adding simple points of interest or correcting minor errors before tackling more complex edits.
-
Familiarize yourself with the editing tools: The online editor and desktop applications offer various tools and functionalities; taking the time to understand these tools improves efficiency and accuracy.
-
Follow the community guidelines: Adherence to established guidelines ensures data consistency and quality.
-
Use reliable sources: When adding new data, rely on verified sources such as official maps or on-the-ground observations.
-
Review your edits before submitting: Careful review helps to identify and correct potential errors before they are integrated into the main database.
Conclusion
OpenStreetMap stands as a testament to the power of collaborative mapping. Its open nature, coupled with a dedicated community, has fostered the creation of a valuable global resource with far-reaching applications. While challenges remain in ensuring consistent data quality and coverage across all regions, the project’s continuous evolution and community-driven approach suggest a promising future for open and collaborative cartography. The platform’s ongoing success hinges on the continued participation and dedication of its global community, ensuring the project remains a dynamic and valuable resource for years to come. The accessibility and freely available nature of the data empowers individuals, organizations, and researchers alike, contributing to a more informed and connected world.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into OpenStreetMaps: A Collaborative Approach to Global Cartography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!