Understanding Wildfire Dynamics in New Mexico: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding Wildfire Dynamics in New Mexico: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Wildfire Dynamics in New Mexico: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Wildfire Dynamics in New Mexico: A Geographic Perspective
![]()
New Mexico’s diverse landscape, characterized by expansive forests, grasslands, and arid shrublands, renders it highly susceptible to wildfires. Analyzing the spatial distribution of these events through cartographic representation offers crucial insights into their patterns, contributing factors, and potential impacts. A wildfire map of the state provides a visual summary of fire occurrences, enabling a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between environmental factors, human activities, and wildfire behavior.
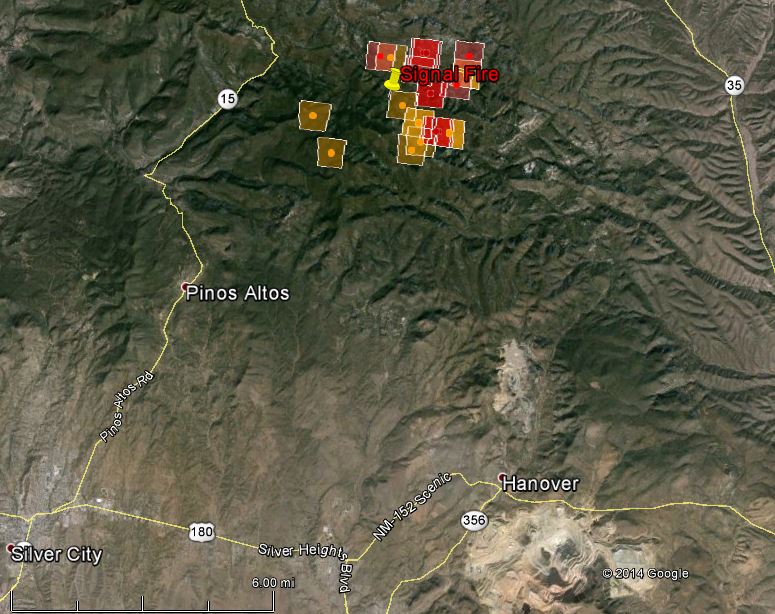
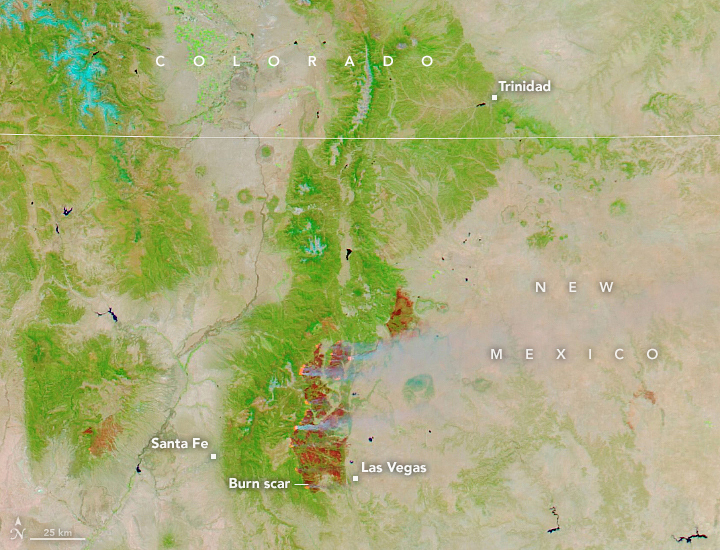
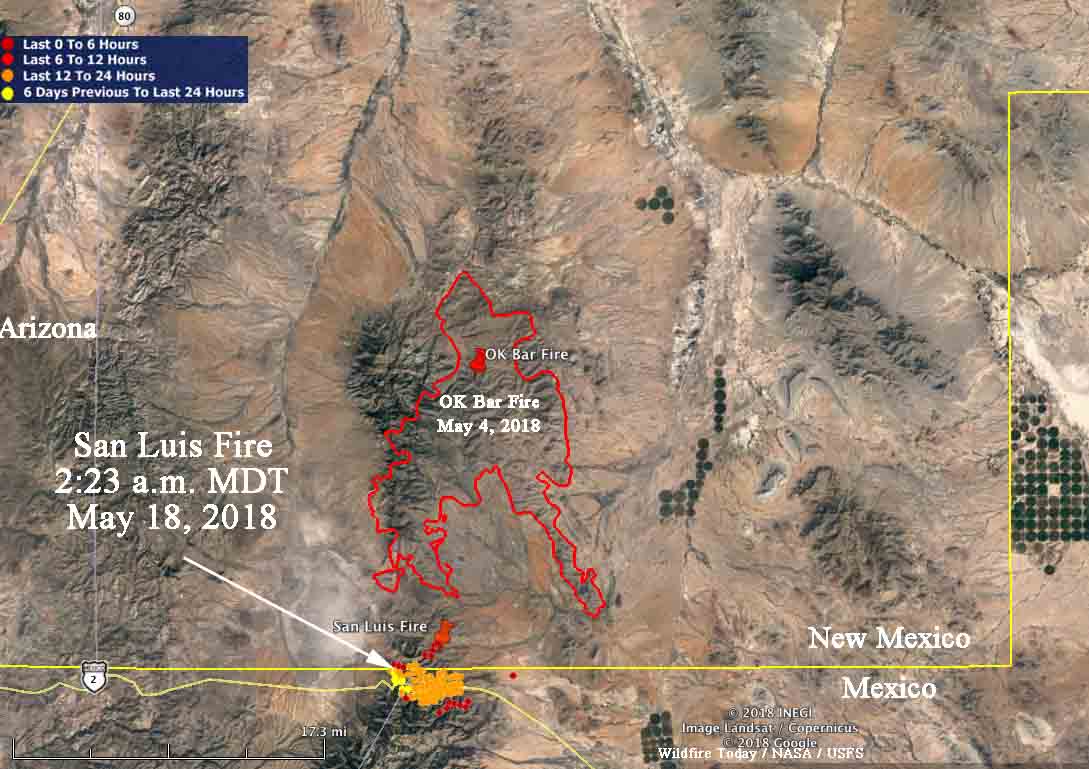
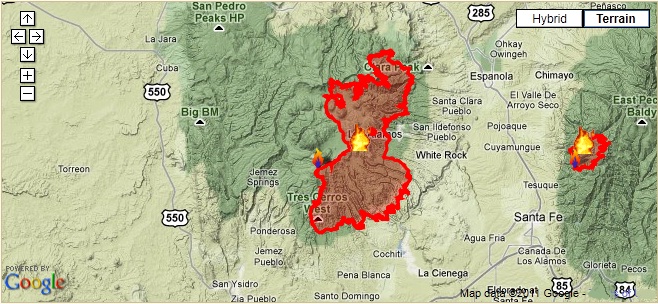
The visual representation of wildfire data on a map allows for immediate identification of high-risk areas. Areas with frequent and intense fire activity are clearly delineated, highlighting regions requiring focused mitigation strategies. This spatial analysis reveals patterns that might otherwise remain obscured in purely statistical data. For example, proximity to human settlements, transportation routes, or specific vegetation types can be readily observed and correlated with fire frequency and severity. The map’s resolution also impacts the level of detail available, with high-resolution maps revealing individual fire perimeters and allowing for precise assessment of burned area. Lower-resolution maps provide a broader overview, useful for identifying regional trends and prioritizing resource allocation.
Several factors influence the spatial distribution of wildfires as depicted on the map. Climate plays a significant role, with prolonged periods of drought increasing fuel dryness and flammability. Topographic features, such as steep slopes and canyons, can influence fire spread, creating complex fire patterns. Wind direction and speed significantly impact fire behavior, often dictating the direction and rate of propagation. Vegetation type also plays a critical role. Dense forests of ponderosa pine or mixed conifer, for example, can support intense and rapidly spreading fires, whereas grasslands may experience more patchy burns. Human activities, including land management practices, infrastructure development, and accidental ignitions, also contribute significantly to the spatial distribution of wildfires. The map can reveal correlations between human activity and wildfire occurrence, highlighting areas where preventative measures are needed.
Furthermore, the temporal component is crucial. Overlaying wildfire data from multiple years on a single map reveals long-term trends and patterns. This allows for the identification of areas consistently prone to wildfires, facilitating the development of long-term fire management plans. Analyzing changes in fire frequency and intensity over time can also help assess the effectiveness of existing mitigation efforts and inform future strategies. The visualization of historical fire data on a map, coupled with climate projections, can also provide valuable insights into future wildfire risk and aid in proactive planning and resource allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Wildfire Mapping in New Mexico:
-
Q: What data sources are used to create New Mexico wildfire maps?
- A: Data sources typically include satellite imagery (e.g., Landsat, MODIS), aerial photography, fire perimeter reports from ground crews, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) databases maintained by state and federal agencies. The accuracy and resolution of the map depend on the quality and availability of these data sources.
-
Q: How are fire perimeters determined for mapping purposes?
- A: Fire perimeters are often determined through a combination of ground observations, aerial surveys, and satellite imagery analysis. GIS software is used to digitize these perimeters, creating vector data that can be displayed on a map. The accuracy of perimeter delineation can vary depending on the method used and the terrain.
-
Q: What is the significance of different colors or shading on a wildfire map?
- A: Different colors or shading usually represent different aspects of the fire, such as the date of the fire, the intensity of the burn, or the type of vegetation burned. A legend accompanying the map will explain the meaning of the different visual representations.
-
Q: How can wildfire maps be used for emergency response and evacuation planning?
- A: Wildfire maps provide crucial information for emergency responders, enabling them to assess the extent and severity of the fire, prioritize resource allocation, and plan evacuation routes. Real-time updates incorporated into the map can enhance situational awareness and facilitate effective response.
-
Q: Are these maps publicly accessible?
- A: Many wildfire maps are publicly accessible through government websites and online GIS platforms. However, access to certain data, especially real-time information during active fire events, may be restricted to authorized personnel.
Tips for Utilizing Wildfire Maps Effectively:
-
Consider the map’s scale and resolution: A large-scale map provides detailed information about specific areas, while a small-scale map shows regional trends. Select the appropriate map scale based on the intended use.
-
Analyze the map legend carefully: The legend provides critical information about the symbols, colors, and shading used on the map, ensuring correct interpretation of the data.
-
Correlate wildfire data with other geographic information: Overlaying wildfire data with data on vegetation type, elevation, and population density can reveal important relationships and improve understanding of wildfire patterns.
-
Consult multiple data sources: Using information from various sources can enhance the accuracy and reliability of the analysis.
-
Understand the limitations of the data: Recognize that maps represent a snapshot in time and may not capture all aspects of wildfire dynamics.
Conclusion:
Wildfire maps are indispensable tools for understanding and managing wildfire risk in New Mexico. Their ability to visualize spatial and temporal patterns of fire occurrences provides crucial insights for various stakeholders, including land managers, emergency responders, policymakers, and the public. By integrating wildfire data with other geographic information, these maps facilitate more effective prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery efforts, ultimately contributing to improved wildfire resilience in the state. Continuous improvement in data collection, analysis, and visualization techniques will further enhance the value of these cartographic representations in mitigating the devastating impacts of wildfires in New Mexico’s unique environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Wildfire Dynamics in New Mexico: A Geographic Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!