Stockholm: A Geographic and Urban Analysis
Related Articles: Stockholm: A Geographic and Urban Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Stockholm: A Geographic and Urban Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Stockholm: A Geographic and Urban Analysis
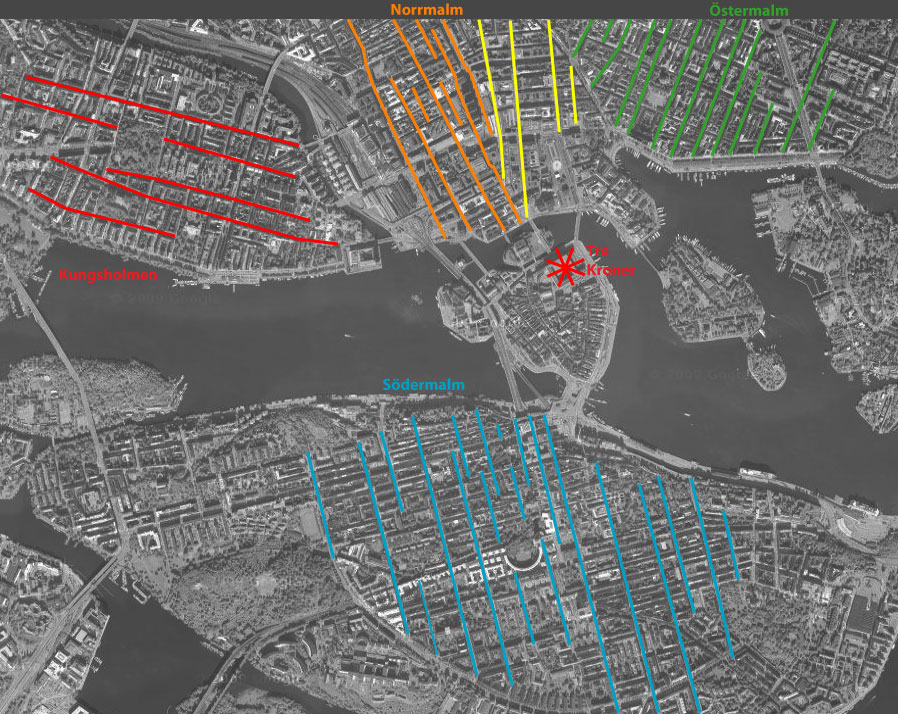
Stockholm, the capital of Sweden, occupies a unique and strategically important position on the map of Scandinavia. Its archipelago setting, comprising fourteen islands and numerous smaller islets, profoundly shapes its urban development, economy, and cultural identity. The city’s location at the confluence of Lake Mälaren and the Baltic Sea provides exceptional natural harborage and access to both inland waterways and the wider maritime world. This strategic placement has been crucial throughout its history, fostering trade, defense, and ultimately, the growth of a major Nordic metropolis.
Geographically, the city’s location is approximately 59°20′N 18°04′E. This high latitude contributes to significant seasonal variations in daylight hours, influencing the city’s lifestyle and urban planning. The archipelago itself is a defining feature, creating a complex and visually stunning urban landscape. The islands are connected by a network of bridges and ferries, forming a dynamic and interconnected urban fabric. This intricate system of waterways and landmasses necessitates a sophisticated transportation infrastructure, including extensive public transport networks, which are crucial for navigating the city’s geographically dispersed districts.
Examining the city on a map reveals its distinct zones. Gamla Stan, the Old Town, represents the historical heart, showcasing medieval architecture and narrow cobblestone streets. This area contrasts sharply with the more modern, expansive districts that extend outwards, reflecting the city’s growth and evolution. Norrmalm, for example, is a central business district, characterized by high-rise buildings and bustling commercial activity. Södermalm, located on a separate island, offers a blend of residential areas, trendy boutiques, and vibrant nightlife. These diverse districts, each with its unique character, contribute to the city’s multifaceted urban structure. Mapping these areas highlights the city’s organic growth pattern, influenced by both natural constraints and deliberate urban planning decisions.
The city’s position on the Baltic Sea has profoundly shaped its economic development. Historically, Stockholm served as a vital trading hub, connecting Scandinavia with the rest of Europe. This maritime heritage continues to influence its economy, with significant activity in shipping, logistics, and related industries. Furthermore, the city’s strong technological sector, coupled with a skilled workforce, has attracted numerous multinational companies, reinforcing its position as a significant European economic center. The accessibility afforded by its location and well-developed infrastructure are key factors in this economic success. Mapping the distribution of key industries and businesses illustrates the concentration of economic activity within the city and its immediate surroundings.
Stockholm’s cultural significance is equally noteworthy. The city boasts a rich history, reflected in its numerous museums, historical sites, and architectural landmarks. Its vibrant arts scene, encompassing music, theatre, and visual arts, contributes significantly to its cultural dynamism. The city’s location, nestled within a stunning natural environment, also provides ample opportunities for outdoor recreation, including boating, kayaking, and hiking. Mapping cultural institutions, parks, and recreational areas reveals the interwoven relationship between the city’s built environment and its natural surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the geographical location of Stockholm? Stockholm is located at approximately 59°20′N 18°04′E, on the eastern coast of Sweden, at the point where Lake Mälaren meets the Baltic Sea.
-
How many islands comprise Stockholm? The Stockholm archipelago comprises fourteen main islands, along with numerous smaller islets, forming the city’s unique urban landscape.
-
What are the major districts of Stockholm? Major districts include Gamla Stan (Old Town), Norrmalm (central business district), Södermalm, Östermalm, and Kungsholmen, each with its distinct character and function.
-
What is the significance of Stockholm’s location? The city’s location at the confluence of Lake Mälaren and the Baltic Sea has historically facilitated trade, provided natural defense, and continues to support its economic and cultural development.
-
What are the main transportation methods in Stockholm? The city relies heavily on a comprehensive public transport system, including metro, buses, trams, and ferries, to navigate its archipelago setting.
Tips for Exploring Stockholm:
-
Utilize public transport: Stockholm’s extensive public transport system is efficient and cost-effective.
-
Explore the archipelago: Take advantage of ferry services to discover the beauty of the islands surrounding the city.
-
Visit Gamla Stan: Explore the historical heart of Stockholm, with its medieval streets and architecture.
-
Experience the cultural scene: Attend a performance, visit a museum, or explore the city’s numerous art galleries.
-
Enjoy the outdoors: Take advantage of the city’s many parks, green spaces, and waterfront areas.
Conclusion:
The geographical location of Stockholm significantly influences its urban development, economic activity, and cultural identity. Its archipelago setting and position on the Baltic Sea have shaped its history and continue to drive its evolution as a major European city. The city’s unique spatial characteristics necessitate a sophisticated urban planning approach and a robust transportation infrastructure. Understanding the interplay between geography, urban design, and economic and cultural factors provides a comprehensive appreciation of Stockholm’s significance as a dynamic and influential Nordic metropolis.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Stockholm: A Geographic and Urban Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!