The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in Russia: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in Russia: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in Russia: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in Russia: A Geographic Perspective
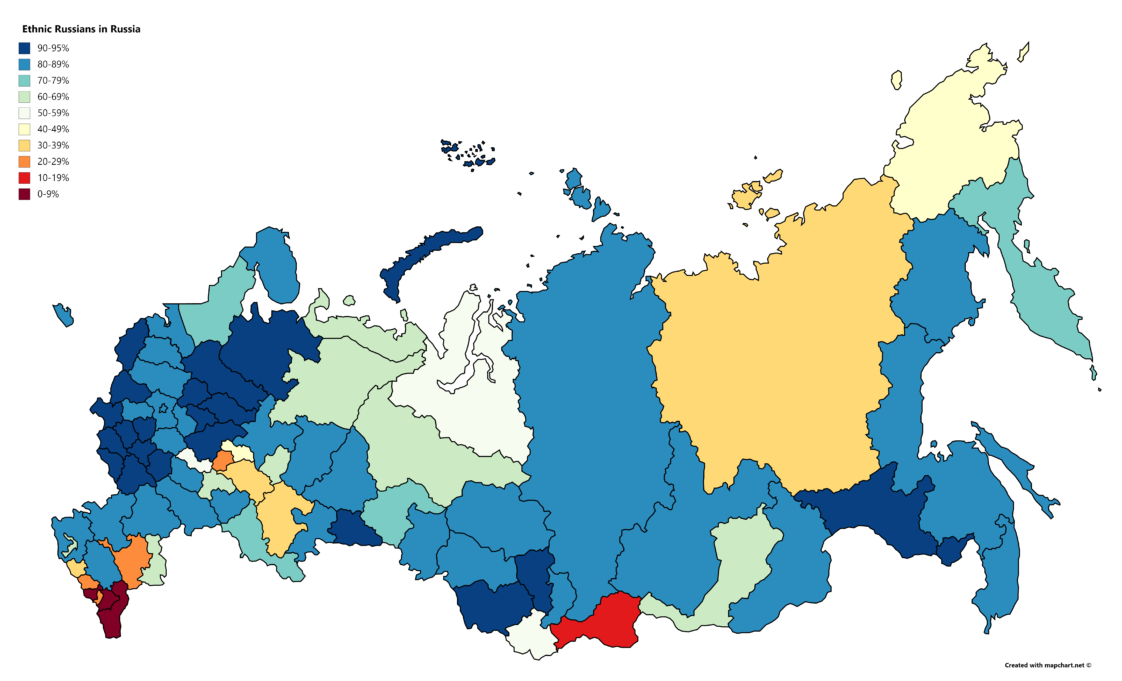
Russia’s ethnic composition is a remarkably diverse and intricate tapestry woven over centuries of migration, conquest, and cultural exchange. Understanding the geographic distribution of ethnic groups within the Russian Federation is crucial for comprehending the nation’s history, political dynamics, and social fabric. Analysis of this demographic landscape reveals a complex interplay of factors, including historical settlement patterns, Soviet-era policies, and contemporary socio-economic forces.
The dominant ethnic group is Russian, comprising a significant majority of the population. However, this group’s distribution is far from uniform. Concentrations are highest in the European portion of the country, particularly in the central regions and around major urban centers. Density diminishes significantly as one moves eastward into Siberia and the Far East. This uneven distribution reflects historical migration patterns, with Russian expansion eastward beginning centuries ago and accelerating under imperial and Soviet rule. The colonization of Siberia, for example, resulted in the establishment of numerous Russian settlements, leading to the displacement and assimilation of indigenous populations in many areas.
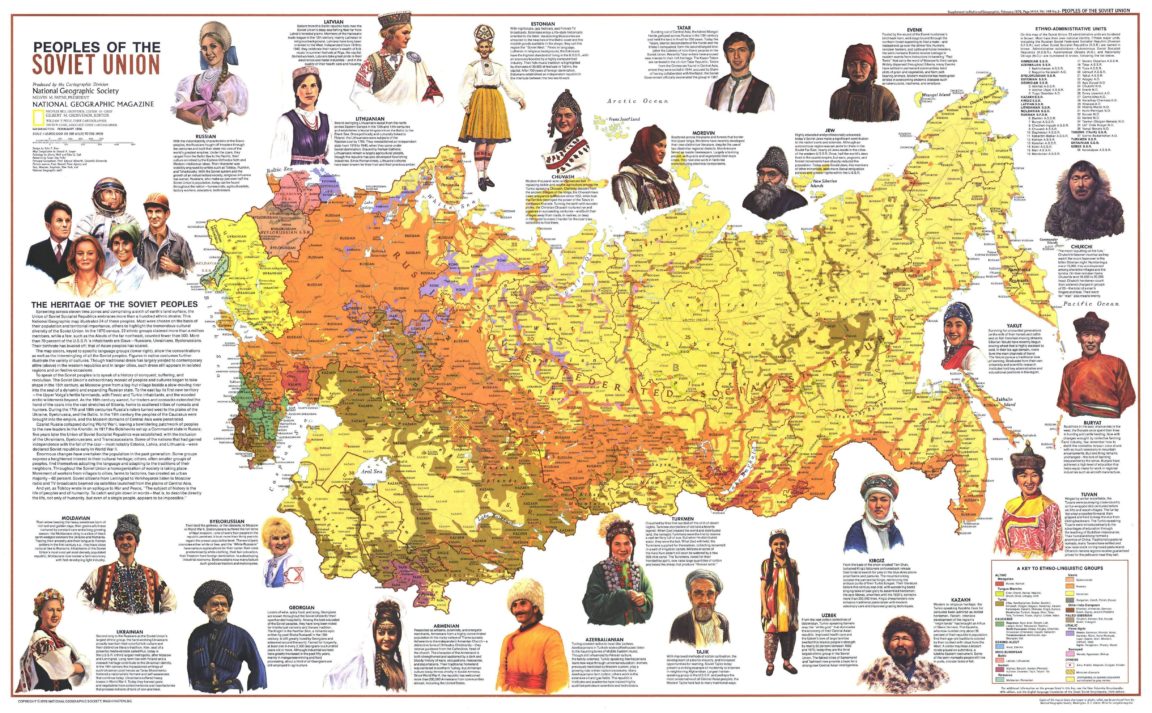
Numerous other ethnic groups call Russia home, each with its own unique history, language, and culture. The Volga region, for instance, is home to significant populations of Tatars, a Turkic-speaking group with a long and rich history in the area. The North Caucasus houses a diverse array of ethnic groups, including Chechens, Ingush, Dagestanis, and Kabardians, each possessing distinct linguistic and cultural identities. These regions have witnessed periods of both cooperation and conflict, shaped by historical power dynamics and competing claims to territory and resources.
In the southern regions bordering Ukraine and Kazakhstan, significant Ukrainian and Kazakh populations exist, reflecting historical migrations and border shifts. The Ural Mountains, a natural dividing line between Europe and Asia, also mark a significant demographic transition. While the western slopes are predominantly Russian, the eastern slopes exhibit a greater diversity, with significant populations of Uralic-speaking groups, such as the Komi and Udmurt. Siberia and the Far East display an even more diverse ethnic mosaic, with numerous indigenous groups, including Buryats, Yakuts, and Evenks, maintaining their distinct cultural heritages amidst a significant Russian presence. These groups often inhabit geographically isolated areas, preserving their traditional ways of life despite the pressures of modernization and integration into the broader Russian state.
Mapping these ethnic distributions reveals important insights into regional disparities in economic development, social cohesion, and political stability. Areas with significant non-Russian populations often experience higher levels of ethnic tension and potential for conflict, particularly when coupled with socio-economic inequalities. Conversely, regions with a more homogeneous ethnic composition may exhibit greater social stability but might also face challenges related to cultural homogeneity and the potential marginalization of minority groups.
The Soviet era significantly impacted the ethnic landscape. While promoting a sense of shared Soviet identity, Soviet policies also resulted in the forced relocation of entire populations, often for political or economic reasons. This led to the resettlement of certain ethnic groups in new regions, altering existing demographic patterns and sometimes contributing to inter-ethnic tensions. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 further complicated the ethnic map, with the emergence of new independent states and subsequent migrations across newly established borders.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the most accurate source for data on Russia’s ethnic composition? The most reliable data comes from the official censuses conducted by the Russian Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat). However, the accuracy of census data is often debated, particularly concerning the self-identification of ethnicity and potential underreporting of certain groups.
-
How does the ethnic map reflect historical events? The current distribution of ethnic groups is a direct reflection of centuries of migration, conquest, colonization, and political decisions. Historical events, from imperial expansion to Soviet resettlement programs, have profoundly shaped the current ethnic mosaic.
-
What are the implications of ethnic diversity for Russia’s political stability? Ethnic diversity can contribute to both political stability and instability. While a diverse society can foster innovation and cultural richness, it can also lead to inter-ethnic tensions and conflict if not managed effectively. Addressing socio-economic disparities and promoting inclusivity are crucial for mitigating potential risks.
Tips for Analyzing the Ethnic Map:
-
Consider the scale of analysis: Analyzing the data at different levels (national, regional, local) reveals different insights. National-level data provides an overview, while regional and local data provide a more nuanced understanding of specific areas.
-
Examine historical context: Understanding the historical events that shaped the current distribution is essential for interpreting the map accurately.
-
Look for patterns and anomalies: Identifying clusters of specific ethnic groups and areas with unusual distributions can highlight significant historical or socio-political processes.
Conclusion:
The ethnic map of Russia is a dynamic and multifaceted representation of the country’s complex history and present-day reality. Understanding this intricate demographic landscape requires careful consideration of historical context, socio-economic factors, and the inherent limitations of available data. Further research and analysis are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between ethnicity, geography, and political dynamics within the Russian Federation. The ongoing evolution of this demographic landscape necessitates continuous monitoring and critical evaluation of the available information. Only through such a rigorous approach can a deeper understanding of this critical aspect of Russia’s identity be achieved.



/bnn/media/post_attachments/content/uploads/2023/11/russia-ukraine-conflict-20231110083024.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in Russia: A Geographic Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
