The Texas-Mexico Border Region: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Analysis
Related Articles: The Texas-Mexico Border Region: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Texas-Mexico Border Region: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Texas-Mexico Border Region: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Analysis
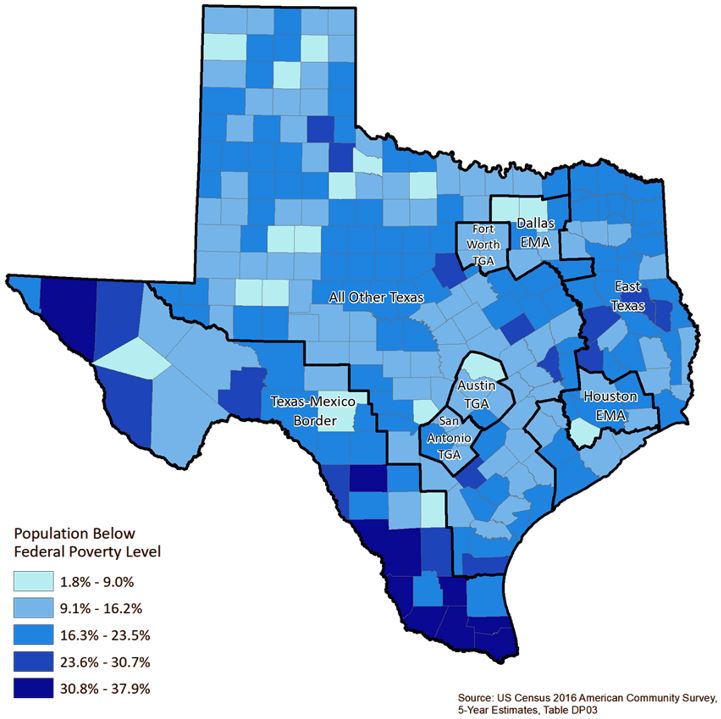
The boundary between Texas and Mexico represents a significant geopolitical and economic interface, shaping the destinies of both nations. Understanding this region requires examining its geographical features, historical context, and contemporary significance. A detailed cartographic representation reveals complexities not immediately apparent from a simple line on a map.
Geographical Features and their Implications:
The Rio Grande River forms the majority of the international boundary, a meandering waterway that creates a naturally variable border. This natural boundary, however, is not consistently defined. The river’s shifting course has historically led to disputes over territorial jurisdiction, highlighting the need for precise surveying and ongoing border management. The terrain varies considerably along the length of the boundary. In some areas, it is characterized by arid deserts and rugged mountains, presenting challenges to infrastructure development and border security. Other sections feature fertile plains and riparian ecosystems, supporting agricultural activities and human settlements on both sides. These geographical variations significantly impact the types of border crossings, the ease of movement, and the effectiveness of border control measures. The presence of significant urban centers on both sides of the border, such as El Paso-Juárez and Laredo-Nuevo Laredo, adds another layer of complexity to the region’s dynamics.
Historical Context and its Shaping Influence:
The current border is the result of centuries of political and territorial negotiation, conflict, and compromise. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which concluded the Mexican-American War, significantly altered the geopolitical landscape, transferring a vast territory encompassing present-day Texas, California, Nevada, and parts of other southwestern states to the United States. This historical event profoundly shaped the demographics and cultural landscape of the border region, creating a complex interplay of Mexican and American influences. The subsequent decades witnessed periods of both cooperation and tension between the two nations, reflected in the evolution of border policies and infrastructure. The legacy of this historical context continues to impact contemporary relations and the challenges faced in managing the border.
Economic Interdependence and its Significance:
The Texas-Mexico border region is characterized by significant economic interdependence. The two nations engage in extensive cross-border trade, with Texas serving as a major gateway for Mexican exports to the United States and vice versa. This trade encompasses a wide range of goods, from agricultural products and manufactured goods to energy resources. The flow of goods and services across the border contributes substantially to the economies of both Texas and Mexico, creating jobs and generating revenue. The cross-border movement of people, both legal and undocumented, further contributes to the economic dynamics of the region. Remittances sent by Mexican workers in the United States to their families in Mexico represent a significant source of income for many Mexican households. However, this economic interdependence also presents challenges, including the need for efficient border infrastructure and effective mechanisms to manage the flow of goods and people.
Security and Migration Challenges:
The border region faces ongoing challenges related to security and migration. The issue of undocumented immigration remains a significant concern, prompting ongoing debate and policy adjustments on both sides of the border. The porous nature of certain sections of the border, combined with the demand for labor in the United States and economic hardship in Mexico, contributes to the continued movement of people across the boundary. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach encompassing border security measures, immigration reform, and economic development initiatives aimed at improving living conditions in Mexico. Furthermore, transnational crime, including drug trafficking and human smuggling, poses a serious threat to the security and stability of the region, requiring cooperation between law enforcement agencies on both sides of the border.
Infrastructure and its Role:
The development and maintenance of adequate infrastructure are crucial for managing the flow of goods, people, and information across the border. This includes border crossing points, transportation networks (roads, railways, and pipelines), communication systems, and other essential facilities. Efficient infrastructure facilitates cross-border trade and travel, contributing to economic growth and regional integration. However, the capacity of existing infrastructure often struggles to keep pace with the increasing volume of cross-border activity, leading to delays and bottlenecks. Investments in modernizing and expanding border infrastructure are essential to address these challenges and optimize the benefits of cross-border interaction.
Environmental Considerations:
The unique environmental characteristics of the border region require careful consideration in the development and management of the area. The Rio Grande River, a vital water resource for both countries, faces challenges related to water scarcity, pollution, and unsustainable water use. Protecting the environment and ensuring the sustainable use of natural resources require collaborative efforts between Texas and Mexico. The conservation of biodiversity, the mitigation of pollution, and the management of shared water resources are critical elements in safeguarding the ecological integrity of the region.
FAQs:
-
What is the length of the Texas-Mexico border? The length is approximately 1,254 miles (2,018 kilometers).
-
What is the primary physical feature defining the border? The Rio Grande River forms the majority of the boundary.
-
What treaties significantly shaped the current border? The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) is the most significant.
-
What are the major economic activities in the border region? Trade, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism are prominent.
-
What are the main challenges faced in the region? Undocumented immigration, drug trafficking, and environmental concerns are key issues.
Tips for Understanding the Region:
- Consult detailed maps showing both physical and political features of the border region.
- Research the historical context of border demarcation and its implications.
- Analyze the economic data related to cross-border trade and migration.
- Consider the environmental vulnerabilities and the need for sustainable management practices.
- Examine the various perspectives on border security and immigration policies.
Conclusion:
The Texas-Mexico border region is a dynamic and complex area characterized by a unique blend of geographical features, historical legacies, and socioeconomic interactions. Understanding this region requires a comprehensive approach that considers its geographical characteristics, historical context, and contemporary challenges. Addressing the multifaceted issues facing this area necessitates collaboration and cooperation between the United States and Mexico, focusing on sustainable development, efficient infrastructure, and effective border management strategies. Continued research and analysis are essential to promote a more comprehensive understanding of this crucial geopolitical and economic interface.



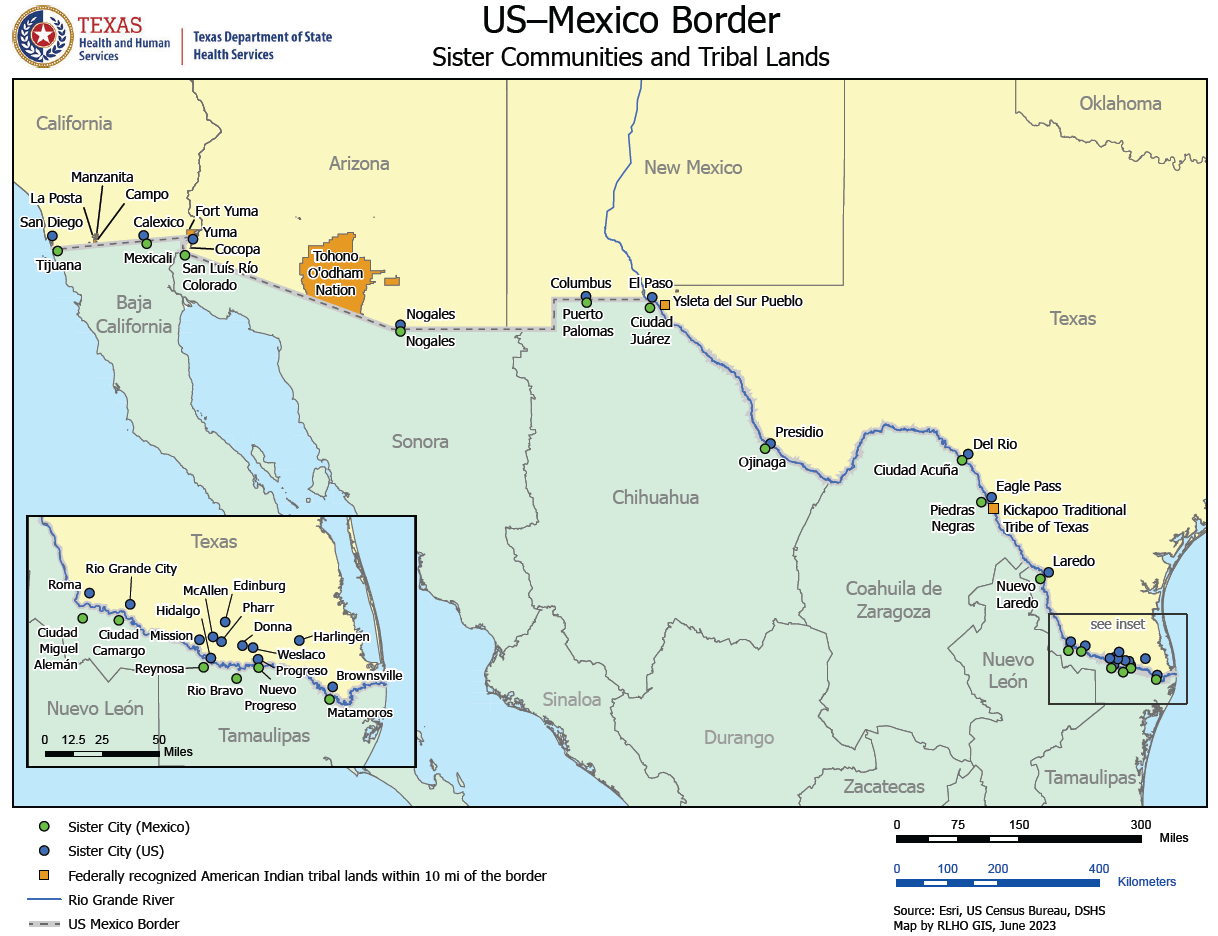
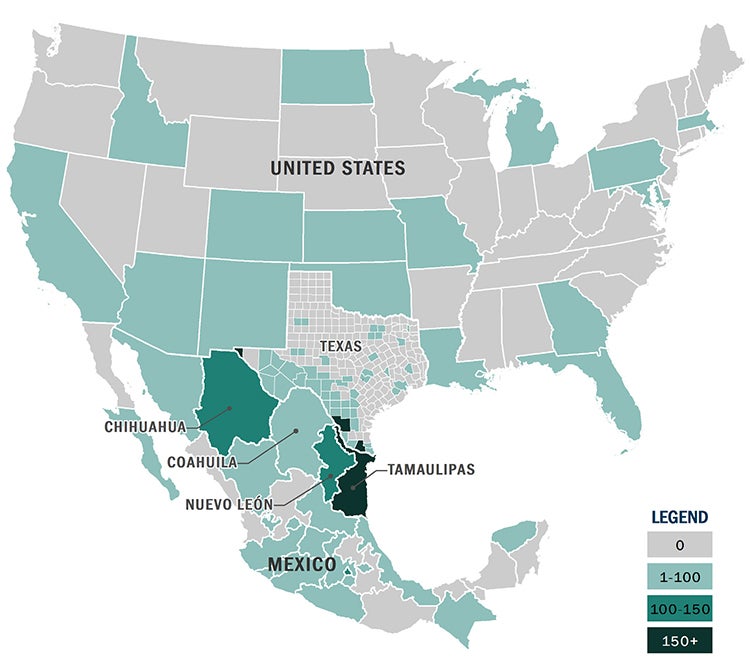


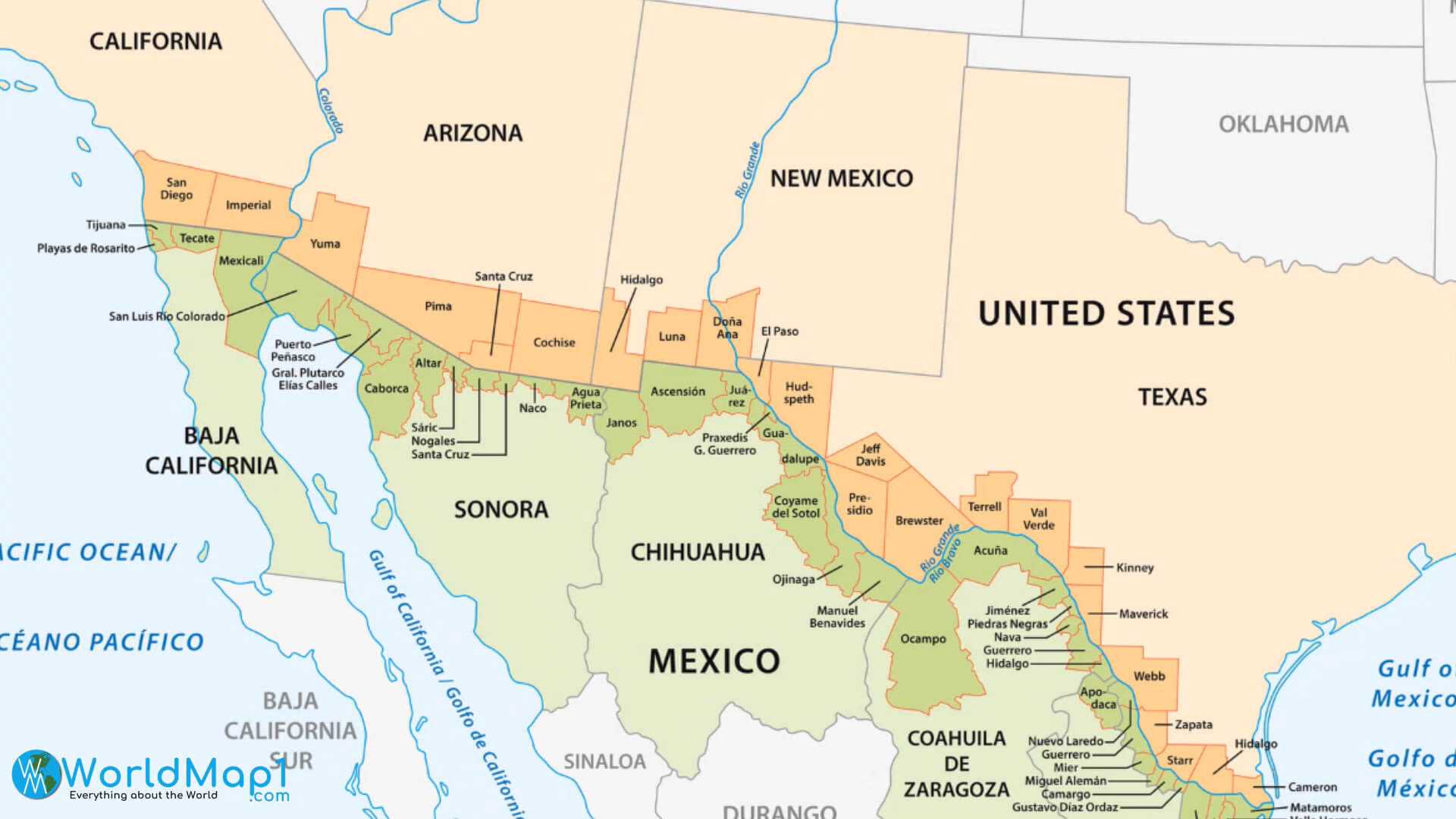
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Texas-Mexico Border Region: A Geographic and Socioeconomic Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!