The Jutland Peninsula: A Geographical Analysis
Related Articles: The Jutland Peninsula: A Geographical Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Jutland Peninsula: A Geographical Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Jutland Peninsula: A Geographical Analysis

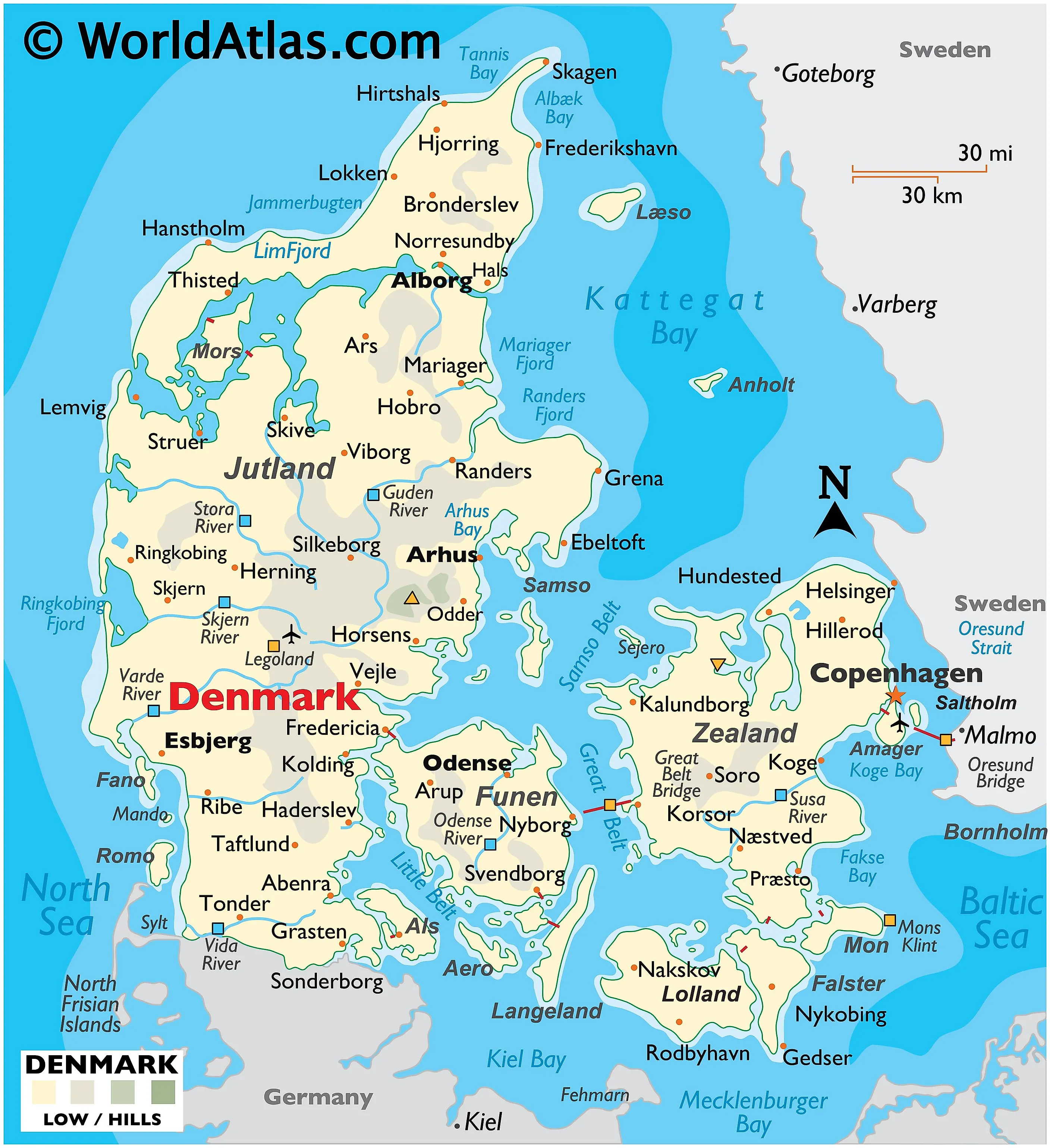
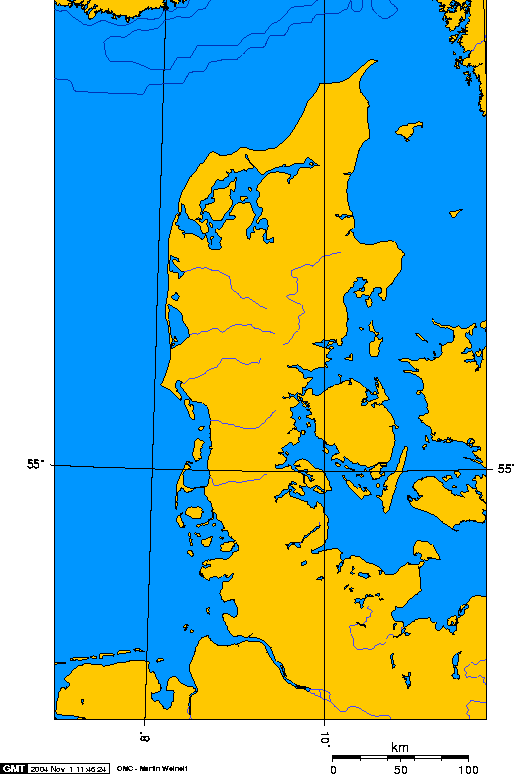
The Jutland Peninsula, a significant landmass in Northern Europe, extends from the southern tip of Denmark into the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Its unique geographical position and varied landscapes have profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy. Understanding its cartographic representation provides crucial insights into these influences.
A map of the peninsula reveals its distinctive elongated shape, roughly resembling a hand pointing south. Its western coast, facing the North Sea, is characterized by rugged cliffs, sandy beaches, and dramatic dune systems, shaped by powerful coastal processes. In contrast, the eastern coast, bordering the Baltic Sea, presents a gentler profile, with numerous fjords, inlets, and shallow coastal waters. This dichotomy in coastal morphology has led to the development of distinct regional economies and cultural identities. The western coast, historically more exposed to maritime influences, developed a strong tradition of fishing and seafaring, while the eastern coast, with its sheltered inlets, supported agriculture and trade.
The peninsula’s internal geography is equally diverse. The central region is dominated by relatively flat, low-lying terrain, characterized by heathland, forests, and fertile agricultural land. This area is crucial for Danish agriculture, producing a significant portion of the nation’s food supply. However, the northern part of the peninsula displays a more undulating landscape, with higher elevations and moraine formations left by past glacial activity. These elevated areas often feature distinctive ecological characteristics, including unique flora and fauna adapted to the harsher conditions. The Limfjord, a long, narrow inlet separating the northern part of Jutland from the island of Vendsyssel-Thy, is a significant geographical feature, impacting both transportation and the local ecosystem. Its unique brackish water environment supports a diverse range of aquatic life.
Several major cities are strategically located across the peninsula, reflecting its historical and economic importance. Aarhus, located on the eastern coast, is Denmark’s second-largest city and a significant center for commerce, culture, and education. Aalborg, situated in the northern part of the peninsula, is a major industrial and port city, playing a crucial role in regional trade. Esbjerg, on the western coast, is a significant port and center for the offshore oil and gas industry. The distribution of these urban centers, as depicted on any accurate map, showcases the peninsula’s strategic importance as a transportation hub and economic powerhouse.
The geological history of the peninsula is also evident in its cartographic representation. The presence of numerous glacial landforms, such as eskers and drumlins, reflects the impact of past ice ages. These features are not only of geological interest but also influence agricultural practices and land use patterns. The underlying geology also affects the distribution of natural resources, including groundwater reserves and mineral deposits.
Transportation infrastructure, as shown on any detailed map, plays a vital role in connecting the peninsula’s various regions and facilitating economic activity. Major highways and railway lines run the length of the peninsula, linking its cities and towns. The numerous ports along both coasts are essential for maritime trade and transport. The strategic placement of these transportation networks significantly impacts the flow of goods, people, and information across the region.
The peninsula’s strategic location has also played a crucial role in its history. Its proximity to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea has made it a crossroads of maritime trade routes for centuries. Its geographical position also made it a vital point of contention in numerous conflicts throughout history, as evidenced by the many historical sites and battlefields scattered across the landscape. A map can serve as a valuable tool for understanding these historical events and their impact on the region’s development.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the total area of the Jutland Peninsula? The area of the Jutland Peninsula is approximately 29,775 square kilometers. This figure may vary slightly depending on the precise boundaries used in the measurement.
-
What are the major rivers of the Jutland Peninsula? The peninsula’s rivers are generally short and relatively small. Significant rivers include the Gudenå, the largest river in Denmark, and the Skjern Å.
-
What is the climate of the Jutland Peninsula? The peninsula experiences a temperate maritime climate, characterized by mild winters and cool summers. The western coast is generally wetter than the eastern coast.
-
What are the main economic activities on the Jutland Peninsula? Agriculture, fishing, manufacturing, and tourism are major economic activities. The offshore oil and gas industry also plays a significant role in the western part of the peninsula.
-
What are the main natural resources found on the Jutland Peninsula? The peninsula possesses significant resources, including arable land, forests, and offshore oil and gas reserves. Groundwater is also an important resource.
Tips for Understanding Maps of the Jutland Peninsula:
-
Pay close attention to the scale of the map to accurately assess distances and relative sizes of geographical features.
-
Examine the map’s legend to understand the symbols used to represent different features, such as cities, roads, rivers, and elevation.
-
Consider the map’s purpose and intended audience. A map designed for tourists will differ significantly from a map intended for geological research.
-
Use multiple maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding. Different maps may emphasize different aspects of the peninsula’s geography.
-
Correlate map data with other information sources, such as historical records, geological surveys, and demographic data, to gain a more holistic understanding of the region.
Conclusion:
The Jutland Peninsula’s geographical diversity, strategic location, and rich history are all clearly reflected in its cartographic representations. By carefully studying maps of the region, one can gain a deeper appreciation for its complex interplay of physical and human geography. The peninsula’s unique characteristics have shaped its development, influencing its economy, culture, and political landscape. Understanding its geography provides a fundamental basis for comprehending its past, present, and future. Further research into specific aspects of the peninsula’s geography, facilitated by detailed map analysis, can provide valuable insights into a wide range of disciplines, from environmental science and history to economics and urban planning.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Jutland Peninsula: A Geographical Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!