The Gulf Stream: A Powerful Ocean Current and its Global Impact
Related Articles: The Gulf Stream: A Powerful Ocean Current and its Global Impact
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Gulf Stream: A Powerful Ocean Current and its Global Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Gulf Stream: A Powerful Ocean Current and its Global Impact
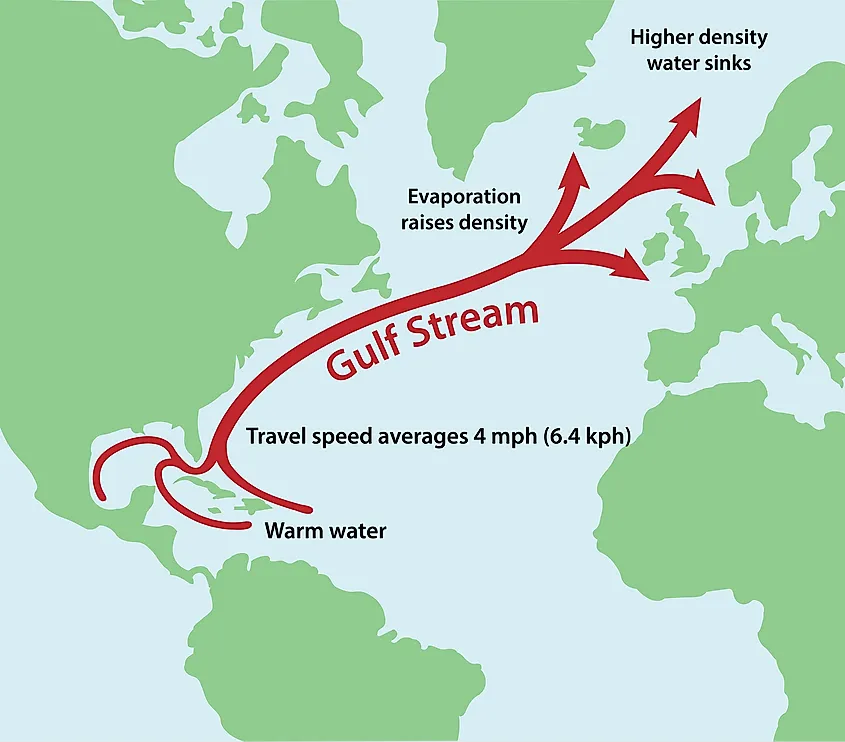
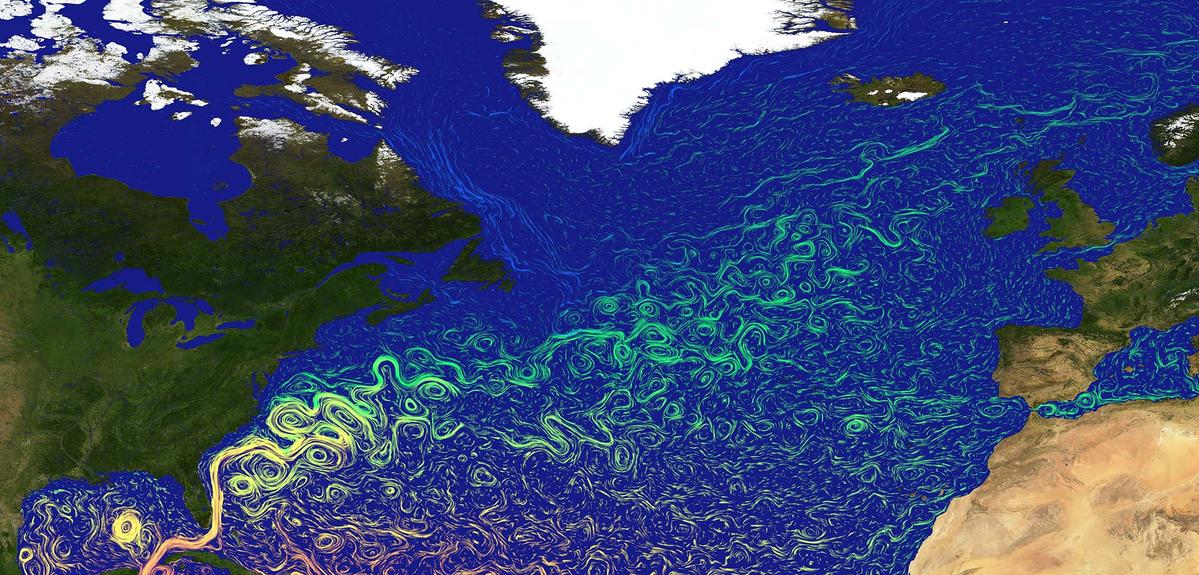
The Gulf Stream is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows northward along the eastern coast of North America before crossing the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. Its influence extends far beyond its immediate path, shaping weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and even human activities across a vast geographical area. Understanding its dynamics is crucial for predicting climate change impacts and managing marine resources.
Physical Characteristics and Formation:
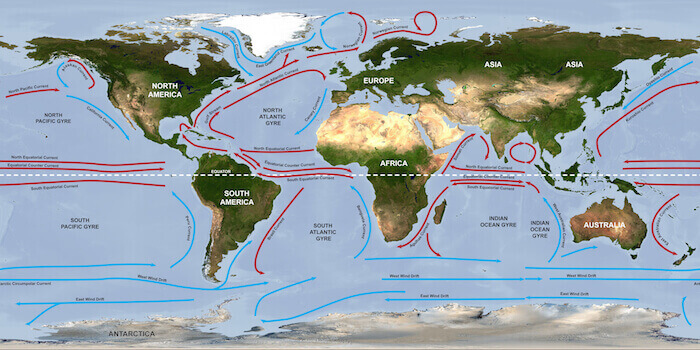
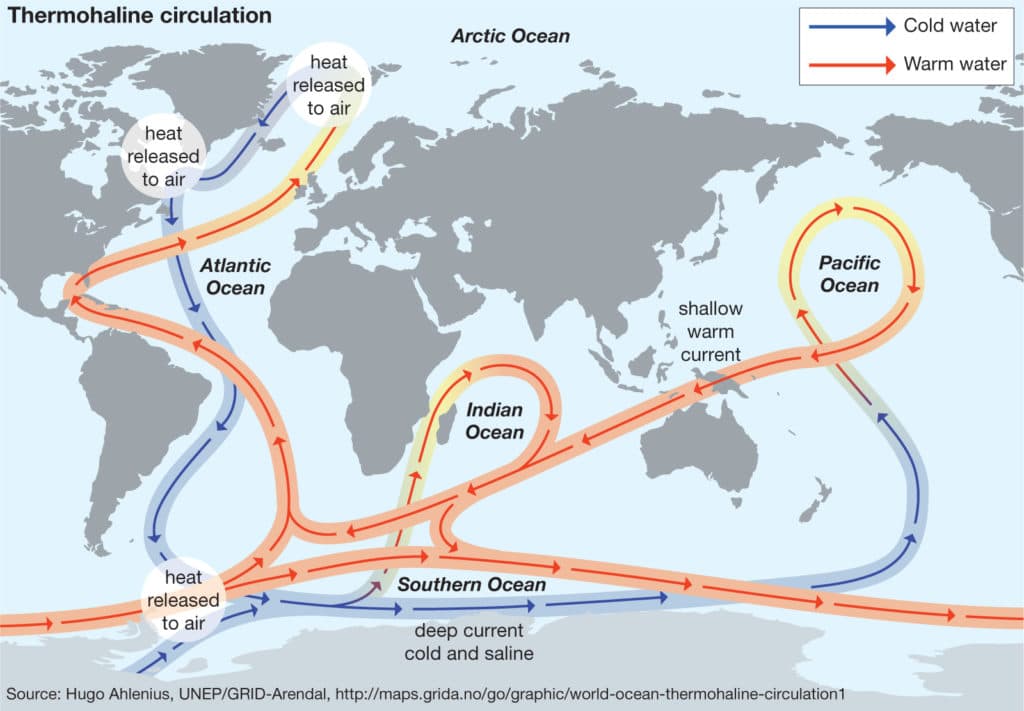
This current forms part of a larger system of interconnected ocean currents known as the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Warm water from the tropics, propelled by trade winds and the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect), accumulates in the Gulf of Mexico. This warm water mass then exits through the Florida Straits, forming the beginning of the powerful current. As it travels northward, it carries vast quantities of heat, significantly impacting the climate of adjacent landmasses. The current’s velocity varies along its path, with speeds reaching up to 5.6 mph (9 km/h) in its strongest sections. Its depth also varies, generally ranging from the surface to several hundred meters. The western boundary current, being relatively narrow and swift, is characterized by strong vertical mixing and significant thermal gradients.
The western intensification of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre leads to the high velocity of the current. This intensification is a consequence of the Earth’s rotation and the geometry of ocean basins. The current’s path is not perfectly linear; it meanders significantly, forming large loops and eddies that transport heat and nutrients both laterally and vertically within the water column. These meanders and eddies play a vital role in the current’s overall heat transport capacity and its influence on regional climates.
Climate Regulation and Weather Patterns:
The immense volume of warm water transported by the current has a profound effect on the climate of western Europe. It moderates temperatures, preventing the continent from experiencing the significantly colder winters that would otherwise be expected at its latitude. The warmth and moisture carried by the current contribute to milder, wetter conditions in regions such as the British Isles and Scandinavia. Conversely, the eastern coast of North America experiences a more continental climate due to the offshore flow of the current. The current’s influence on weather patterns extends beyond temperature and precipitation. It also plays a role in the formation and movement of storms, influencing the intensity and track of atmospheric systems. Changes in the current’s strength and trajectory can have significant consequences for regional weather patterns, including increased frequency or severity of extreme weather events.
Marine Ecosystems and Biodiversity:
The current plays a vital role in shaping marine ecosystems along its path. The warm waters support a rich biodiversity, providing habitat for a wide variety of marine species, including commercially important fish stocks. The upwelling of nutrient-rich waters along the current’s edges further enhances biological productivity, creating zones of high abundance for phytoplankton and zooplankton, which form the base of the food web. The current also facilitates the dispersal of marine organisms, allowing species to migrate and colonize new areas. Understanding the current’s influence on marine ecosystems is essential for effective fisheries management and conservation efforts. Changes in the current’s strength or temperature can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, affecting the distribution and abundance of various species.
Navigation and Human Activities:
Historically, the current has played a crucial role in navigation, assisting sailors in transatlantic voyages. Its strong and predictable flow provided a significant advantage, reducing travel times and improving the efficiency of seafaring. Today, the current continues to be important for maritime transport, influencing shipping routes and schedules. However, its strong currents and potential for unpredictable meandering also present challenges for navigation, requiring careful planning and consideration of safety protocols. Furthermore, the current’s influence extends to offshore energy development, impacting the siting and operation of offshore wind farms and other marine infrastructure. Changes in the current’s behavior due to climate change could affect the viability and safety of such projects.
Impact of Climate Change:
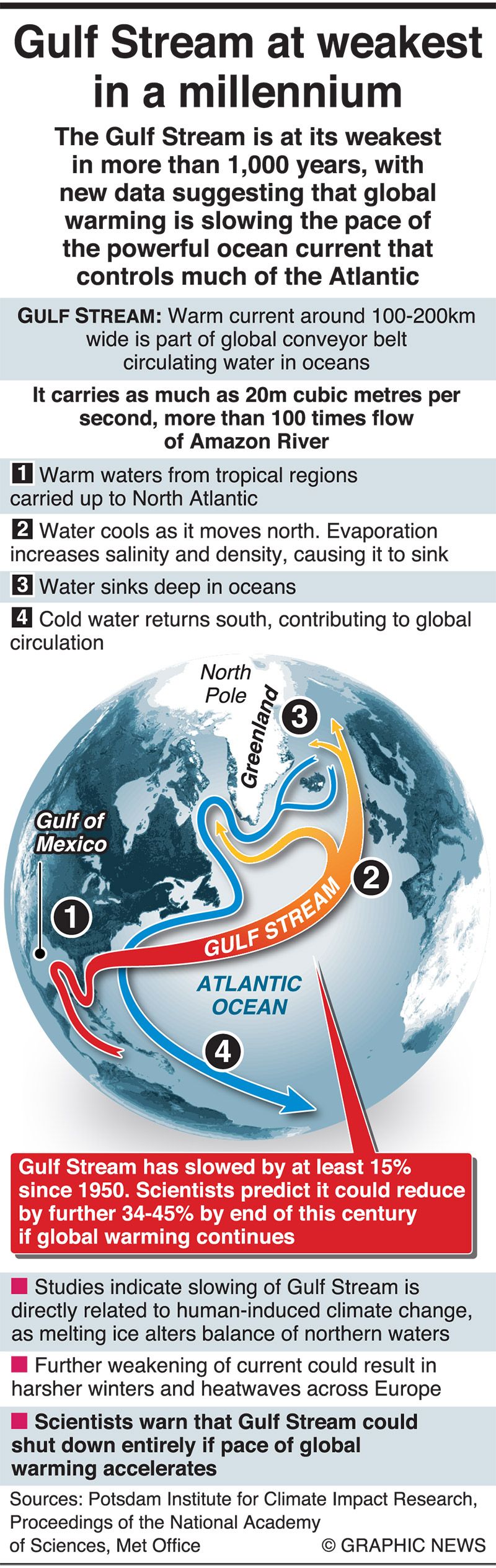
Climate change poses a significant threat to the stability and function of the current. Rising global temperatures are affecting the salinity and temperature gradients that drive the current, potentially leading to changes in its strength and trajectory. A weakening or disruption of the current could have far-reaching consequences, including significant alterations to regional climate patterns, marine ecosystems, and human activities that rely on the current’s predictable behavior. Scientific research is focused on understanding the extent and potential impacts of these changes, developing models to predict future scenarios and informing strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Q: How deep is the Gulf Stream? A: The depth varies, generally ranging from the surface to several hundred meters.
- Q: How fast does the Gulf Stream flow? A: Its speed varies, reaching up to 5.6 mph (9 km/h) in its strongest sections.
- Q: What is the impact of the Gulf Stream on European climate? A: It moderates temperatures, making winters significantly milder than would be expected at that latitude.
- Q: How does climate change affect the Gulf Stream? A: Rising temperatures are impacting salinity and temperature gradients, potentially weakening or altering its trajectory.
- Q: What is the role of the Gulf Stream in marine ecosystems? A: It supports rich biodiversity and influences the distribution and abundance of marine species.
Tips for Understanding the Gulf Stream:
- Utilize oceanographic data and visualizations to track the current’s movement and characteristics.
- Consult scientific literature and reports on the current’s dynamics and climate impacts.
- Consider the interconnectedness of the Gulf Stream with other ocean currents and atmospheric systems.
- Integrate knowledge of the Gulf Stream into assessments of climate change vulnerability and adaptation strategies.
- Support research efforts aimed at understanding and predicting changes in the current’s behavior.
Conclusion:
The Gulf Stream represents a crucial component of the global ocean circulation system, exerting a profound influence on climate, ecosystems, and human activities across a vast geographical area. Its powerful currents and immense heat transport capacity have shaped the environments and societies of both North America and Europe for millennia. However, the ongoing impacts of climate change present a significant challenge to the stability and predictability of this vital current. Continued research, monitoring, and international collaboration are essential to understand the potential consequences of these changes and to develop effective strategies for mitigation and adaptation. The future of this powerful ocean current is inextricably linked to the future of the planet, making its study a critical endeavor for understanding and addressing global environmental challenges.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gulf Stream: A Powerful Ocean Current and its Global Impact. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!