The Enclave within Rome: A Geographic and Symbolic Analysis of Vatican City
Related Articles: The Enclave within Rome: A Geographic and Symbolic Analysis of Vatican City
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enclave within Rome: A Geographic and Symbolic Analysis of Vatican City. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enclave within Rome: A Geographic and Symbolic Analysis of Vatican City

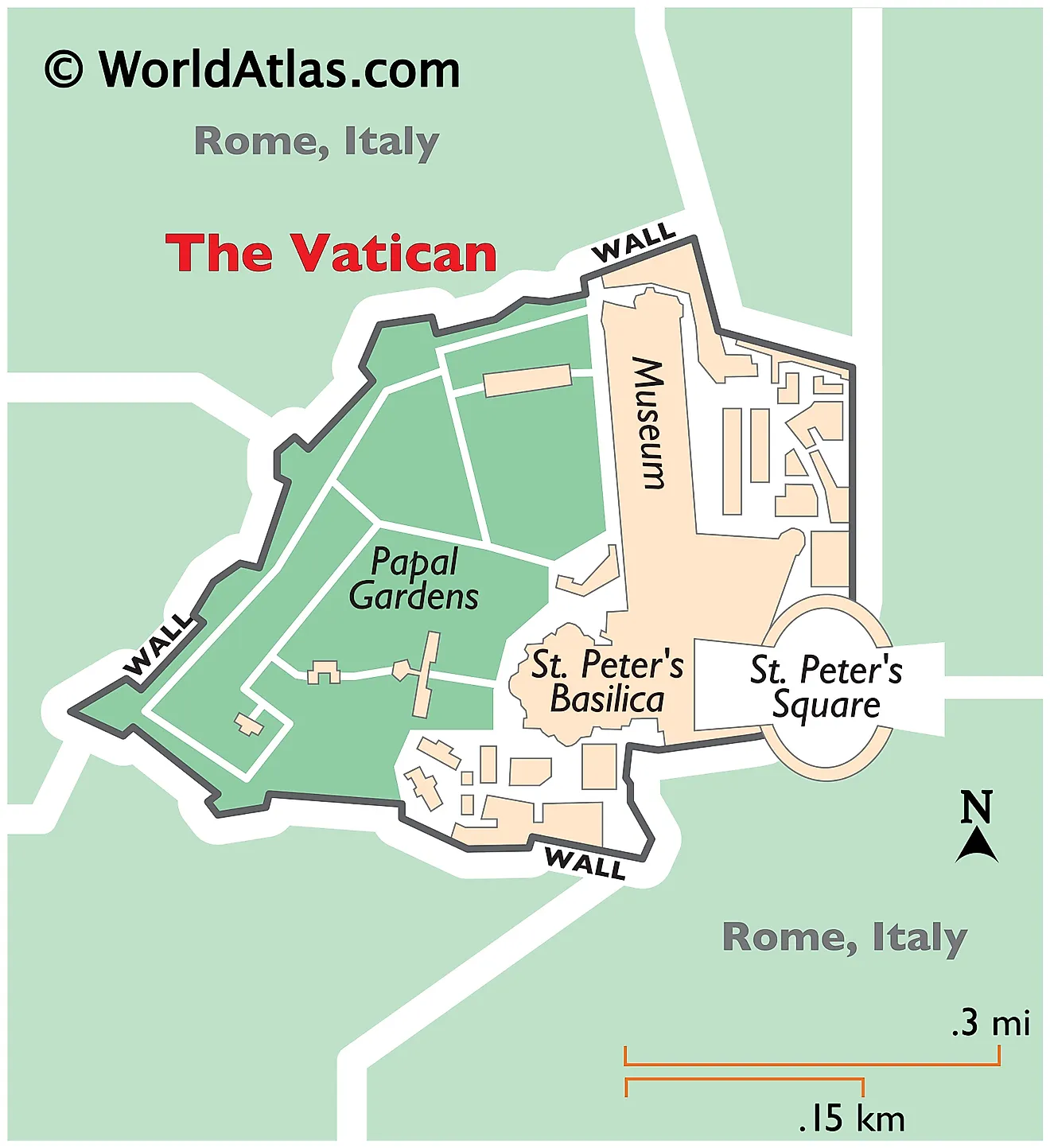
Vatican City, the smallest country globally, occupies a unique position within the city of Rome, Italy. Its geographical boundaries, though minuscule, hold immense historical, religious, and political significance. Understanding its location and spatial characteristics requires examining its relationship with Rome and its broader European context. The enclave’s map reveals a compact area, roughly 0.44 square kilometers, situated on the right bank of the Tiber River, west of the city center. This seemingly insignificant area houses St. Peter’s Basilica, the Vatican Museums, and the Apostolic Palace, structures that represent centuries of papal power and artistic achievement. The precisely defined boundaries, established through international treaties, are clearly demarcated, separating the Holy See’s sovereign territory from Italian territory.
The historical evolution of the enclave’s borders is crucial to understanding its current configuration. The papal states, a significant territorial entity throughout the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, progressively diminished in size over centuries. The unification of Italy in the 19th century resulted in a significant reduction of papal authority and territory. The Lateran Treaty of 1929, a landmark agreement between the Kingdom of Italy and the Holy See, formally established Vatican City as an independent state, resolving the "Roman Question" that had lasted for decades. This treaty defined the precise boundaries of the new state, granting it extraterritoriality and sovereign immunity. The resulting map reflects a deliberate choice to consolidate key papal properties into a compact and easily defensible area.
The geographical compactness of the state contributes to its unique administrative and logistical challenges. The limited space necessitates careful urban planning and resource management. The concentration of significant historical and artistic treasures within such a small area poses unique preservation challenges, requiring specialized expertise and significant investment in conservation efforts. The close proximity to Rome, however, offers advantages in terms of accessibility and infrastructure, mitigating some of the challenges inherent in its small size. The city’s location within a major European capital also facilitates communication and diplomatic relations with other nations.
The symbolic importance of the location surpasses its physical dimensions. Situated within the heart of a city steeped in ancient Roman history and Christian tradition, the enclave’s location serves as a powerful reminder of the enduring influence of the Catholic Church. The proximity to significant historical sites, such as the Pantheon and the Colosseum, underscores the continuity between the ancient world and the present. The location also reflects the historical claims of the papacy to spiritual authority, reinforcing its role as a global center of religious influence. The Vatican’s strategic location within Europe, a continent with a rich history of religious and political conflict, underscores its continued relevance in shaping contemporary international affairs.
The map of Vatican City, therefore, is more than a simple geographical representation; it is a visual testament to a complex history and an enduring institution. The precise delineation of its borders reflects the delicate balance between religious authority and political realities, a testament to the enduring legacy of the Lateran Treaty. The enclave’s compact nature presents unique challenges, yet also emphasizes the concentration of power and influence within a small, easily identifiable space.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the exact boundaries of Vatican City? The boundaries are defined by the Lateran Treaty of 1929 and are clearly demarcated. Precise coordinates are available through various geographical resources.
-
Is Vatican City completely surrounded by Italy? Yes, Vatican City is an entirely landlocked enclave within the city of Rome, Italy.
-
What is the significance of the Lateran Treaty in defining the city’s boundaries? The Lateran Treaty formally established Vatican City as an independent state, resolving the "Roman Question" and defining its precise geographical limits.
-
How does the size of Vatican City impact its administration? The small size necessitates efficient resource management, specialized urban planning, and careful consideration of space allocation.
-
What is the relationship between Vatican City and the Italian government? While Vatican City is an independent state, its close proximity to Rome necessitates ongoing diplomatic relations and cooperation with the Italian government.
Tips for Visiting Vatican City:
-
Plan ahead: Book tickets in advance for museums and St. Peter’s Basilica, especially during peak season.
-
Dress modestly: Appropriate attire is required when visiting religious sites.
-
Be prepared for crowds: The Vatican is a popular tourist destination; expect large crowds, especially at popular attractions.
-
Utilize public transportation: Rome’s public transportation system offers easy access to the Vatican.
-
Allow ample time: Exploring the Vatican Museums and St. Peter’s Basilica requires several hours.
Conclusion:
The map of Vatican City represents more than just a geographical location; it embodies a unique confluence of history, religion, and politics. The enclave’s small size belies its immense global influence, reflecting centuries of papal authority and artistic achievement. Its location within Rome serves as a powerful symbol of continuity between ancient and modern history, while its independent status highlights the complex relationship between religious authority and secular governance. Understanding the geographical context of Vatican City is essential to comprehending its enduring significance within the European landscape and on the world stage.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enclave within Rome: A Geographic and Symbolic Analysis of Vatican City. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!