Southern California Wildfires: A Geographic Analysis and Risk Mitigation
Related Articles: Southern California Wildfires: A Geographic Analysis and Risk Mitigation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Southern California Wildfires: A Geographic Analysis and Risk Mitigation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Southern California Wildfires: A Geographic Analysis and Risk Mitigation

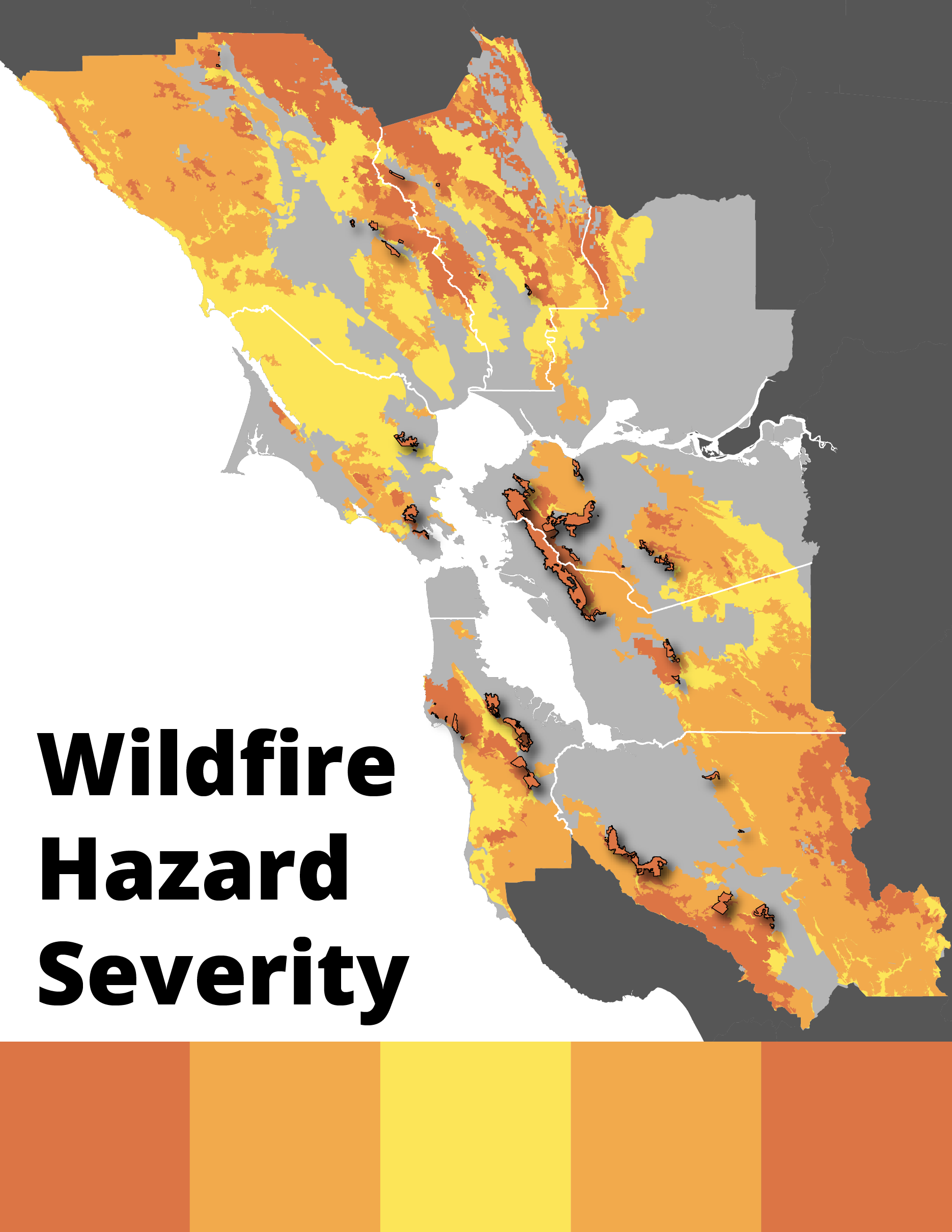
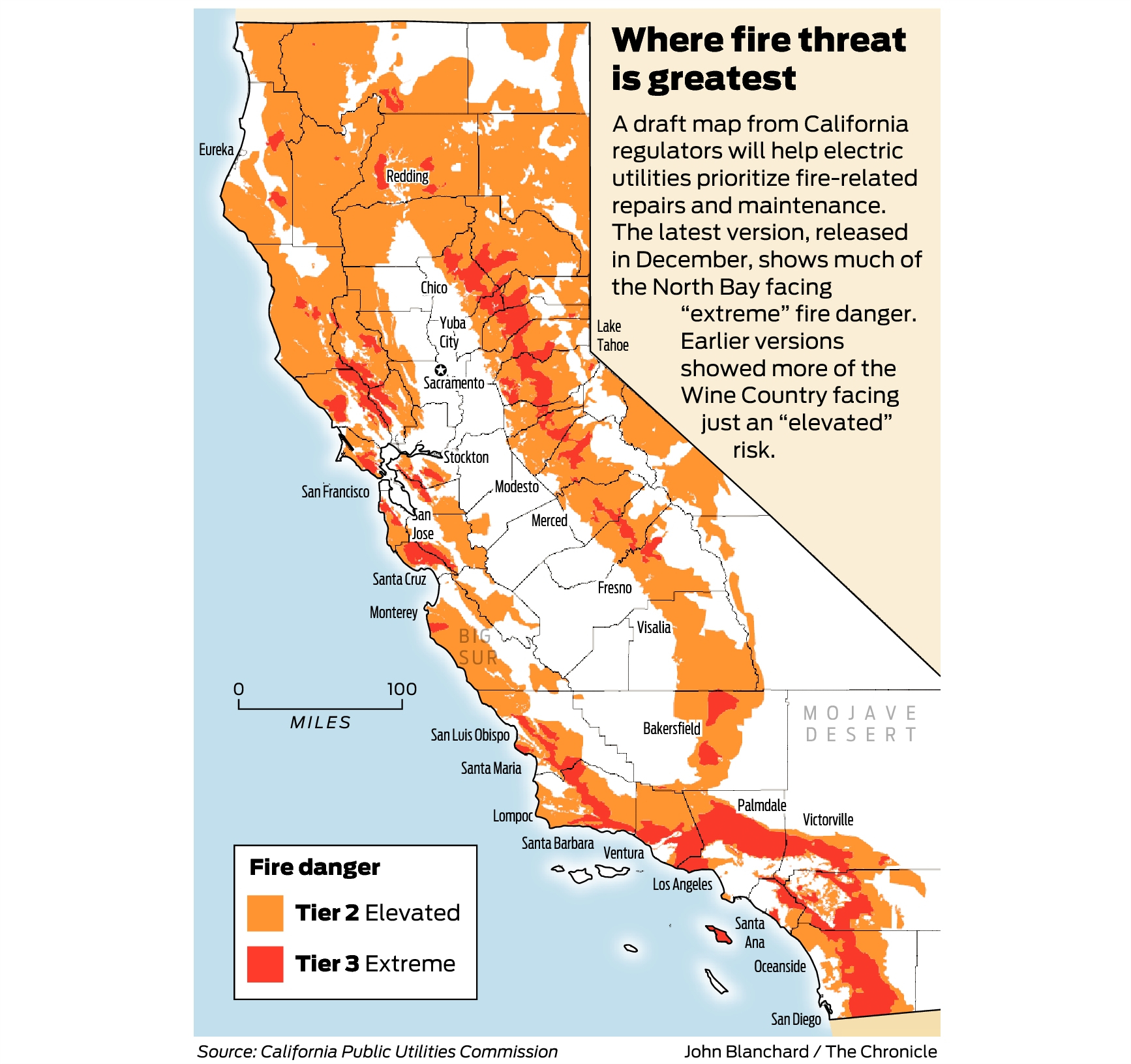
Southern California’s unique geography, climate, and vegetation create a landscape highly susceptible to wildfires. Understanding the spatial distribution of these events, as depicted on a wildfire map, is crucial for effective prevention, response, and long-term land management strategies. This analysis examines the geographic patterns of wildfires in the region, highlighting key factors contributing to their occurrence and outlining strategies for minimizing future risks.
Geographic Patterns and Contributing Factors:
The region’s topography plays a significant role in wildfire behavior. Mountainous terrain, characterized by steep slopes and canyons, facilitates rapid fire spread. Santa Ana winds, strong, dry winds originating from the inland deserts, are a major driver of intense and unpredictable fire behavior. These winds funnel through canyons and mountain passes, accelerating fire progression and making containment efforts extremely challenging. The chaparral ecosystem, prevalent throughout much of Southern California, is highly flammable. Its dense, dry vegetation, composed of shrubs and small trees adapted to drought conditions, readily ignites and burns rapidly.
A wildfire map reveals distinct areas of high fire risk. These areas often correlate with the presence of chaparral, proximity to canyons and mountain passes, and historical fire activity. Coastal regions, while not entirely immune, generally experience lower fire risk due to higher humidity and less intense winds. However, proximity to urban areas in these coastal zones can still lead to significant property damage and loss of life. The map also illustrates the impact of human activity. Accidental ignitions, such as power line failures, discarded cigarettes, and uncontrolled debris burning, contribute significantly to the number of wildfires. Furthermore, urban sprawl encroaching on wildlands increases the interface between human development and fire-prone vegetation, exacerbating the risk of devastating wildfires.
Analyzing the Data: Insights from Mapping Wildfire Events:
A comprehensive wildfire map, updated regularly, serves as an invaluable tool for various purposes. It allows for the identification of high-risk zones, enabling targeted preventative measures such as controlled burns and improved forest management practices. The spatial data can be used to model fire spread under different wind conditions and fuel loads, informing evacuation planning and resource allocation during active fire events. Historical fire data, displayed on such a map, reveals long-term trends and patterns, informing the development of more effective long-term strategies for wildfire mitigation. Analysis of the mapped data can also identify correlations between wildfire occurrence and factors like drought severity, land use changes, and climate variability. This information is crucial for adapting to a changing climate and mitigating the escalating risks associated with increasingly frequent and intense wildfires.
Effective Mitigation Strategies:
Effective wildfire management requires a multi-pronged approach. Fuel management strategies, such as controlled burns and the creation of defensible space around structures, are essential in reducing the intensity and spread of wildfires. Improved infrastructure, including upgraded power lines and better early warning systems, can minimize the risk of accidental ignitions. Public education campaigns promoting fire safety awareness are crucial in preventing human-caused fires. Furthermore, robust emergency response plans, encompassing effective evacuation strategies and efficient resource allocation, are vital in minimizing damage and loss of life during active fire events. Land-use planning that discourages development in high-risk areas and promotes fire-resistant building materials can also significantly reduce the impact of wildfires. Collaboration between government agencies, fire departments, and local communities is essential for the successful implementation of these strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What are the most common causes of wildfires in Southern California?
- A: A combination of factors contributes, including dry vegetation, Santa Ana winds, and human activities such as accidental ignitions (power lines, equipment use, discarded cigarettes) and intentional acts of arson.
-
Q: How can individuals protect their homes from wildfires?
- A: Creating defensible space around homes by removing flammable vegetation, using fire-resistant building materials, and having an evacuation plan are crucial steps.
-
Q: What role does climate change play in wildfire frequency and intensity?
- A: Climate change contributes to increased temperatures, prolonged drought conditions, and more intense Santa Ana winds, all of which exacerbate wildfire risk.
-
Q: What are the economic impacts of wildfires in Southern California?
- A: Wildfires cause significant economic losses through property damage, disruption of businesses, and the costs associated with firefighting and recovery efforts.
Tips for Wildfire Preparedness:
- Develop and practice a family evacuation plan, identifying multiple escape routes.
- Create defensible space around your home by clearing flammable vegetation.
- Regularly maintain and inspect your property for potential fire hazards.
- Stay informed about current fire weather conditions and evacuation orders.
- Prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies, including water, food, medications, and important documents.
Conclusion:
Southern California’s wildfire risk is a complex issue requiring a comprehensive and ongoing approach. Utilizing geographic information systems and wildfire maps to analyze spatial patterns and trends is fundamental to effective risk management. By combining robust mitigation strategies with proactive public education and emergency response planning, the region can work towards minimizing the devastating impacts of wildfires and ensuring the safety and well-being of its communities. Continuous monitoring, research, and adaptation to a changing climate are essential for long-term success in wildfire prevention and management.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Southern California Wildfires: A Geographic Analysis and Risk Mitigation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!