The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
- 3.1 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.2 Tips for Analyzing Maps of Persia
- 3.3 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
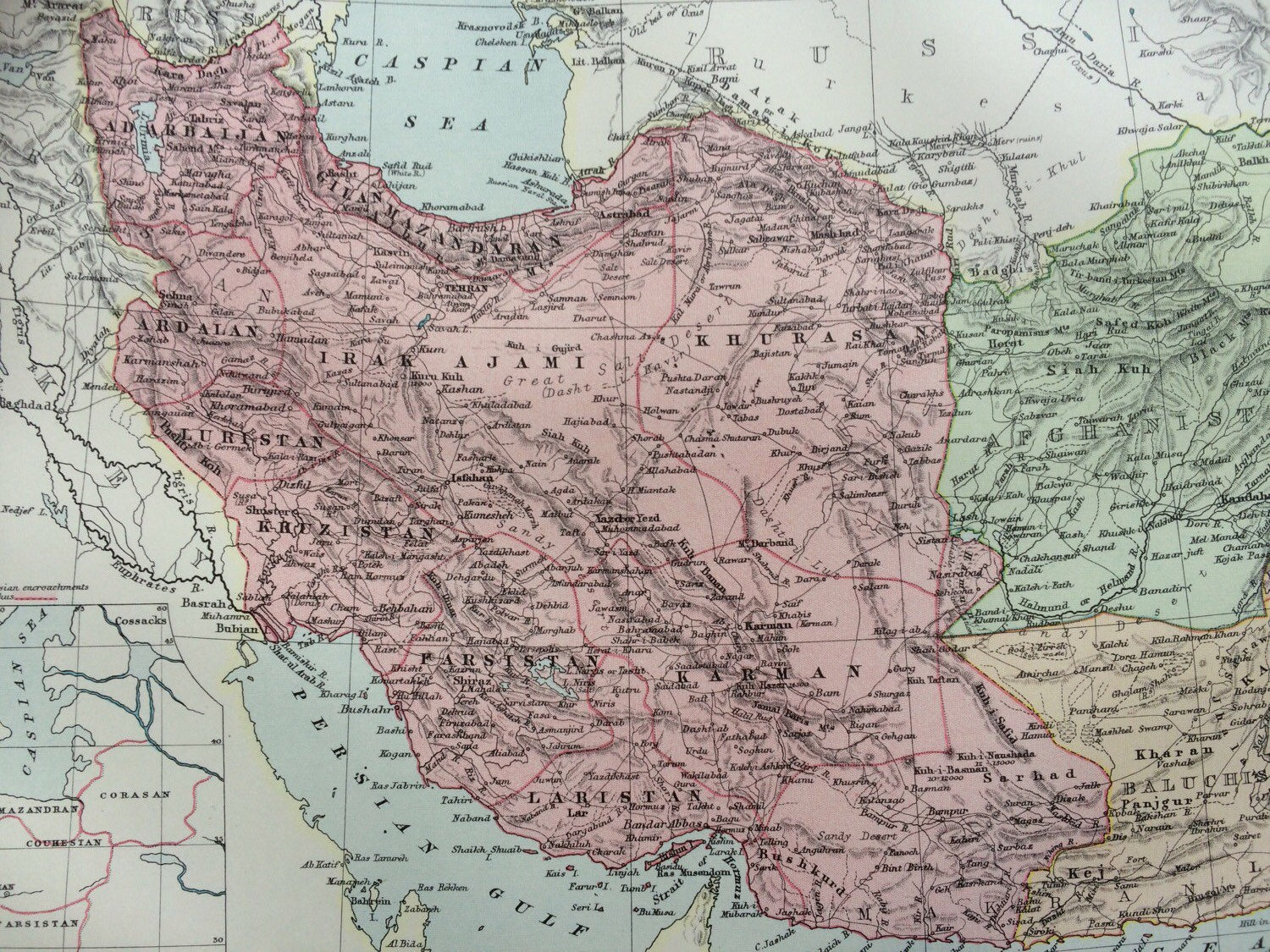
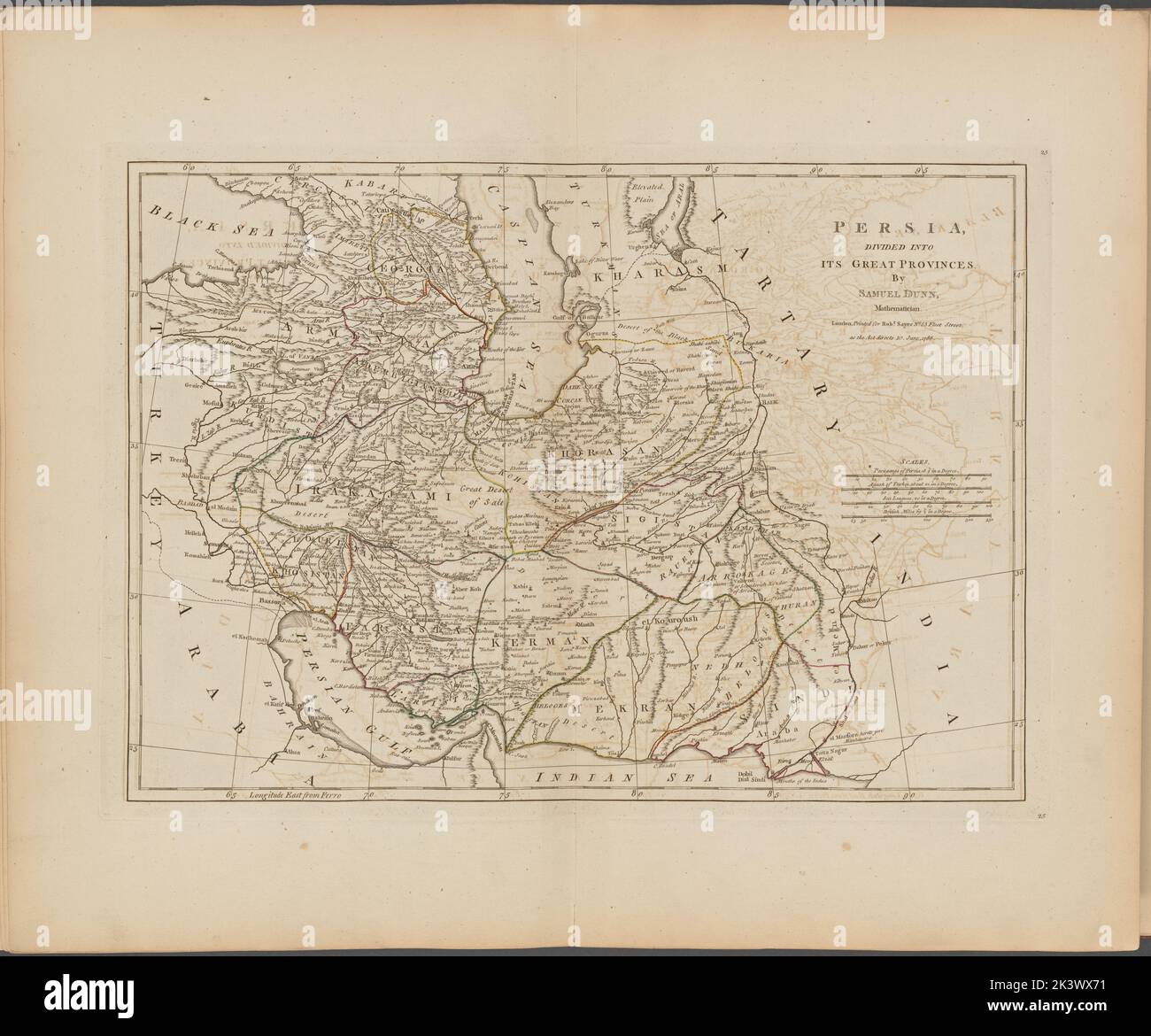
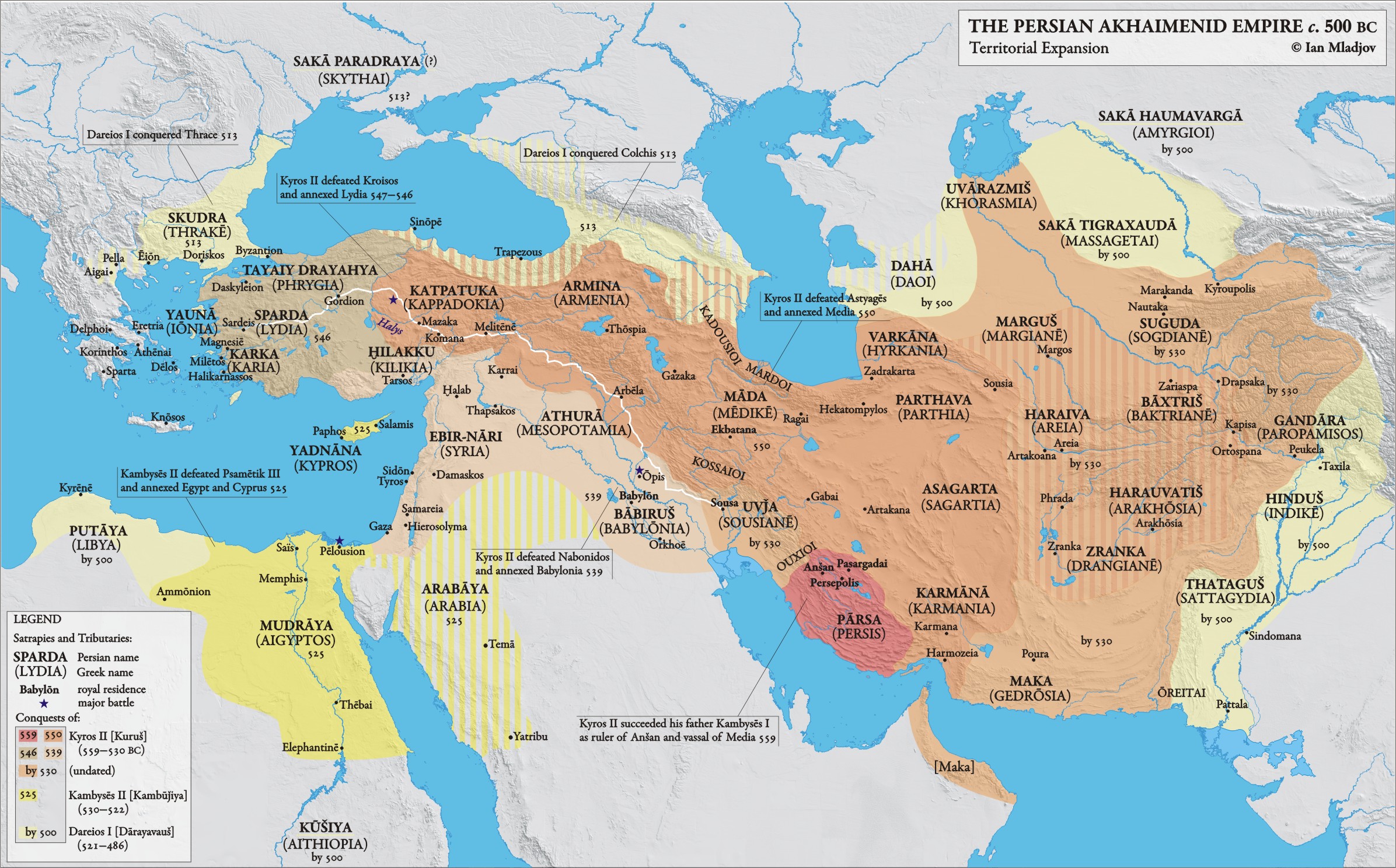
The geographical area historically known as Persia, encompassing modern-day Iran and surrounding regions, has been depicted on countless maps throughout history. These cartographic representations reflect not only the evolving understanding of the region’s physical geography but also the shifting political landscapes and cultural interactions that shaped its identity. Analyzing these maps provides valuable insight into the historical development of Persia, its connections to neighboring civilizations, and the enduring impact of its geographical location on its culture and power.
Early depictions of Persia, often found on world maps created in classical antiquity and the medieval period, frequently displayed a less precise and more symbolic representation of the region. These maps prioritized the placement of significant cities and landmarks rather than detailed geographical accuracy. The relative size and location of Persia often varied depending on the mapmaker’s perspective and the prevailing geopolitical context. For example, maps produced in the Hellenistic world might emphasize Persia’s relationship to the Greek world, while maps created in the Islamic Golden Age would highlight its central position within a broader Islamic empire.
The development of cartography during the Renaissance and the subsequent Age of Exploration led to a significant improvement in the accuracy and detail of maps depicting Persia. European explorers and cartographers, spurred by trade and imperial ambitions, began to produce maps based on more reliable geographical data gathered through surveys, observations, and the accounts of travelers. These maps provide a more nuanced understanding of Persia’s physical features, including its mountainous terrain, vast deserts, and fertile river valleys. The inclusion of increasingly detailed geographical information reflects a growing interest in the region’s natural resources and its potential for economic exploitation.
However, even with improved cartographic techniques, the portrayal of Persia on maps often reflected the biases and political agendas of the mapmakers. Colonial-era maps, for instance, frequently emphasized Persia’s strategic location within the broader context of European imperial ambitions in Asia. These maps often highlighted potential trade routes, resource-rich areas, and strategic military positions, reflecting the colonial powers’ desire to control and exploit the region’s resources.
The 20th and 21st centuries have witnessed the emergence of highly accurate and detailed maps of Persia, facilitated by advancements in surveying technologies, satellite imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS). Modern maps accurately depict the region’s topography, hydrography, and political boundaries. These maps are invaluable tools for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, resource management, environmental monitoring, and disaster response. Furthermore, the digitalization of historical maps has made it possible to analyze and compare various cartographic representations of Persia over time, offering a unique perspective on the region’s historical evolution and its enduring geographical significance.
The study of Persia’s representation on maps reveals the interplay between geographical reality, political power, and cultural perception. The changing portrayal of the region reflects the shifting geopolitical landscape, the evolution of cartographic techniques, and the enduring fascination with this historically significant area. Analyzing these maps provides a rich source of information for historians, geographers, and other scholars seeking to understand Persia’s past, present, and future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How did the depiction of Persia on maps change over time?
A: The depiction of Persia evolved from relatively imprecise and symbolic representations in antiquity to highly accurate and detailed maps in the modern era. Early maps prioritized key cities and landmarks, while later maps incorporated more detailed geographical information, reflecting improvements in cartographic techniques and access to data. Political and cultural biases also influenced how Persia was portrayed.
Q: What information can be gleaned from historical maps of Persia?
A: Historical maps offer valuable insights into the region’s physical geography, political boundaries, urban development, trade routes, and cultural interactions. They can reveal changes in the understanding of the region’s geography, the shifting political landscape, and the influence of different cultures and empires.
Q: How do modern maps of Persia differ from historical maps?
A: Modern maps benefit from advanced technologies, resulting in significantly improved accuracy and detail. They utilize satellite imagery and GIS to provide precise representations of topography, hydrography, and political boundaries. Modern maps also incorporate a broader range of data, including demographic information, resource distribution, and infrastructure networks.
Q: What is the significance of studying the cartographic representation of Persia?
A: Studying the cartographic representation of Persia provides a multi-faceted understanding of the region’s historical development, its relationship with neighboring civilizations, and the impact of its geography on its culture and political power. It allows for a critical analysis of how geographical knowledge has been shaped by political and cultural factors.
Tips for Analyzing Maps of Persia
- Consider the map’s context: Examine the map’s creation date, the mapmaker’s background, and the intended audience. Understanding the context helps to interpret the map’s biases and limitations.
- Analyze the geographical features: Pay attention to the depiction of mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastlines. Compare different maps to identify variations in accuracy and detail.
- Examine the political boundaries: Observe how political boundaries are represented on different maps, noting any changes over time. This reveals shifts in political control and territorial disputes.
- Identify key cities and landmarks: Note the location and prominence of major cities and other significant features. This provides insights into urban development and the importance of specific locations.
- Compare maps from different periods: Comparing maps from various historical periods reveals how the understanding of Persia’s geography and political landscape evolved over time.
Conclusion
The cartographic representation of Persia offers a compelling lens through which to examine the region’s historical trajectory and its enduring geographical significance. The evolution of its portrayal on maps reflects not only advancements in cartographic techniques but also the interplay between geographical reality, political power, and cultural perception. By analyzing these maps, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of Persia’s complex past, its multifaceted interactions with neighboring civilizations, and its continuing relevance in the modern world. The continued study of these historical and contemporary maps remains crucial for a complete understanding of the region’s multifaceted history and its ongoing importance in the global context.
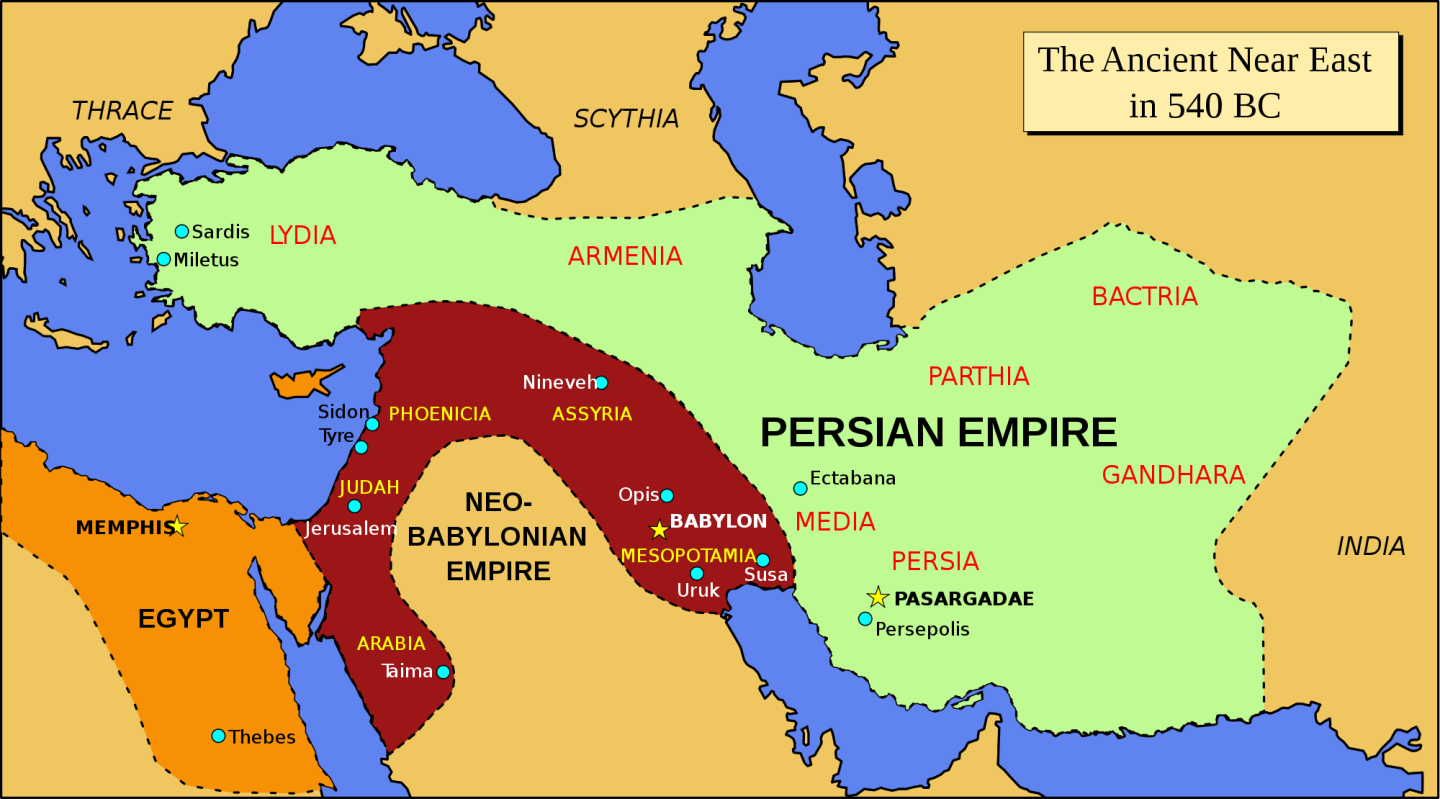
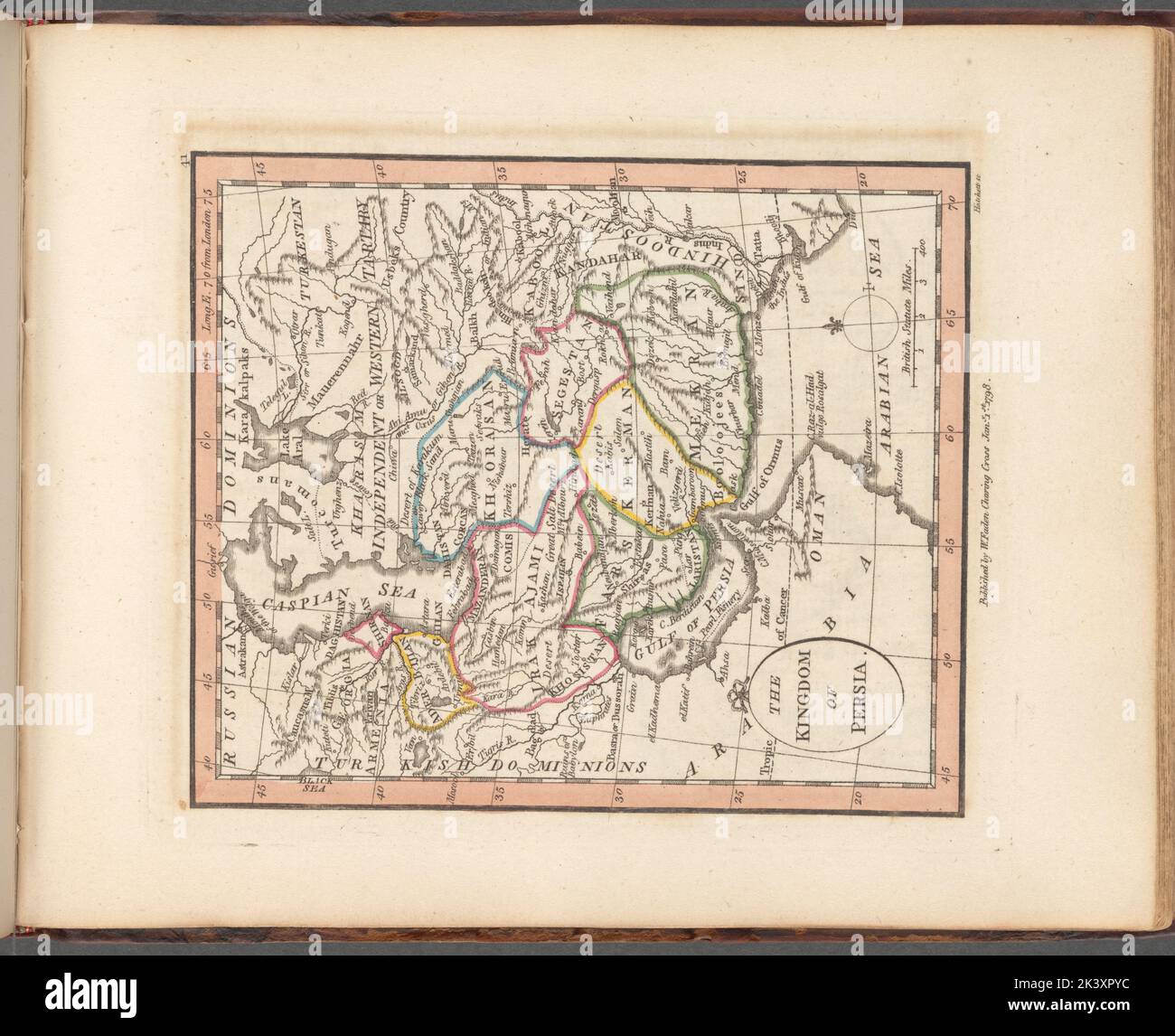

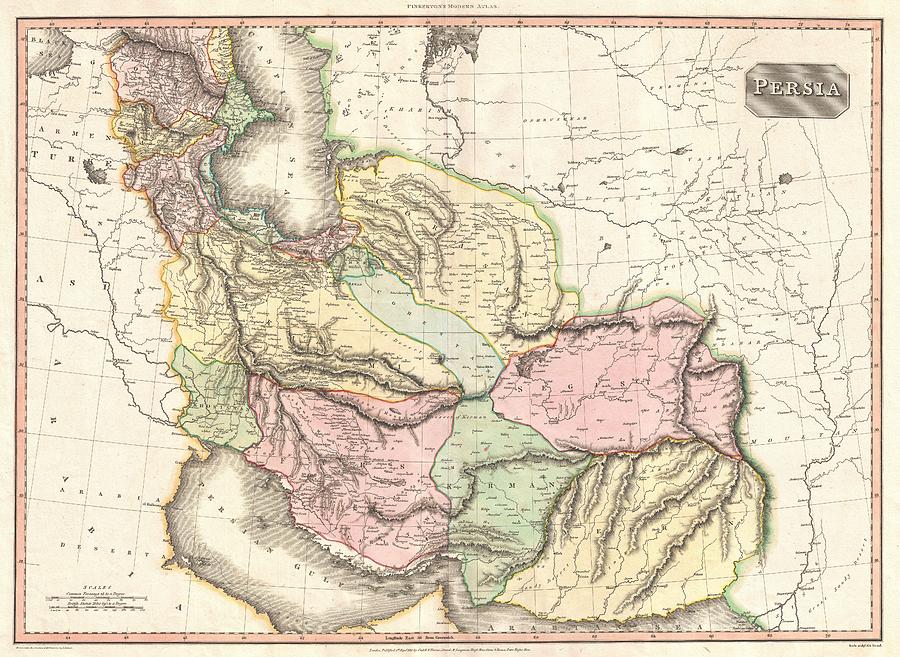


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cartographic Representation of Persia: A Historical and Geographical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!