The Cervical Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Cervical Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Cervical Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Cervical Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Overview
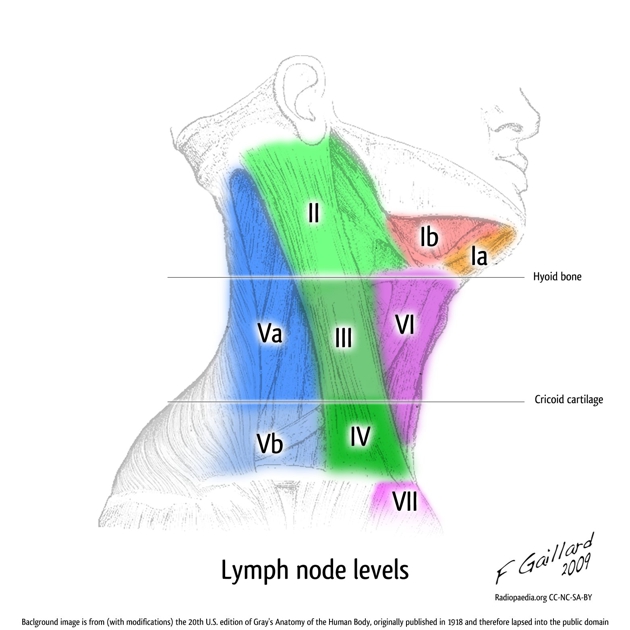
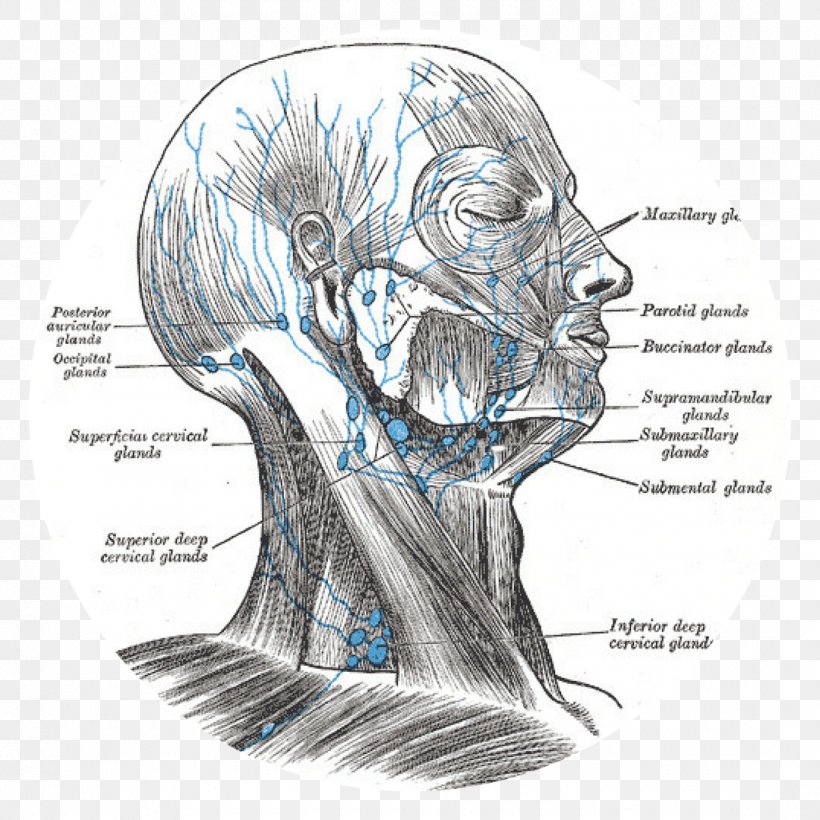
The neck houses a complex network of lymph nodes, crucial components of the body’s immune system. These nodes, strategically positioned throughout the cervical region, play a vital role in filtering lymph fluid and defending against infection and disease. Understanding their location and function is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of various medical conditions.
Anatomical Distribution and Regional Groups:
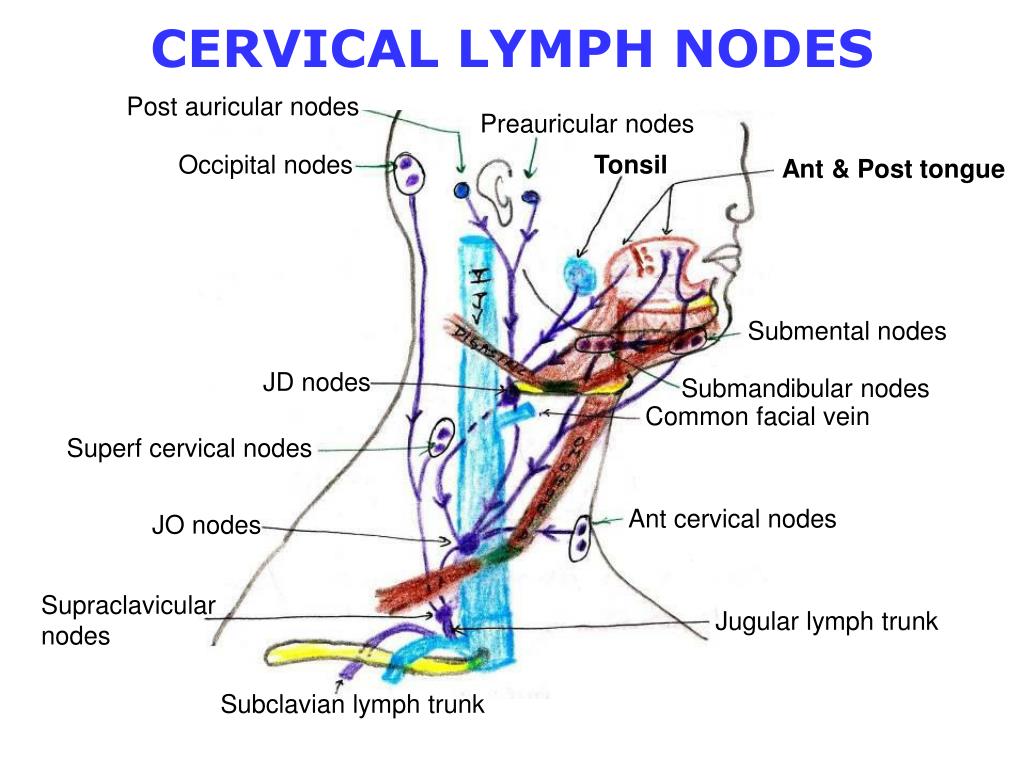
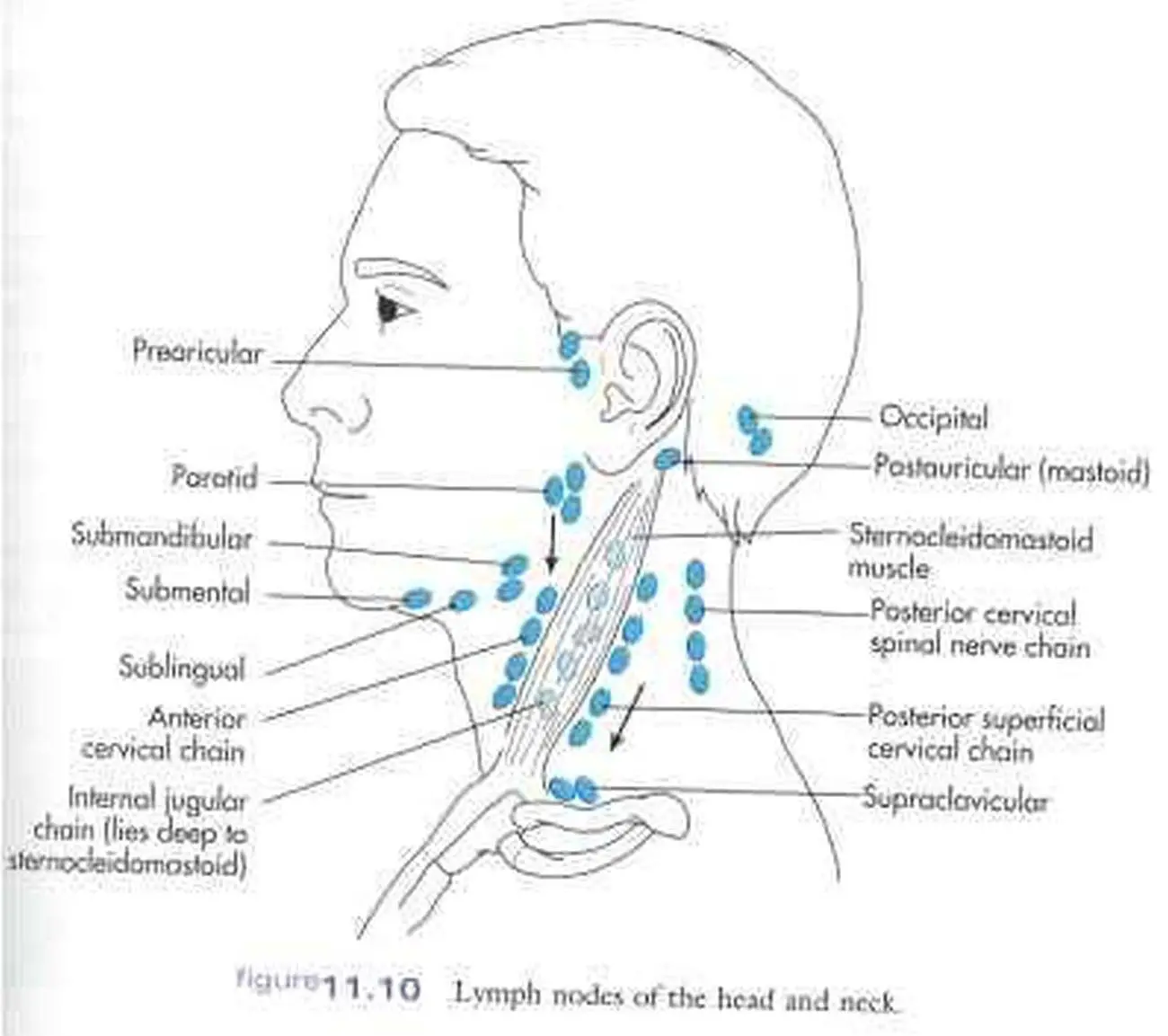
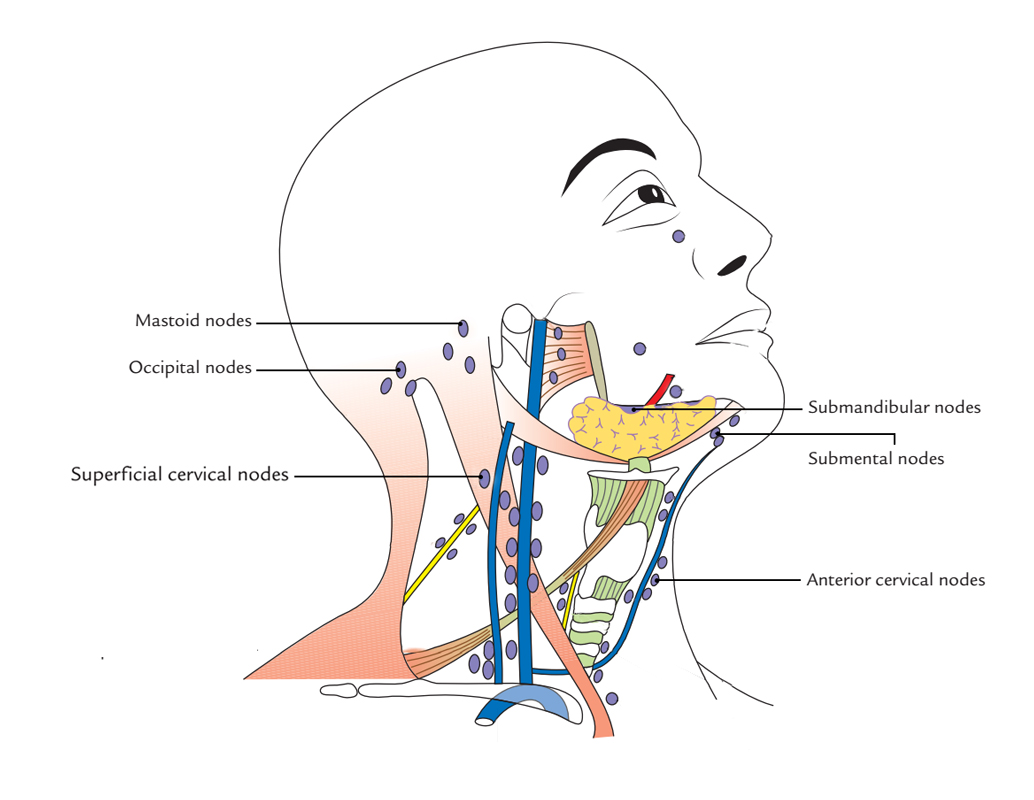
The cervical lymph nodes are not haphazardly scattered; instead, they are organized into distinct groups, each draining specific areas of the head, neck, and upper torso. Precise delineation of these groups is crucial for clinicians to interpret findings from physical examinations and imaging studies. These groupings include:
-
Anterior Cervical Chain: Located along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, this chain drains lymph from the anterior aspects of the neck, including the thyroid gland, larynx, and floor of the mouth. Subgroups within this chain can be further identified based on their precise location.
-
Posterior Cervical Chain: This group lies along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and drains lymph from the scalp, posterior neck, and upper back.
-
Lateral Cervical Chain: Situated along the sternocleidomastoid muscle itself, this chain receives lymph from various sources, including the anterior and posterior cervical chains, as well as the parotid and submandibular glands. It plays a significant role in overall neck drainage.
-
Superficial Cervical Nodes: These nodes are located superficially in the subcutaneous tissue of the neck and drain the skin and superficial structures.
-
Deep Cervical Chain: This chain, situated deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, is often considered the most important group in the neck. It receives lymph from the other cervical chains and also drains the pharynx, tonsils, and oral cavity. The jugulodigastric node, a particularly important node within this group, is often examined for signs of infection or malignancy.
-
Submandibular Nodes: Located beneath the mandible, these nodes drain the floor of the mouth, lower lip, and submandibular salivary gland. Enlargement of these nodes can be indicative of oral infections or tumors.
-
Preauricular and Postauricular Nodes: Located in front of and behind the ear, respectively, these nodes drain the scalp and external ear.
-
Occipital Nodes: Situated at the base of the skull, these nodes drain the posterior scalp.
Functional Significance:
The primary function of these nodes is filtration of lymph fluid. Lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, collects waste products, bacteria, and other foreign substances from tissues throughout the body. As lymph passes through the lymph nodes, specialized cells, including lymphocytes and macrophages, actively filter and remove these harmful substances, preventing their spread throughout the system. This filtering process is vital for maintaining overall health and preventing infection. When infection or malignancy occurs in an area drained by a specific node, that node may become enlarged and tender, a clinically significant sign.
Clinical Importance and Diagnostic Significance:
Examination of the cervical lymph nodes is a crucial component of any physical examination, particularly in patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of infection or malignancy in the head and neck region. Enlarged or tender lymph nodes can indicate a variety of conditions, ranging from simple infections to serious malignancies. The location of the affected nodes can provide valuable clues regarding the source of the problem. For instance, enlarged submandibular nodes might suggest an infection in the mouth or throat, while enlarged posterior cervical nodes could indicate scalp infection or a more systemic process.
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a vital role in further evaluating suspicious lymph nodes. These modalities can provide detailed images of the nodes, revealing their size, shape, and internal structure, helping differentiate benign from malignant processes. Biopsy, the removal of a small tissue sample for microscopic examination, may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis in ambiguous cases.
FAQs:
-
Q: What causes swollen lymph nodes in the neck? A: Swollen lymph nodes, or lymphadenopathy, can be caused by various factors, including infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and malignancies.
-
Q: Are swollen neck lymph nodes always serious? A: Not always. Many cases of swollen lymph nodes are caused by benign infections that resolve spontaneously. However, persistent or rapidly enlarging nodes warrant medical evaluation to rule out more serious conditions.
-
Q: What tests are used to diagnose the cause of swollen lymph nodes? A: Physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI), and biopsy are commonly used to determine the cause of swollen lymph nodes.
-
Q: What is the treatment for swollen lymph nodes? A: Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Infections may be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications, while malignancies require more extensive treatment, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Tips for Maintaining Cervical Lymphatic Health:
-
Maintain good hygiene: Regular handwashing and oral hygiene can help prevent infections that can lead to swollen lymph nodes.
-
Address infections promptly: Seeking medical attention for infections promptly can prevent their spread and minimize the risk of lymphadenopathy.
-
Avoid exposure to potential irritants: Limiting exposure to allergens and irritants can reduce inflammation and the risk of swollen lymph nodes.
-
Maintain a healthy immune system: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep contribute to a strong immune system, helping the body fight off infections more effectively.
Conclusion:
The cervical lymphatic system plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and immunity. A thorough understanding of the anatomical distribution and functional significance of cervical lymph nodes is essential for clinicians to accurately diagnose and manage various medical conditions. Prompt medical evaluation of any persistent or concerning changes in the neck lymph nodes is crucial to ensure timely and appropriate intervention. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the overall health of the lymphatic system and reduce the risk of developing lymphadenopathy.


:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/inferior-deep-lateral-cervical-lymph-nodes/9owLDNI9JFcUupxnIJFg_Inferior_deep_cervical_lymph_nodes.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cervical Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!