The Great Lakes Region: A Geographic and Economic Powerhouse
Related Articles: The Great Lakes Region: A Geographic and Economic Powerhouse
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Great Lakes Region: A Geographic and Economic Powerhouse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Great Lakes Region: A Geographic and Economic Powerhouse

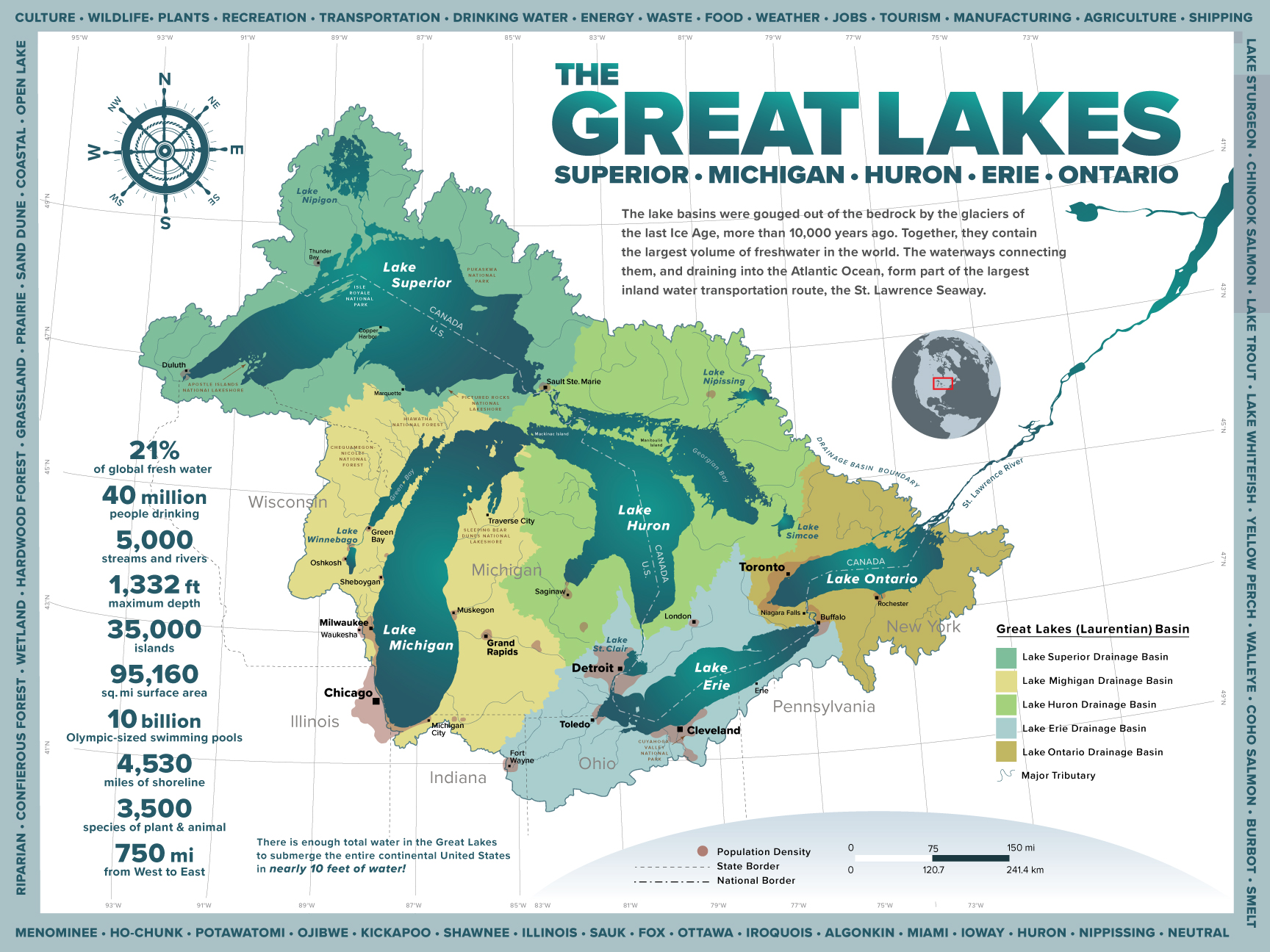
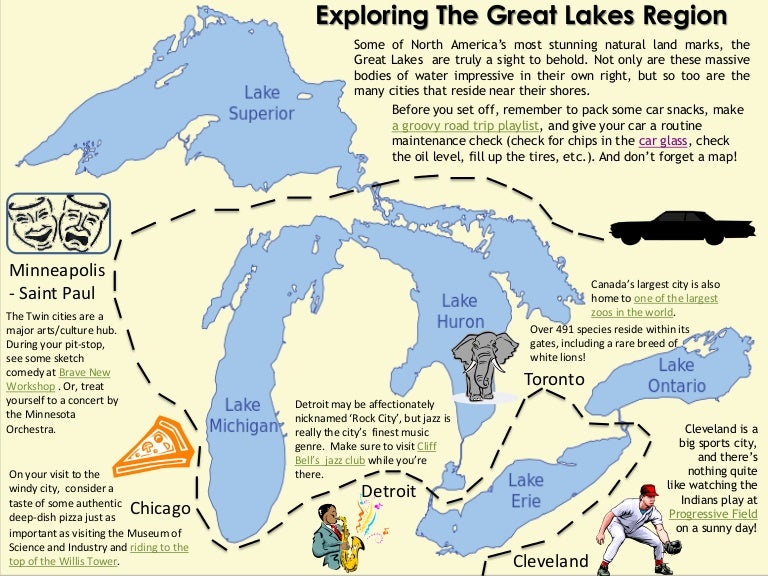
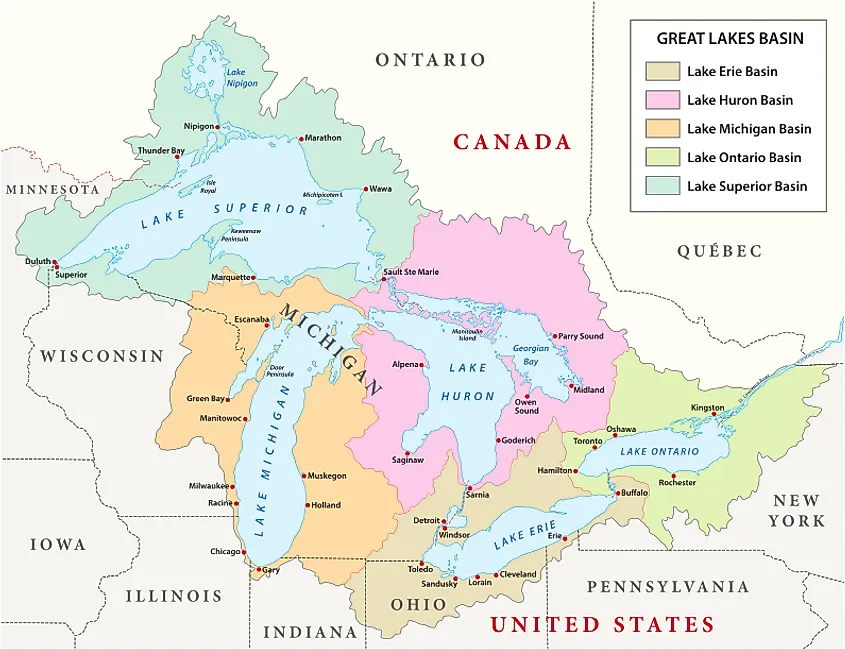
The Great Lakes region, encompassing parts of the United States and Canada, is a significant geographical and economic entity. Its defining characteristic is the five interconnected freshwater lakes – Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario – collectively forming the largest surface freshwater system on Earth. This vast expanse of water profoundly shapes the region’s climate, ecology, and human development. A detailed examination of the region’s geography, its ecological significance, and its economic impact reveals its multifaceted importance.
Geographical Features and Boundaries:
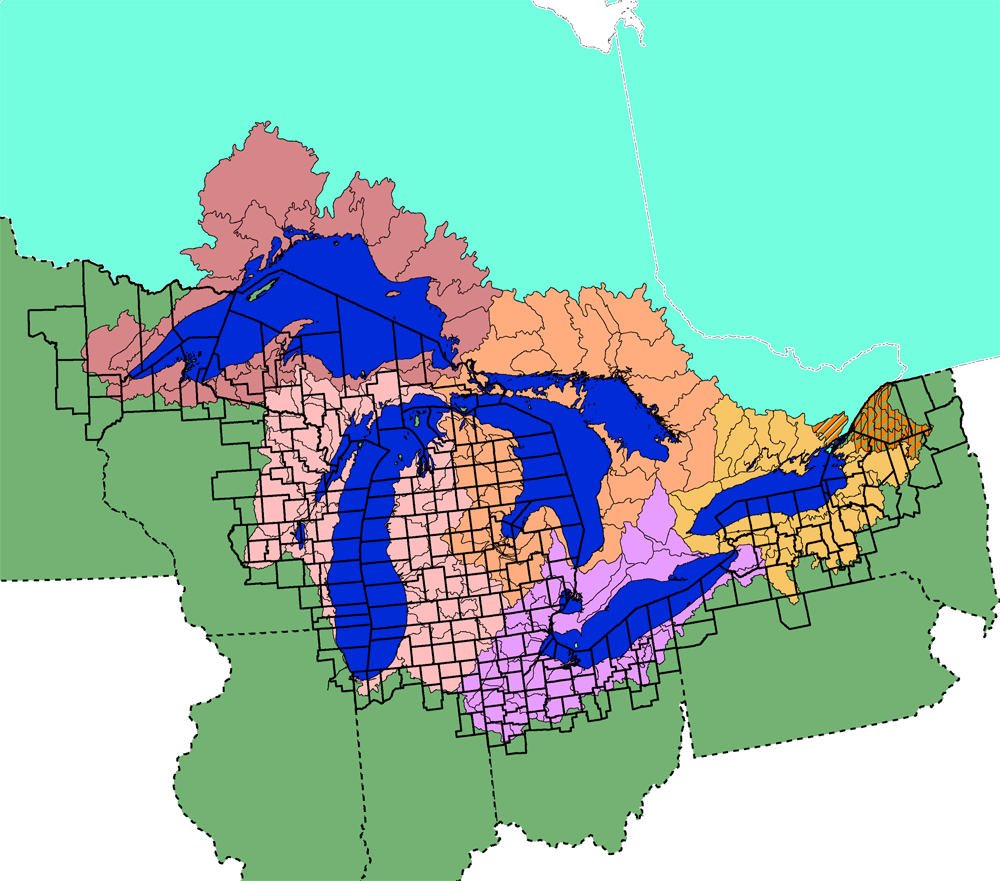
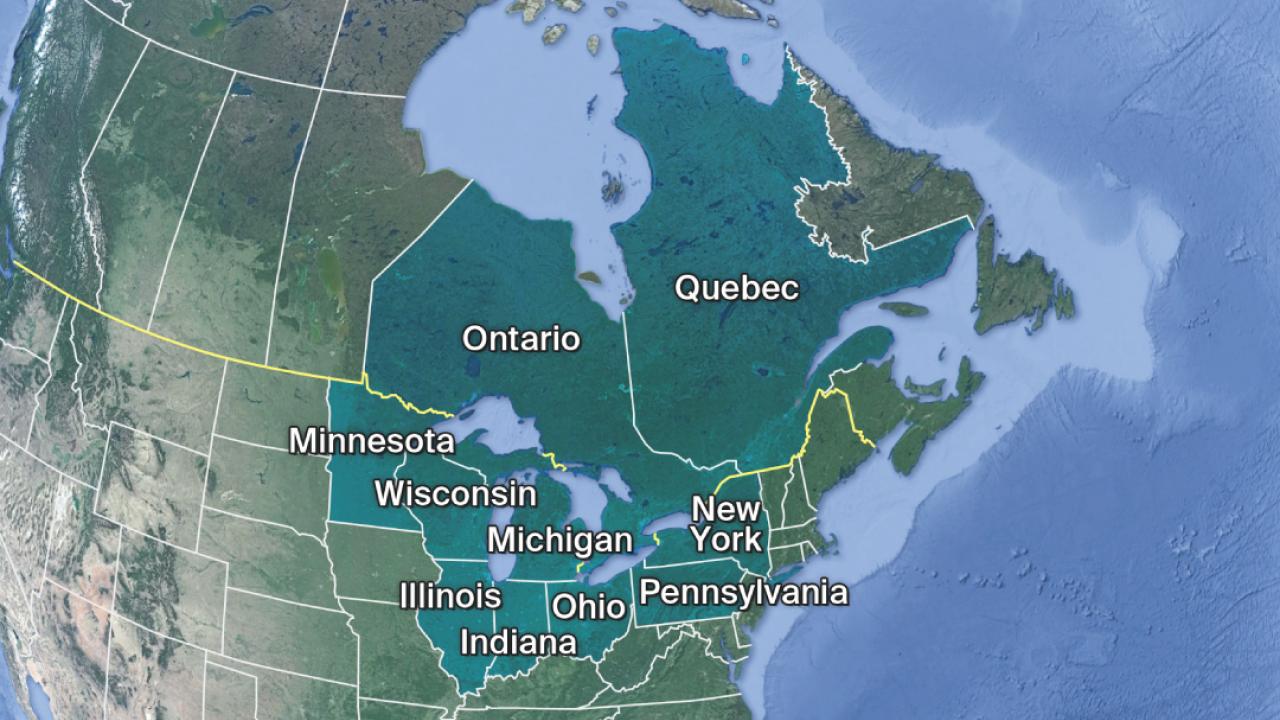
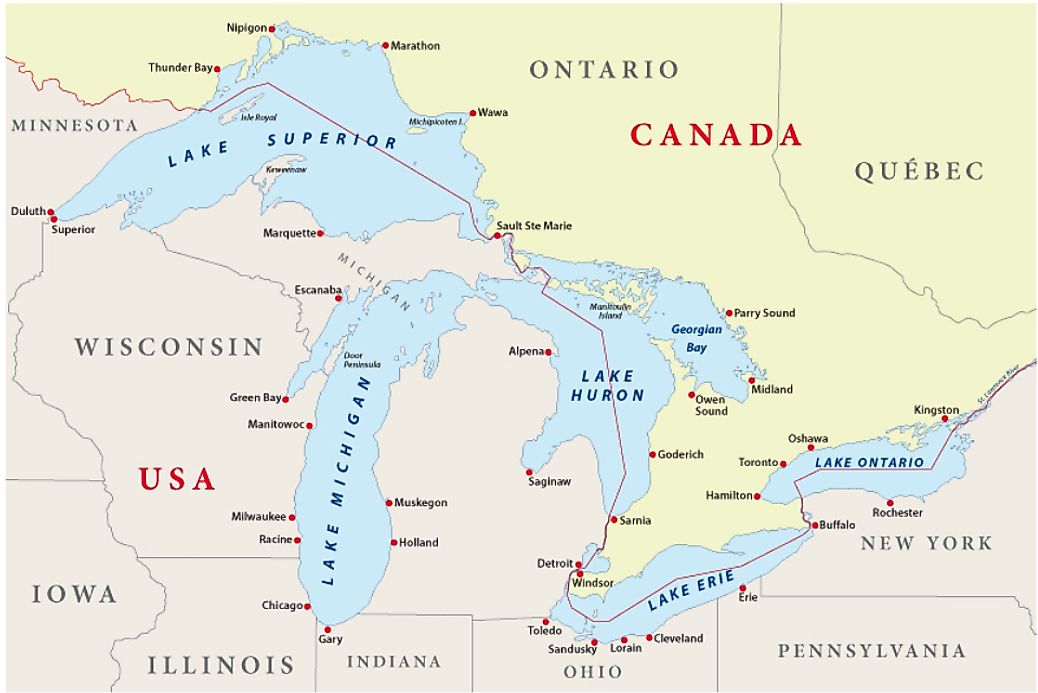
The lakes themselves are the dominant geographical feature, occupying a significant portion of the region’s land area. Lake Superior, the largest and deepest, is located in the northwest, bordering Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan in the US, and Ontario in Canada. Lake Michigan is entirely within the US, bordered by Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Lake Huron, partially separated from Michigan by the Straits of Mackinac, shares a border with Michigan, Ontario, and the Canadian province of Manitoba. Lake Erie, the shallowest of the five, lies south of Huron, separating Ontario from Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Finally, Lake Ontario, the easternmost lake, borders New York and Ontario. The St. Lawrence River connects Lake Ontario to the Atlantic Ocean.
The surrounding land varies significantly. The northern shores often exhibit rugged, rocky coastlines and boreal forests, transitioning southwards into diverse landscapes encompassing deciduous forests, prairies, and agricultural lands. Major rivers, such as the St. Mary’s River, the St. Clair River, the Detroit River, and the Niagara River, connect the lakes and contribute to the hydrological complexity of the system. The region also includes significant elevation changes, ranging from relatively flat plains to higher elevations in areas like the Adirondack Mountains and the Niagara Escarpment.
Ecological Significance:
The Great Lakes support a rich and diverse ecosystem. The lakes themselves provide habitat for a wide array of fish species, including commercially important ones like lake trout, salmon, and whitefish. The surrounding wetlands, forests, and prairies offer critical habitat for numerous bird species, mammals, and other wildlife. The interconnectedness of the lakes and their surrounding ecosystems creates a complex web of life, with significant biodiversity and ecological interdependence.
However, the ecosystem is not without its challenges. Invasive species, such as zebra mussels and sea lampreys, have had significant negative impacts on native populations. Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and urban runoff also poses a considerable threat to water quality and ecosystem health. Ongoing efforts focus on invasive species management, pollution control, and habitat restoration to maintain the ecological integrity of this vital system.
Economic Importance:
The Great Lakes region plays a vital role in the North American economy. The lakes themselves facilitate significant transportation, with commercial shipping carrying vast quantities of goods. Major ports along the lakeshore support industries ranging from manufacturing and agriculture to tourism and technology. The region is a significant producer of iron ore, automobiles, and agricultural products. Furthermore, the abundant freshwater resource is crucial for various industries and for the provision of drinking water to millions of people.
Tourism is another major economic driver, with the region attracting millions of visitors annually. The natural beauty of the lakes, their surrounding landscapes, and various recreational opportunities contribute significantly to regional economies. The combination of manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and tourism creates a diverse and robust economic base.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the total surface area of the Great Lakes? The combined surface area of the five Great Lakes is approximately 94,250 square miles (244,100 square kilometers).
-
What is the primary source of water for the Great Lakes? Precipitation, including rain and snow, is the primary source of water for the Great Lakes.
-
What are the major environmental challenges facing the Great Lakes? Invasive species, pollution, and climate change are major environmental challenges facing the Great Lakes.
-
What is the economic significance of the Great Lakes shipping industry? The Great Lakes shipping industry is crucial for transporting bulk goods, such as iron ore, grain, and coal, supporting manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
-
How does tourism contribute to the Great Lakes region’s economy? Tourism generates significant revenue through visitor spending on accommodation, recreation, and other services.
Tips for Understanding the Great Lakes Region:
-
Utilize maps and geographical resources: Detailed maps highlighting the lakes, surrounding landforms, and major cities provide crucial context.
-
Explore resources on ecosystem dynamics: Understanding the interconnectedness of the lakes and their surrounding ecosystems is essential.
-
Research the history of human settlement and development: The region’s history significantly shaped its current economic and social structures.
-
Consider the impact of climate change: Climate change presents significant challenges to the region’s water resources and ecosystems.
-
Analyze economic data and reports: Economic data provides insights into the region’s economic strengths and vulnerabilities.
Conclusion:
The Great Lakes region stands as a testament to the profound influence of geography on human activity and ecological systems. The interconnectedness of the five Great Lakes, their surrounding landscapes, and the human communities that thrive within this area create a complex and dynamic region. Understanding the geographical features, ecological importance, and economic significance of this area requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating geographical, ecological, and economic perspectives. Continued research, effective management practices, and sustainable development strategies are crucial for ensuring the long-term health and prosperity of this vital North American region.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Great Lakes Region: A Geographic and Economic Powerhouse. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!