Understanding Tennessee’s Tornado Risk: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding Tennessee’s Tornado Risk: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Tennessee’s Tornado Risk: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Tennessee’s Tornado Risk: A Geographic Perspective
Tennessee’s geographic location and unique meteorological conditions contribute to a significant risk of tornadoes. Visualizing this risk effectively requires a robust and readily accessible representation of tornado occurrences, historically and potentially in the future. This analysis examines the importance of comprehensive data visualization in understanding and mitigating the threat posed by these powerful storms within the state.
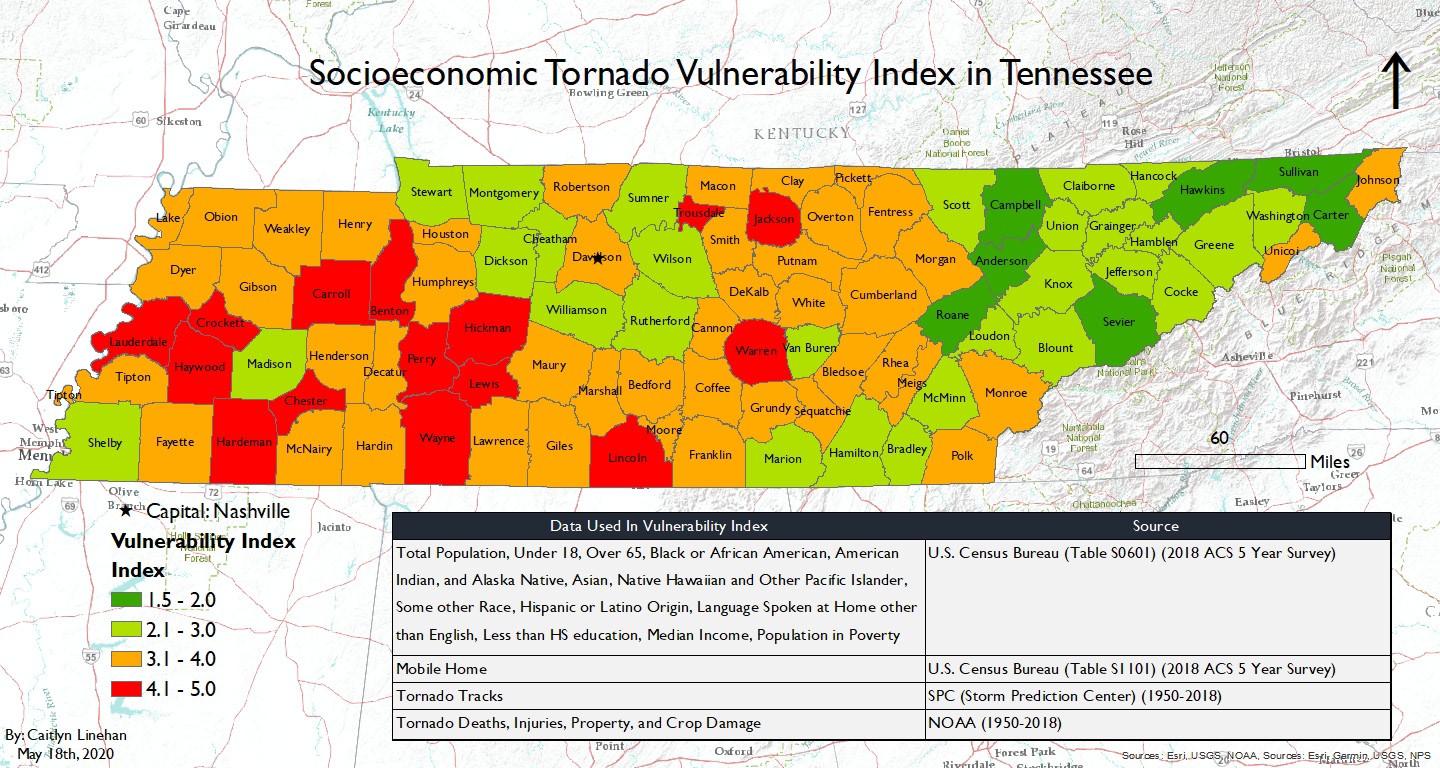
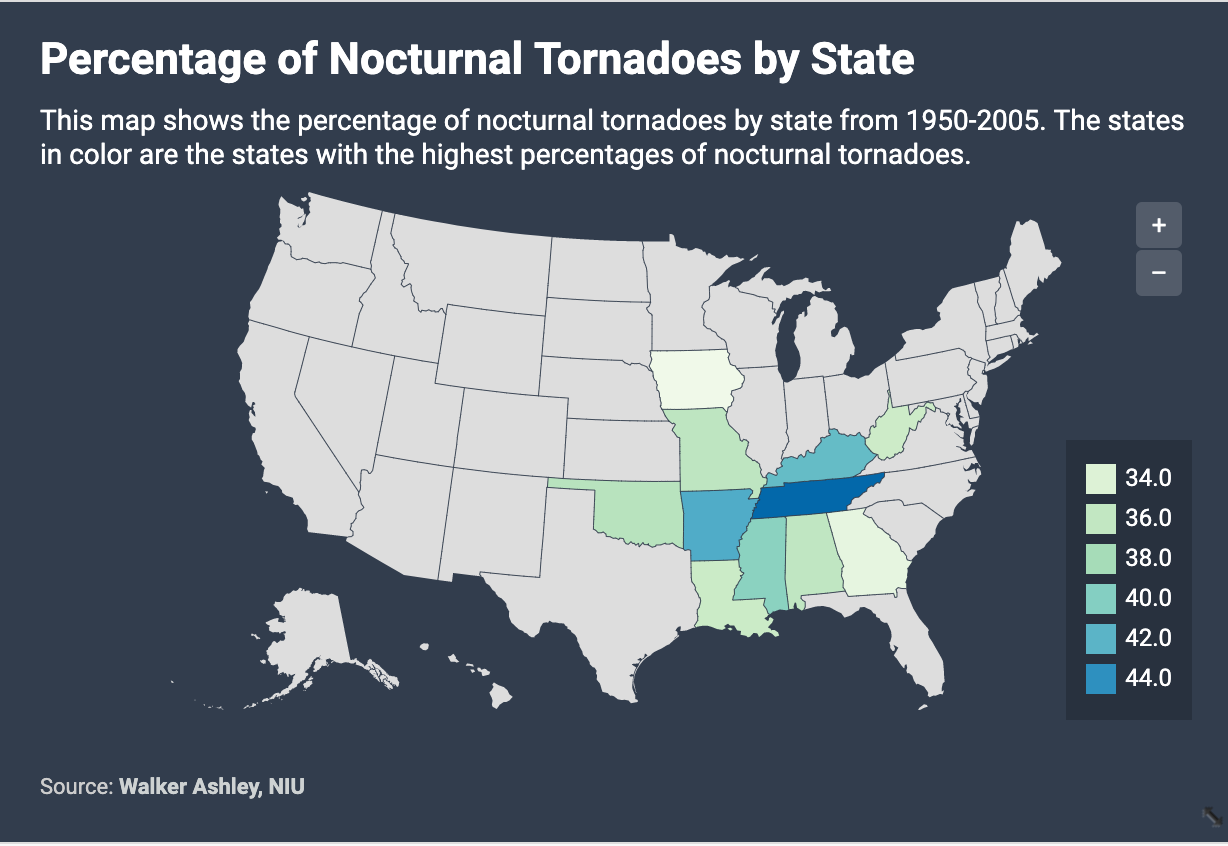
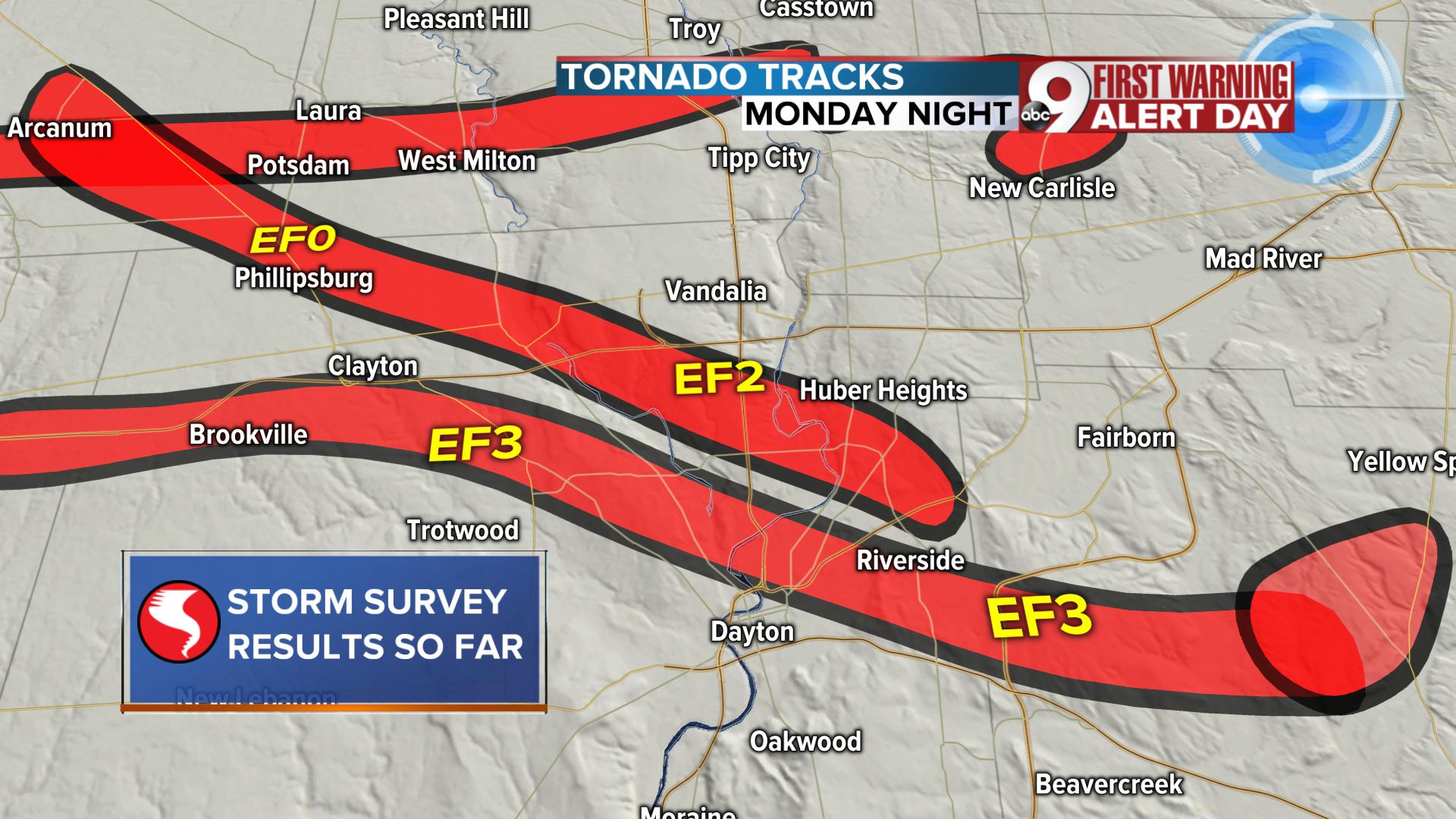
The creation of a detailed map depicting tornado activity in Tennessee involves compiling data from multiple sources. These sources include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Storm Prediction Center’s database, which contains detailed records of confirmed tornadoes, including their location, time, intensity (using the Enhanced Fujita scale), and path length. Local weather service offices also contribute valuable data, often refining the details of tornado tracks based on eyewitness accounts and damage surveys. Historical records, spanning decades, are crucial for establishing long-term trends and identifying areas of higher frequency or intensity.
The resulting map is not simply a collection of points representing tornado touchdowns. Sophisticated cartographic techniques are employed to present the data effectively. Color-coding can represent tornado frequency, intensity, or a combination of both. The intensity of the color can correspond to the number of tornadoes in a specific area or the maximum intensity recorded there. This allows for a clear visual representation of areas with higher risk profiles. The map might also incorporate geographic features, such as topography, population density, and infrastructure, to highlight areas of particular vulnerability. For example, areas with significant population density overlaid on high-frequency tornado zones immediately reveal areas requiring enhanced preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, advanced mapping techniques can utilize spatial analysis to identify potential tornado "hotspots" – regions exhibiting a statistically significant higher frequency of tornado activity than surrounding areas. This identification is critical for targeted preparedness efforts, enabling resource allocation to areas most in need of improved warning systems, community education programs, and infrastructure improvements to withstand extreme weather events.
The benefits of such a comprehensive visualization extend beyond simply identifying high-risk areas. The map facilitates improved understanding of the spatial patterns of tornado activity. This is crucial for several reasons:
-
Improved Forecasting: By identifying patterns and trends in historical data, meteorologists can refine forecasting models, potentially leading to more accurate and timely warnings. This allows for more effective dissemination of warnings to the affected populations, giving individuals and communities more time to take protective action.
-
Targeted Mitigation Strategies: Understanding the spatial distribution of tornado risk enables the development of targeted mitigation strategies. This may include building codes designed to withstand high winds, land-use planning that avoids development in high-risk areas, and the strategic placement of storm shelters.
-
Emergency Response Planning: A detailed map of tornado activity allows emergency management agencies to better prepare for and respond to tornado events. This includes optimizing the deployment of emergency personnel and resources, ensuring effective communication channels, and planning evacuation routes.
-
Insurance and Risk Assessment: Insurance companies utilize these maps to assess risk, allowing them to develop more accurate pricing models and inform risk mitigation strategies for their policyholders.
-
Public Awareness and Education: Visual representations of tornado risk are powerful tools for public awareness campaigns. A clear and accessible map can effectively communicate the potential threat to the public, motivating individuals and communities to take necessary precautions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
How often is the map updated? The map is typically updated annually, incorporating new data as it becomes available from NOAA and other sources. Real-time updates during active weather events are provided through separate channels, such as weather alerts and warnings.
-
What data sources are used to create the map? The primary data sources are the NOAA Storm Prediction Center’s database and local weather service offices. Historical data, damage surveys, and eyewitness accounts also contribute to the accuracy and completeness of the map.
-
What does the color-coding on the map represent? Color-coding usually represents tornado frequency and/or intensity. A legend accompanying the map provides a clear explanation of the color scheme.
-
Are there limitations to the map’s accuracy? While the map strives for accuracy, limitations exist. Historical data may be incomplete for older events, and the accuracy of tornado tracks can be affected by factors such as visibility and damage assessment limitations.
Tips for Using the Tornado Risk Map:
-
Understand the legend: Pay close attention to the legend to interpret the color-coding and symbols used on the map.
-
Consider multiple factors: Don’t rely solely on the map; consider other factors such as topography, proximity to bodies of water, and local building codes when assessing your risk.
-
Use the map in conjunction with other resources: Combine the map with official weather warnings and forecasts for a comprehensive understanding of current risks.
-
Develop a preparedness plan: Use the information provided by the map to develop a family emergency plan, including shelter locations and communication strategies.
Conclusion:
A comprehensive map of tornado activity in Tennessee serves as a critical tool for understanding, mitigating, and responding to the threat of tornadoes. By visualizing historical data and spatial patterns, it facilitates improved forecasting, targeted mitigation strategies, effective emergency response planning, informed risk assessment, and enhanced public awareness. While limitations in data availability and accuracy exist, the benefits of this visual representation significantly outweigh the limitations, making it an indispensable resource for individuals, communities, and governmental agencies alike in their efforts to protect lives and property from the devastating impact of tornadoes.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Tennessee’s Tornado Risk: A Geographic Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!