The Global Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude and Their Significance
Related Articles: The Global Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Global Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Global Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude and Their Significance

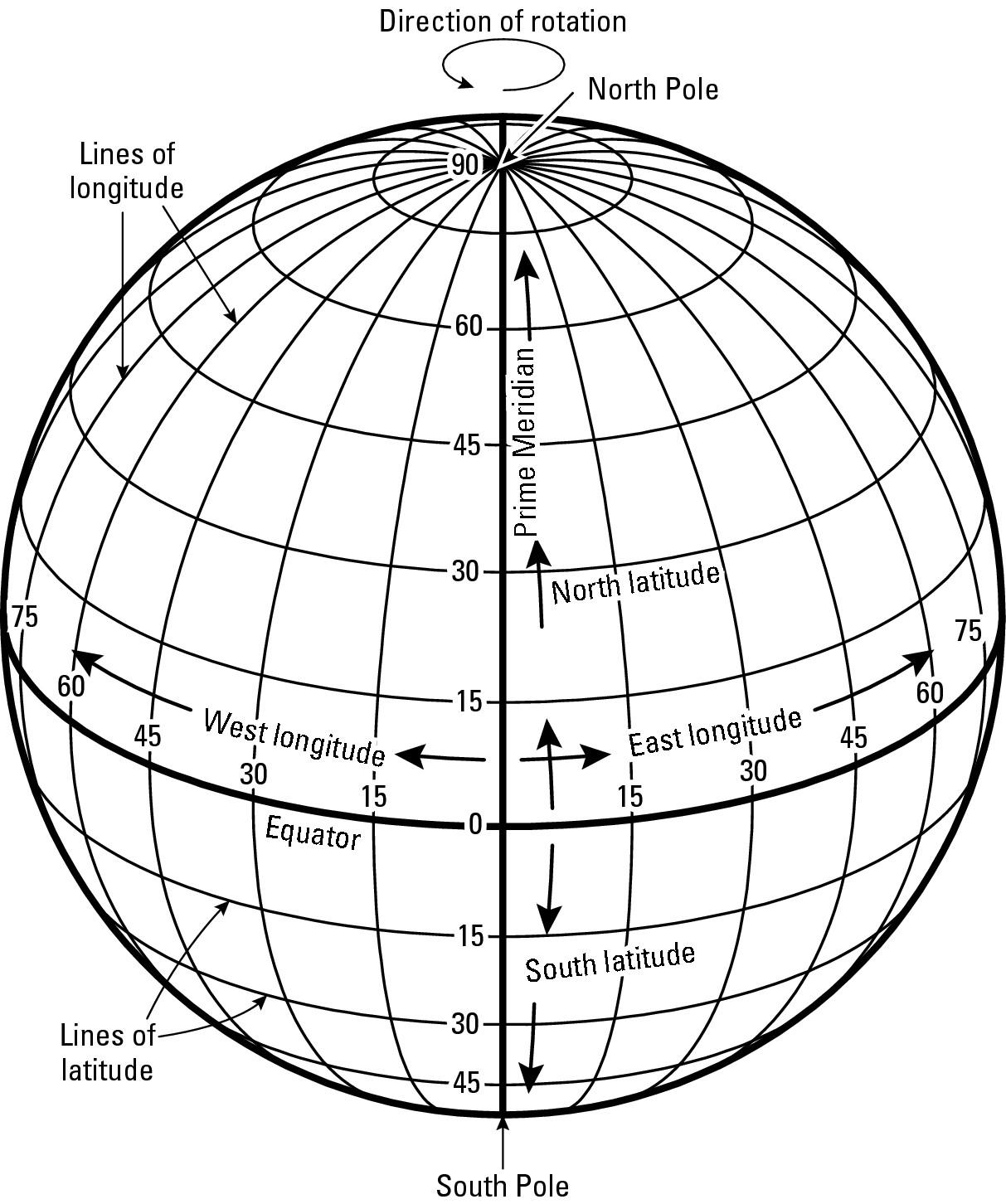
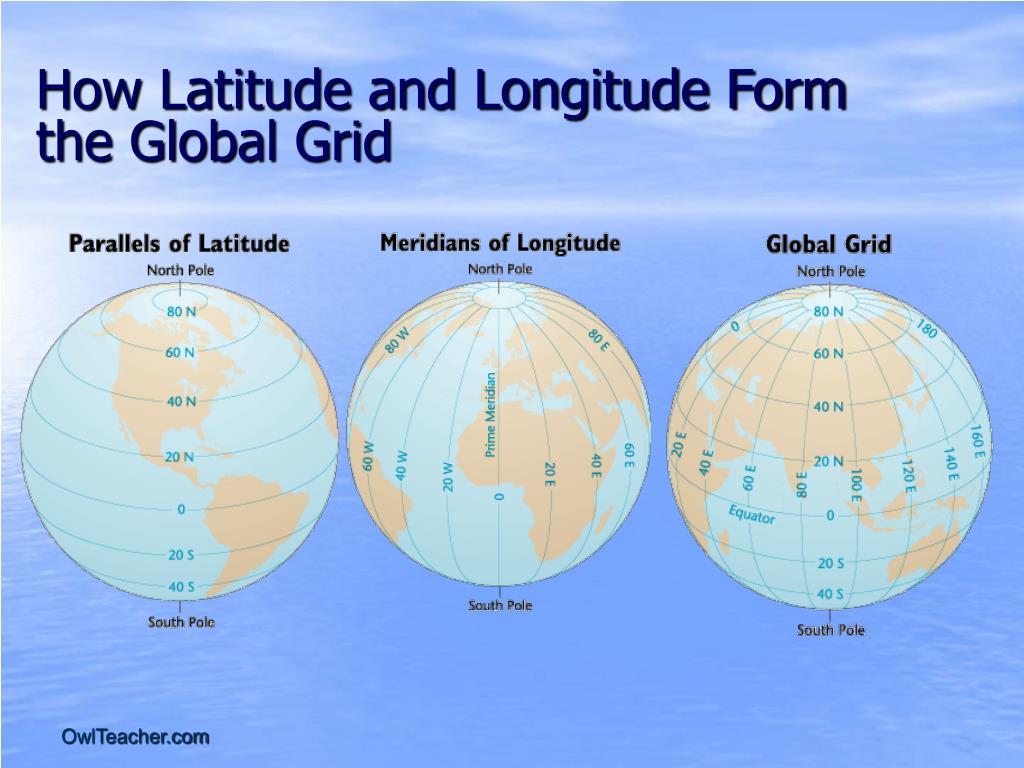
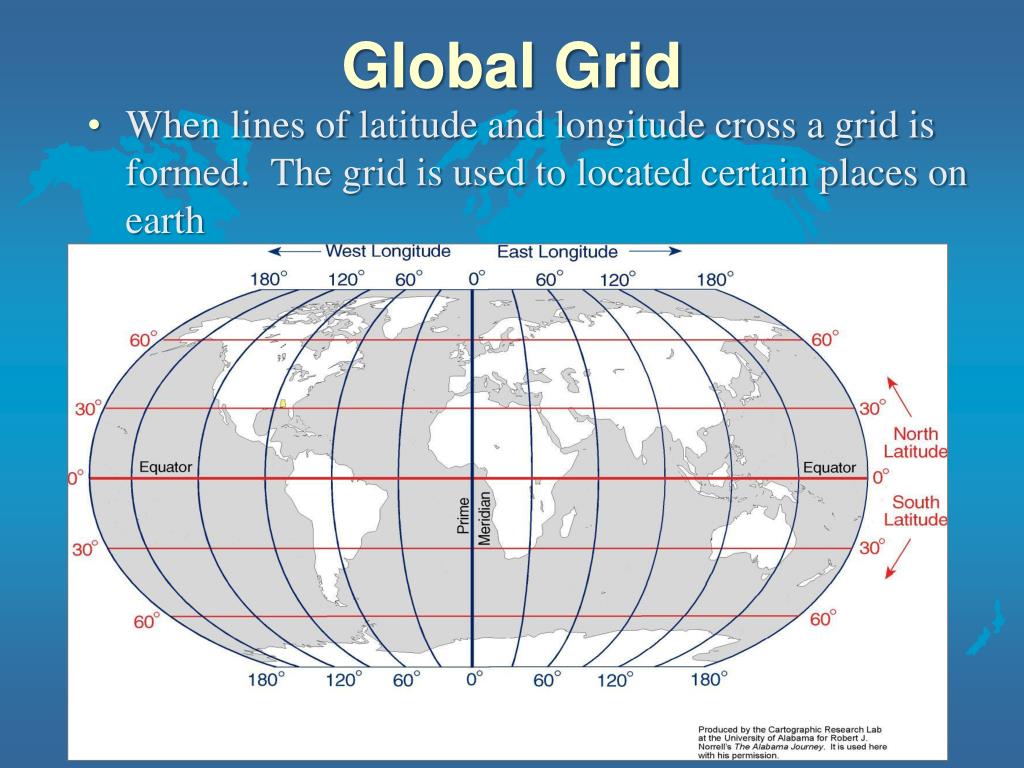
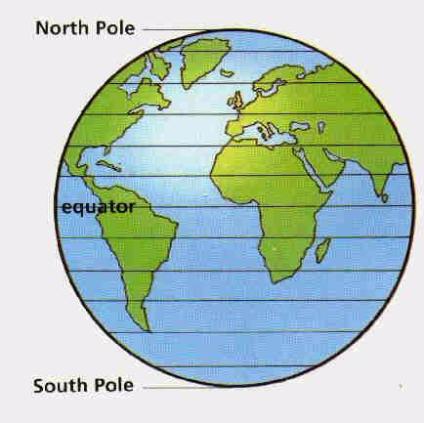
The Earth’s surface is a sphere, a three-dimensional object requiring a system for precise location identification. This system relies on a grid composed of imaginary lines, one set running east-west and the other running north-south. This article focuses on the east-west lines, known as parallels of latitude. These lines are crucial for navigation, mapping, understanding climate patterns, and a multitude of other applications.
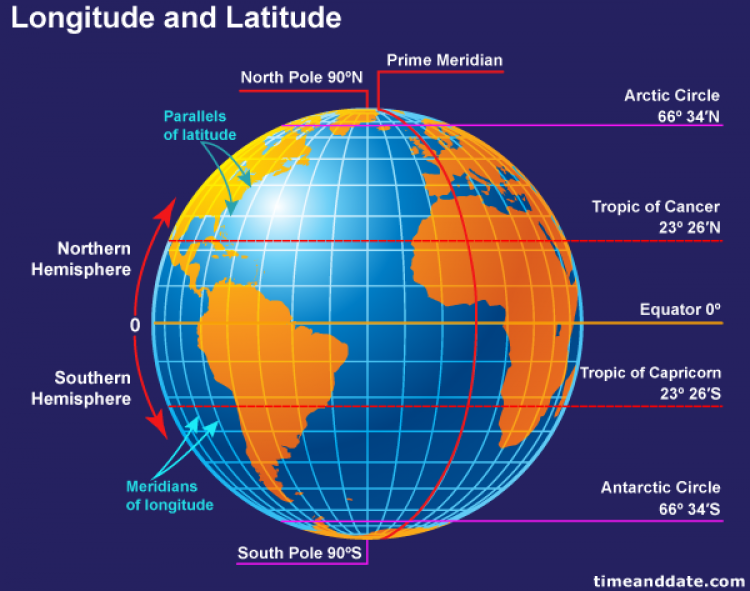
Parallels of latitude are circles that run parallel to the equator, an imaginary line equidistant from the North and South Poles. The equator is designated as 0 degrees latitude. Lines of latitude north of the equator are designated as positive values, ranging from 0° to 90° North at the North Pole. Similarly, lines south of the equator are designated as negative values, ranging from 0° to 90° South at the South Pole. Each degree of latitude is further subdivided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. This precise system allows for the pinpointing of locations with remarkable accuracy.
The significance of these lines extends far beyond simple location identification. Their relationship to the sun’s angle directly influences temperature and daylight hours. The equator, receiving the most direct sunlight throughout the year, experiences consistently warm temperatures and approximately equal day and night lengths. As one moves north or south from the equator, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, resulting in cooler temperatures and varying day lengths throughout the year. This effect is most dramatically seen at the poles, where the sun remains above or below the horizon for extended periods, leading to the phenomena of the midnight sun and polar night.
These variations in solar radiation drive global climate patterns. The tropical zone, lying between the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (approximately 23.5° South), experiences consistently high temperatures and rainfall due to the high angle of the sun. Temperate zones, located between the tropics and the polar circles (approximately 66.5° North and South), experience more moderate temperatures and seasonal variations in daylight hours. Polar zones, extending from the polar circles to the poles, are characterized by extremely cold temperatures and long periods of darkness or daylight.
The understanding of latitude is fundamental to various scientific disciplines. Oceanographers utilize latitude to study ocean currents and their impact on climate. Climatologists use latitude to analyze temperature and precipitation patterns, contributing to climate modeling and prediction. Biologists use latitude to understand the distribution of plant and animal species, revealing patterns of biodiversity and adaptation to different climates. Even fields like astronomy rely on latitude for accurate celestial observations and calculations.
Furthermore, the geographic information system (GIS) extensively utilizes latitude as a fundamental coordinate for spatial data analysis. This technology is crucial for urban planning, resource management, disaster response, and numerous other applications requiring precise location data. Navigation systems, both terrestrial and maritime, heavily depend on latitude and longitude coordinates for accurate positioning and route planning. Global positioning systems (GPS) rely on this grid system to provide location information with remarkable precision. Accurate location data is essential for a wide range of modern applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between latitude and longitude? Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Together, these coordinates provide a unique location on the Earth’s surface.
-
How are lines of latitude used in navigation? Latitude, in conjunction with longitude, provides the precise location of a vessel or aircraft. This information is critical for safe and efficient navigation.
-
What is the significance of the tropics? The tropics, defined by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, are regions that receive the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently warm temperatures and high rainfall.
-
How does latitude affect climate? The angle of the sun’s rays varies with latitude, directly influencing temperature and daylight hours. This variation in solar radiation drives global climate patterns and creates distinct climatic zones.
-
Are lines of latitude equally spaced? No. Lines of latitude are circles, and their circumference decreases as one moves towards the poles. The equator is the longest line of latitude.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Latitude
-
Visualize the globe: A globe provides a clearer understanding of how latitude lines work compared to a flat map.
-
Use online mapping tools: Interactive maps offer a dynamic way to explore and understand the relationship between latitude and location.
-
Correlate latitude with climate: Observe the relationship between latitude and temperature or precipitation patterns in different regions.
-
Study maps: Analyzing maps that incorporate latitude lines helps to develop a sense of spatial awareness and geographic relationships.
-
Learn about different climatic zones: Understanding how latitude affects climate is crucial for appreciating the diversity of environments on Earth.
Conclusion
The system of parallels of latitude forms a crucial component of the global grid, providing a framework for precise location identification and understanding global spatial relationships. Its importance transcends simple mapping; it is fundamental to understanding climate patterns, biodiversity distribution, navigation, and a multitude of scientific disciplines. The accurate measurement and application of latitude remain essential for numerous modern technologies and scientific endeavors. A thorough grasp of this fundamental geographic concept is critical for navigating the complexities of our planet and its diverse environments.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Global Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!