The Geographic Power of Postal Codes: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Geographic Power of Postal Codes: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geographic Power of Postal Codes: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geographic Power of Postal Codes: A Comprehensive Overview

Postal codes, also known as zip codes in some regions, are alphanumeric codes assigned to geographic areas for efficient mail sorting and delivery. Their significance extends far beyond simple mail routing, however. These codes serve as crucial locational identifiers, underpinning a vast array of applications across various sectors, from logistics and commerce to public health and urban planning. This article explores the multifaceted role of these codes, their underlying structure, and their impact on modern society.
Understanding the Structure and Functionality
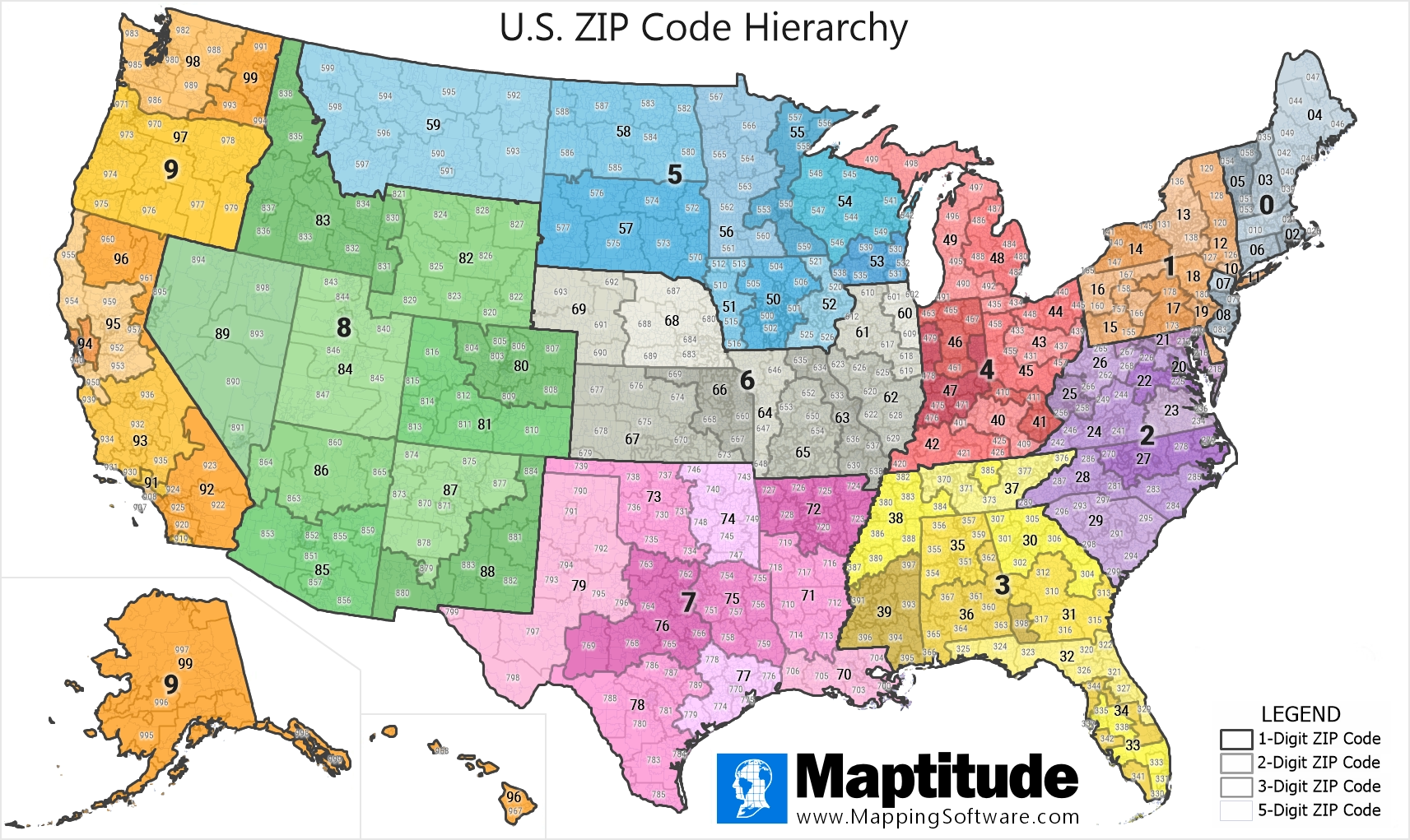
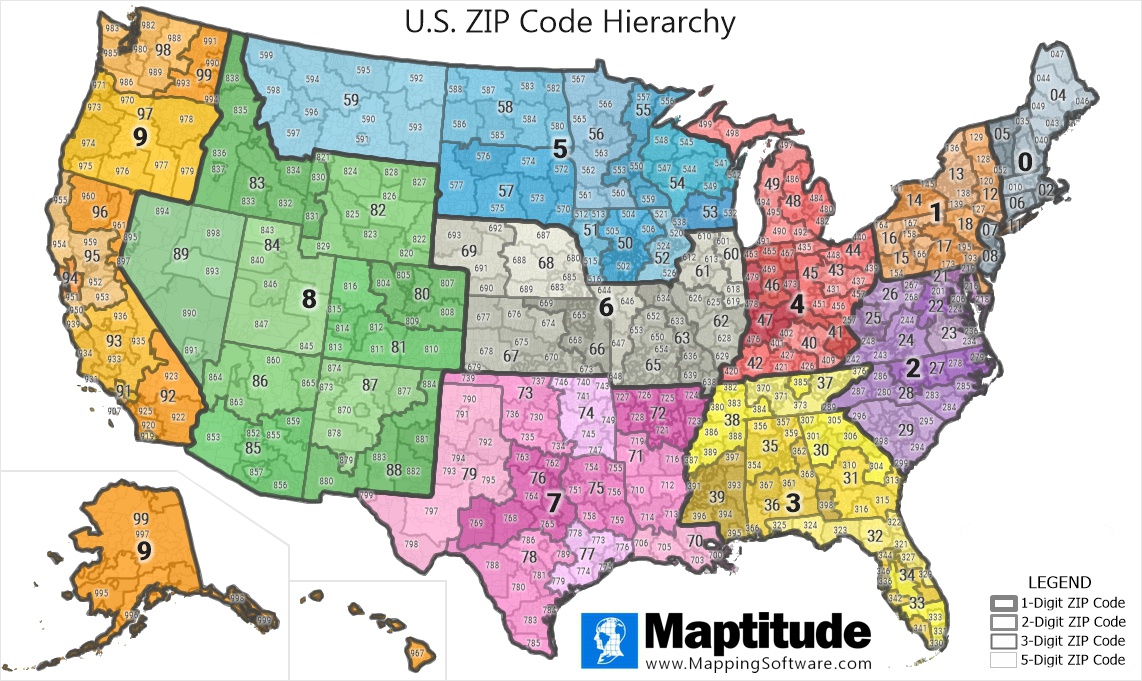
The structure of a postal code varies depending on the country. Many systems utilize a hierarchical structure, with components representing progressively smaller geographic areas. For example, a code might consist of a region code, a district code, and a local delivery area code. This hierarchical design allows for efficient sorting and routing of mail, minimizing transit times and improving delivery accuracy. The precise format and length of the code are determined by national postal authorities, reflecting the specific geographic and administrative divisions of a country. These codes are often integrated into national address databases, ensuring consistency and facilitating data analysis.
Applications Beyond Mail Delivery
The utility of these codes extends far beyond mail delivery. Their precise geographic association makes them invaluable tools in various contexts:
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Businesses rely heavily on these codes for efficient shipping and tracking of goods. E-commerce platforms utilize them to calculate shipping costs and delivery times, providing customers with accurate delivery estimates. Warehouse management systems employ them to optimize inventory management and order fulfillment. Real-time tracking systems often leverage these codes to monitor the location of shipments, providing transparency and accountability.
-
Market Research and Business Intelligence: These codes facilitate market segmentation and analysis. Businesses can identify target demographics and analyze consumer behavior based on geographic location. This information is crucial for marketing campaigns, sales forecasting, and strategic business decisions. The ability to aggregate data based on these codes provides valuable insights into market trends and consumer preferences.
-
Public Health and Emergency Services: In public health initiatives, these codes are used to track disease outbreaks, monitor health outcomes, and allocate resources effectively. Emergency services utilize them to quickly locate individuals in need of assistance, optimizing response times and improving emergency care. Epidemiological studies often rely on these codes to analyze disease patterns and identify risk factors.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners use these codes to analyze population density, housing patterns, and infrastructure needs. This data is crucial for informed decision-making regarding infrastructure development, resource allocation, and urban renewal projects. Analysis of demographic data linked to these codes aids in predicting future population growth and planning for sustainable urban development.
-
Geocoding and Mapping: These codes serve as a fundamental element in geocoding, the process of converting addresses into geographic coordinates. This allows for the visualization of data on maps, facilitating spatial analysis and providing a visual representation of geographic patterns. Many mapping applications rely on these codes to accurately locate addresses and provide directions.
-
Financial Services: Financial institutions use these codes for fraud detection and risk assessment. By analyzing transaction patterns linked to specific locations, financial institutions can identify suspicious activities and mitigate financial risks. Credit scoring models may also incorporate these codes to assess the risk associated with loan applications.
Data Integration and Interoperability
The effectiveness of postal codes is significantly enhanced through their integration with other data sources. Linking these codes to demographic data, socioeconomic indicators, and environmental information creates a rich dataset for analysis. Interoperability between different databases, ensuring consistent use of these codes, is crucial for effective data management and analysis. Standardized data formats and data sharing agreements are essential for maximizing the value of this information.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their widespread use, challenges remain. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date postal code databases requires ongoing effort. Changes in administrative boundaries and address modifications necessitate regular updates to ensure data accuracy. The evolving nature of urban environments and the increasing use of dynamic addresses, such as those associated with mobile devices, pose further challenges. Future developments may involve the integration of more granular geographic identifiers, potentially incorporating sub-address level precision, to improve the accuracy and granularity of location data.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is the difference between a postal code and a zip code?
-
A: The terms "postal code" and "zip code" are often used interchangeably, though "zip code" is primarily used in the United States. Both refer to alphanumeric codes used for mail sorting and delivery.
-
Q: Are postal codes standardized internationally?
-
A: No, the structure and format of postal codes vary significantly across countries. Each country’s postal authority establishes its own system.
-
Q: How are postal codes assigned?
-
A: Postal authorities assign postal codes based on geographic areas, often reflecting administrative divisions and population density.
-
Q: Can postal codes be used to identify individuals?
-
A: While postal codes identify geographic areas, they do not directly identify individuals. However, when combined with other data, they can contribute to identifying potential individuals within a specific geographic area. Ethical considerations related to privacy must be carefully addressed when using postal codes in conjunction with other personal data.
Tips for Effective Use of Postal Codes
-
Verify Accuracy: Always verify the accuracy of the postal code before using it for any application. Inaccurate codes can lead to delays or errors.
-
Utilize Standardized Formats: Adhere to the standardized format for the specific country or region. Inconsistent formatting can cause problems with data processing.
-
Consider Data Privacy: When using postal codes in conjunction with other data, prioritize data privacy and comply with relevant regulations.
-
Regularly Update Databases: Ensure that the postal code databases used are regularly updated to reflect changes in administrative boundaries and addresses.
Conclusion
Postal codes are fundamental components of modern infrastructure, extending far beyond their original purpose of mail delivery. Their role in numerous sectors highlights their crucial contribution to efficient operations, data analysis, and informed decision-making. Ongoing efforts to maintain accuracy, improve interoperability, and address emerging challenges are essential to ensuring their continued effectiveness and relevance in an increasingly data-driven world. The future of these codes likely involves greater integration with other geographic data sources and the development of more granular, dynamic location identifiers.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geographic Power of Postal Codes: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!