Understanding Oregon’s Wildfire Landscape: A Geographic Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding Oregon’s Wildfire Landscape: A Geographic Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Oregon’s Wildfire Landscape: A Geographic Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Oregon’s Wildfire Landscape: A Geographic Analysis
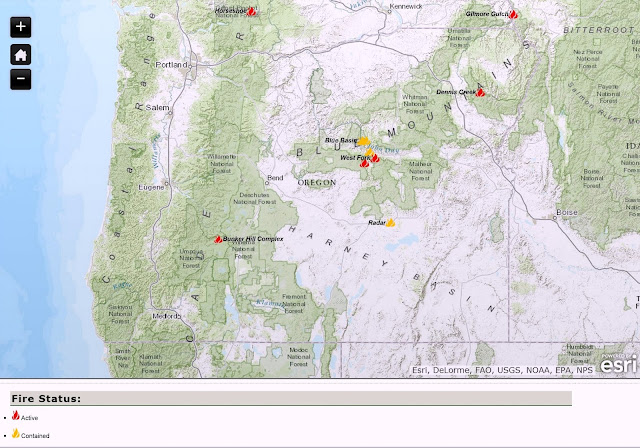
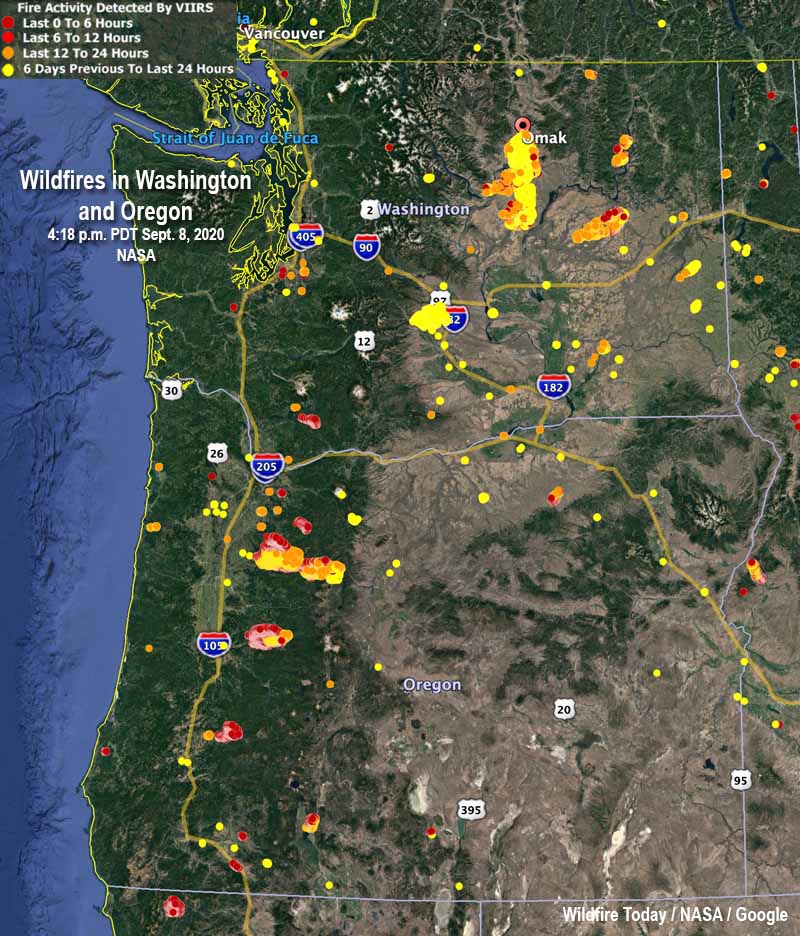
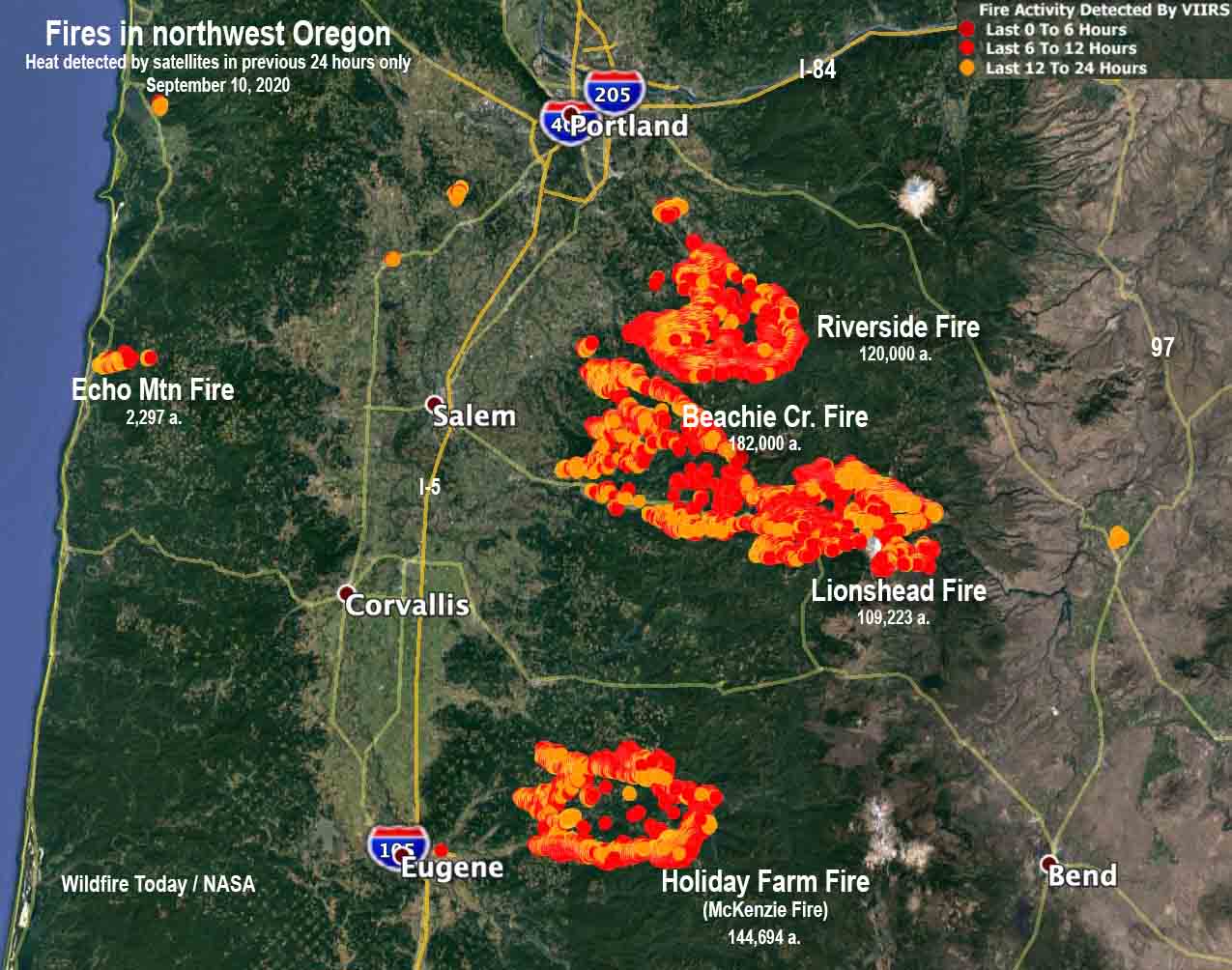
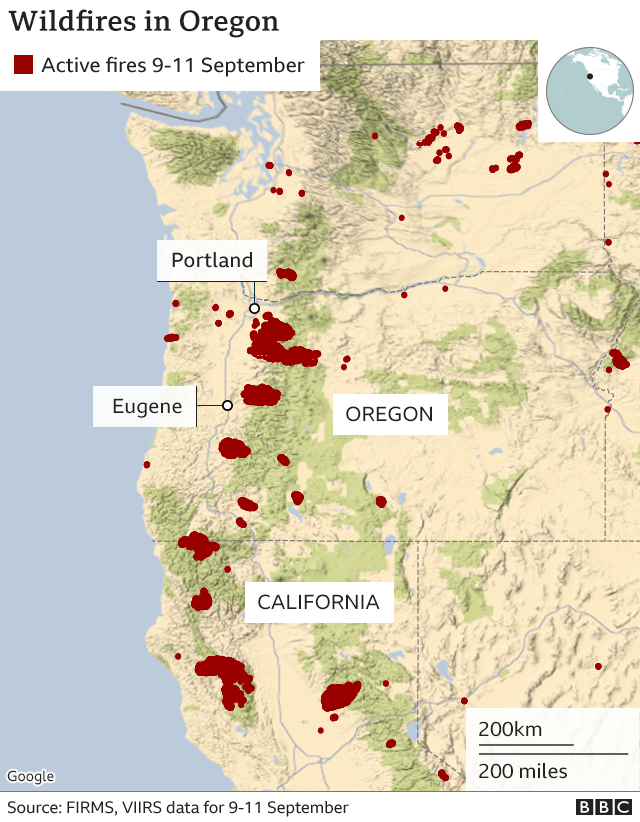
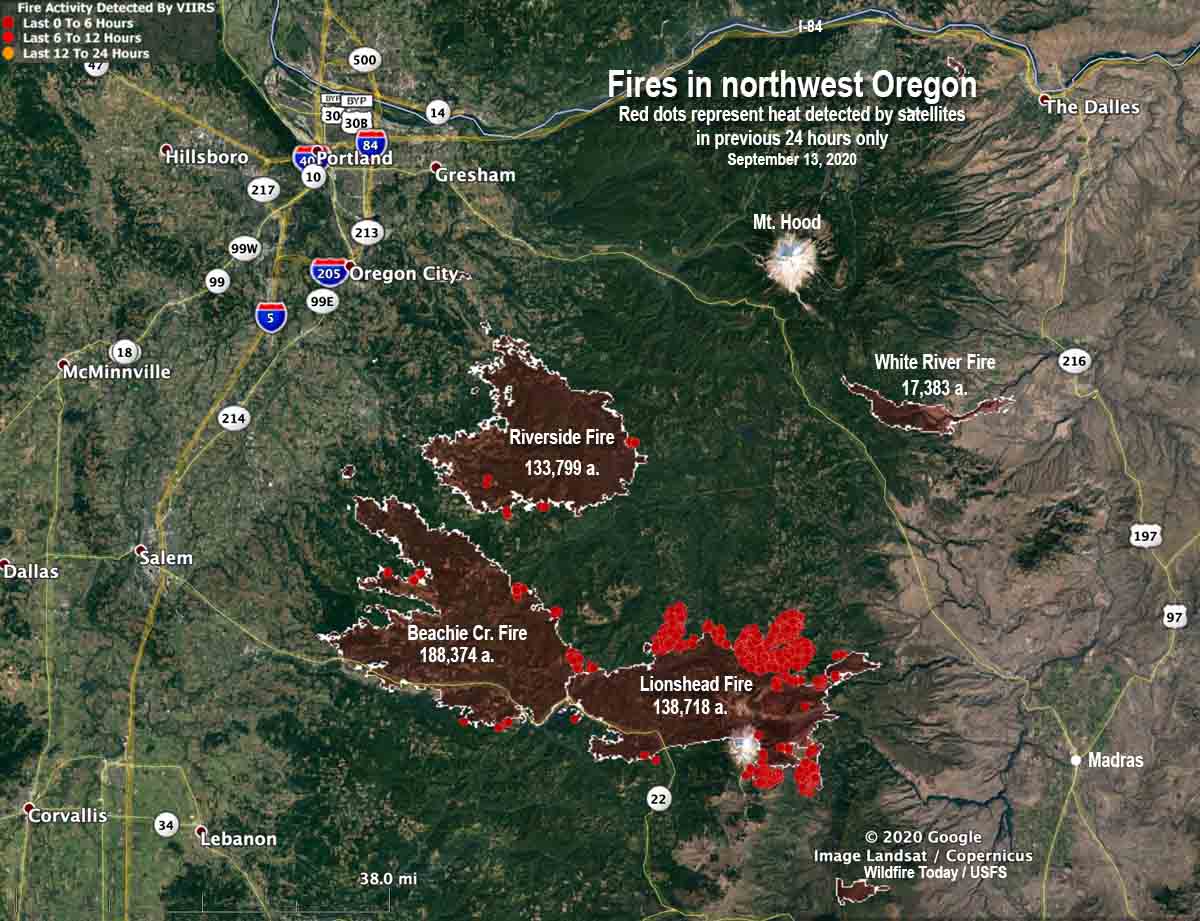
Oregon’s geography and climate contribute to a significant wildfire risk annually. Visual representations of active and historical wildfire incidents, often displayed as interactive maps, provide critical information for various stakeholders, including firefighters, emergency management agencies, residents, and researchers. These tools offer a dynamic overview of fire activity, enabling informed decision-making and resource allocation.
The information presented on these maps generally includes location data, fire perimeters, acreage burned, containment status, and sometimes even projected spread based on weather conditions and fuel models. Data sources commonly include satellite imagery, aerial surveys, ground reports from fire crews, and weather data. The maps’ temporal resolution varies; some may show only current active fires, while others may incorporate historical data spanning decades, providing a valuable long-term perspective on fire patterns and trends.
Different types of maps serve different purposes. Real-time operational maps focus on immediate fire activity, guiding firefighting efforts and emergency response. Historical maps, conversely, help identify high-risk areas, inform land management practices, and analyze long-term fire behavior patterns. These historical analyses can reveal crucial insights into the relationship between fire frequency, intensity, and environmental factors such as drought, vegetation type, and topography. For instance, maps can highlight areas with a history of frequent or severe fires, indicating the need for proactive mitigation strategies like controlled burns or forest thinning.
Geographic Factors Influencing Wildfire Risk in Oregon:
Oregon’s diverse topography significantly influences wildfire behavior. The state’s Cascade Range, with its steep slopes and varying elevations, creates challenging terrain for firefighting efforts. Strong winds funneling through canyons and valleys can rapidly spread flames, making containment difficult. The presence of numerous interconnected river systems, while offering water sources for firefighting, can also create barriers to fire suppression efforts.
The state’s vegetation plays a crucial role. Extensive areas of dry forests, particularly those dominated by ponderosa pine and other flammable species, provide abundant fuel for wildfires. The density of these forests, influenced by past fire suppression policies and forest management practices, can significantly impact fire behavior. Dense underbrush and accumulated deadwood create conditions for intense and rapidly spreading fires.
Climate change exacerbates Oregon’s wildfire risk. Increased temperatures and prolonged periods of drought contribute to drier vegetation, making forests more susceptible to ignition and rapid fire spread. Changes in precipitation patterns, including earlier snowmelt and more intense rainfall events, further complicate the situation.
The Importance of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Wildfire Management:
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are fundamental to wildfire management in Oregon. GIS technology integrates various spatial data layers – topography, vegetation, weather patterns, fire history, and infrastructure – to create comprehensive and dynamic maps. This integrated approach enables analysts to assess risk, predict fire behavior, and optimize resource allocation.
GIS-based modeling tools simulate fire spread under various scenarios, allowing for proactive planning and decision-making. These models can evaluate the effectiveness of different mitigation strategies and identify areas requiring immediate attention. Further, GIS facilitates communication and coordination among multiple agencies and stakeholders, ensuring efficient response to wildfire incidents.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: Where can I find reliable wildfire maps for Oregon?
- A: Several sources provide up-to-date information, including the Oregon Department of Forestry (ODF), the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC), and various county-level emergency management agencies. Many of these agencies offer interactive online maps.
-
Q: What information is typically included on these maps?
- A: Common information includes fire location, perimeter, acreage burned, containment status, date of ignition, and sometimes cause. Some maps also integrate weather data and topography.
-
Q: How are these maps updated?
- A: Updates occur frequently, often several times daily, reflecting changes in fire perimeter, containment, and other relevant information. Data sources include satellite imagery, aerial observations, and ground reports.
-
Q: How are these maps used in wildfire management?
- A: These maps are essential for resource allocation, fire suppression strategies, public safety planning, and post-fire recovery efforts. They are used by firefighters, emergency management personnel, land managers, and researchers.
-
Q: Are there historical wildfire maps available?
- A: Yes, many agencies maintain archives of historical fire data, providing valuable insights into long-term fire patterns and trends. These data are crucial for understanding fire regimes and informing future land management decisions.
Tips for Utilizing Wildfire Information Maps:
- Understand the map’s legend and data sources to interpret information accurately.
- Pay attention to the map’s temporal resolution; some maps show only current fires, while others incorporate historical data.
- Utilize multiple map sources for a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
- Be aware of limitations in map accuracy; real-time data can lag, and fire behavior can be unpredictable.
- Integrate map information with other sources, such as weather forecasts and official advisories.
Conclusion:
Oregon’s wildfire maps are critical tools for understanding, managing, and responding to the state’s significant wildfire risk. These maps, powered by advanced GIS technologies and diverse data sources, provide crucial information for a range of stakeholders. By integrating spatial data, historical trends, and predictive modeling, these tools enable proactive planning, efficient resource allocation, and improved public safety. Continued investment in data collection, technological advancements, and public education is essential to enhance the effectiveness of these vital resources in mitigating the impact of wildfires in Oregon.
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/35R6DWKJAZHEPOLRB6QV2VU2RI.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Oregon’s Wildfire Landscape: A Geographic Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!