The 2016 United States Presidential Election: A State-by-State Analysis
Related Articles: The 2016 United States Presidential Election: A State-by-State Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The 2016 United States Presidential Election: A State-by-State Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The 2016 United States Presidential Election: A State-by-State Analysis

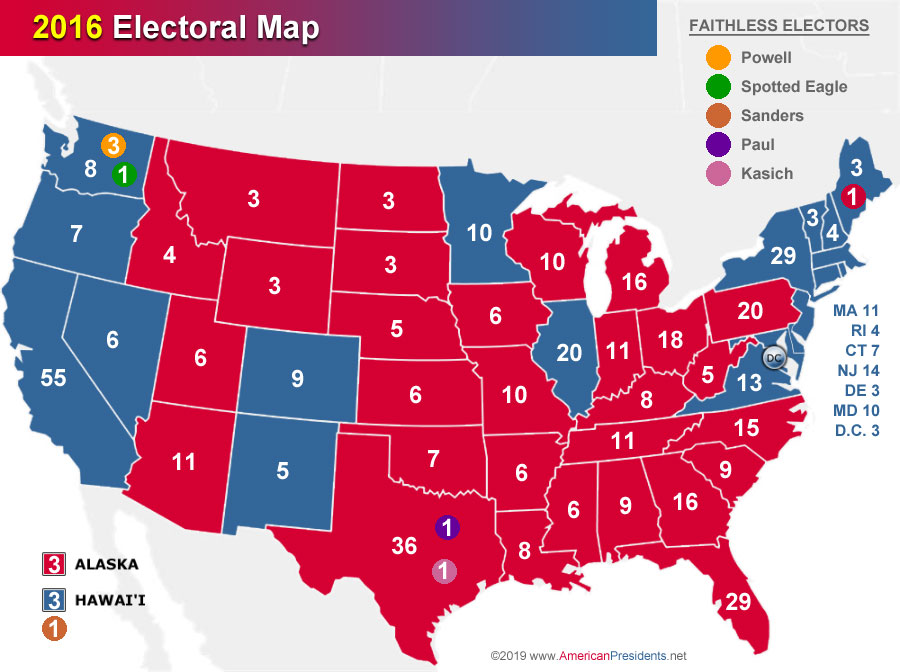
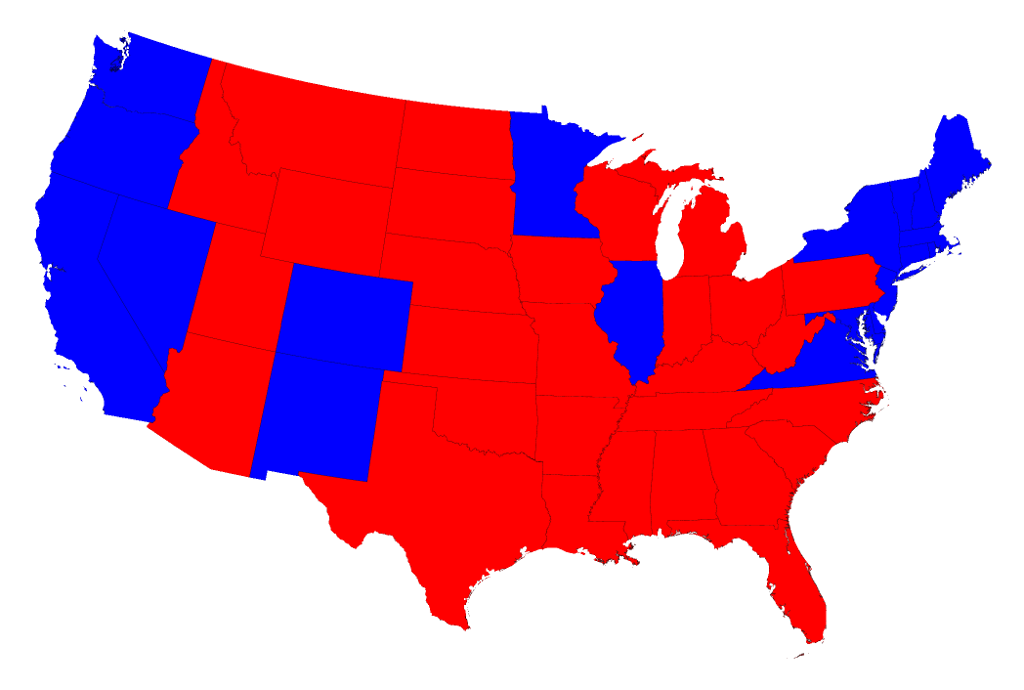
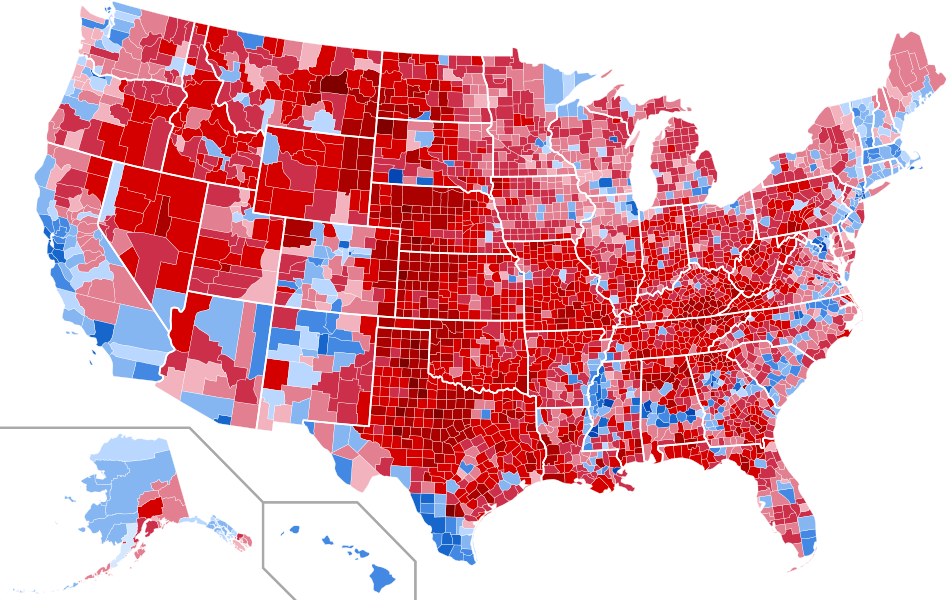
The 2016 United States presidential election resulted in a geographically fragmented outcome, vividly illustrated by the electoral map. Understanding this map requires examining the distribution of electoral votes across states, the underlying demographic and political factors that shaped voting patterns, and the implications of the result for the American political landscape.
The United States employs a winner-take-all system for presidential elections at the state level. Each state receives a number of electoral votes equal to its total number of senators (always two) and representatives in the House of Representatives (proportional to population). This allocation means that a candidate winning the popular vote in a state receives all of that state’s electoral votes. This system, while designed to balance the interests of smaller and larger states, often leads to situations where the national popular vote winner does not win the presidency, as was the case in 2000 and 2016.
The 2016 map showcased a clear geographical division. Republican candidate Donald Trump secured victory in a majority of states, predominantly in the South, Midwest, and Great Plains. These states, often characterized by rural populations and a higher proportion of white voters, demonstrated strong support for Trump’s populist message and promises of economic revitalization. Conversely, Democratic candidate Hillary Clinton won a majority of states on the coasts and in the Northeast. These regions, typically characterized by more urban populations and greater ethnic and racial diversity, were more receptive to Clinton’s platform focused on social justice, economic equality, and international cooperation.
Several key states proved pivotal in determining the election’s outcome. Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin, traditionally considered Democratic strongholds, unexpectedly swung to Trump. These "blue wall" states, crucial for Democratic victories in past elections, shifted due to a combination of factors, including economic anxieties among working-class voters, concerns about trade and globalization, and a perception that the Democratic Party was out of touch with the concerns of these communities. Florida, North Carolina, and Ohio, frequently considered swing states, also played a significant role, with their electoral votes ultimately contributing to Trump’s victory.
Analyzing the 2016 map reveals the importance of understanding the underlying demographic shifts and political realignments occurring across the nation. The rise of populism, fueled by economic uncertainty and social divisions, played a significant role in shaping voting patterns. The impact of social media and the spread of misinformation also deserve consideration, as these factors influenced public opinion and campaign strategies. Furthermore, the influence of gerrymandering – the practice of manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor a particular party – should not be overlooked, as it can impact the overall competitiveness of elections at the state and national levels.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: Why is the electoral map significant?
-
A: The electoral map provides a visual representation of the distribution of electoral votes across states, crucial for understanding the outcome of presidential elections. It highlights the importance of swing states and reveals the geographical divisions in the electorate.
-
Q: How are electoral votes allocated?
-
A: Each state receives a number of electoral votes equal to its total number of senators (two) and representatives in the House of Representatives (based on population). A candidate winning the popular vote in a state receives all of its electoral votes.
-
Q: What factors influenced the 2016 electoral map?
-
A: Numerous factors contributed, including demographic shifts, economic anxieties, the rise of populism, the impact of social media, and gerrymandering.
-
Q: Why did some traditionally Democratic states vote for Trump?
-
A: A combination of economic concerns, anxieties about globalization, and a perception that the Democratic Party was not adequately addressing the needs of working-class voters contributed to the shift in these "blue wall" states.
Tips for Interpreting the 2016 Electoral Map:
-
Focus on swing states: Pay close attention to states with closely contested elections, as these often determine the outcome.
-
Consider demographic data: Analyze population demographics (age, race, ethnicity, income) alongside voting patterns to understand regional variations.
-
Examine political party affiliation: Compare the map with data on party registration and voter turnout to gain a clearer picture of political alignment.
-
Account for historical context: Consider past election results and historical trends to better understand shifts in voting patterns.
-
Analyze media coverage: Examine the role of media coverage in shaping public opinion and influencing voting decisions.
Conclusion:
The 2016 electoral map serves as a powerful illustration of the complexities of the American political system. It reveals the importance of understanding not only national trends but also regional variations in political sentiment and the influence of various socio-economic factors. Analysis of this map provides valuable insights into the dynamics of presidential elections and underscores the need for ongoing research into the evolving political landscape of the United States. Further study should delve into the long-term implications of the 2016 results, considering the impact on policy, political discourse, and the future of American democracy. The map’s enduring significance lies in its ability to illuminate the ongoing debate about electoral reform and the ongoing search for a more representative and effective system of governance.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/7437967/2016_3.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The 2016 United States Presidential Election: A State-by-State Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!